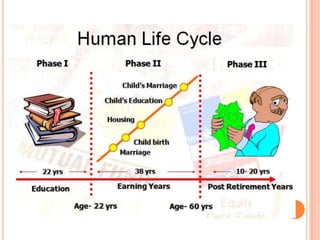
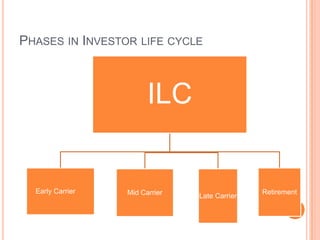
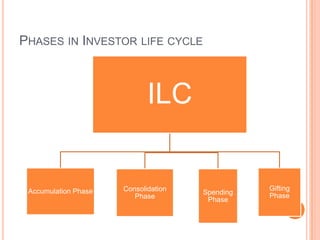
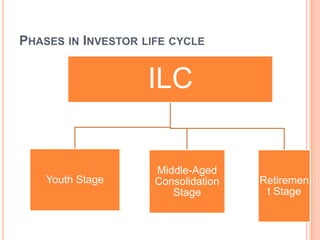
1. The investor life cycle describes the different phases investors go through over their lifetime from early career to retirement.
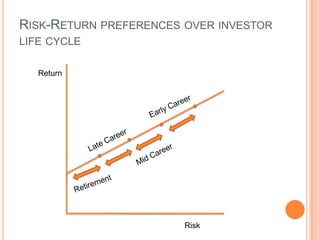
2. In the early career phase, investors have a small net worth and are willing to take on higher risks in anticipation of higher returns.
3. As investors move through their mid-career, they accumulate assets and take on less risk by prioritizing capital preservation.
4. In retirement, investments become the primary source of income and capital preservation is the overriding concern with lower risk investments.