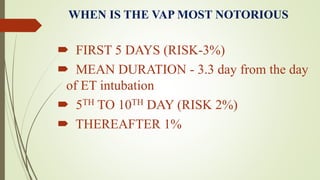
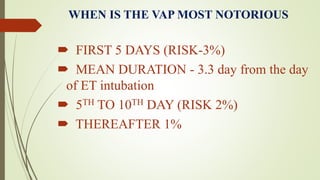
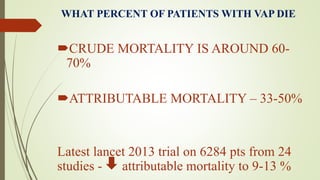
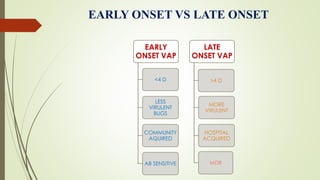
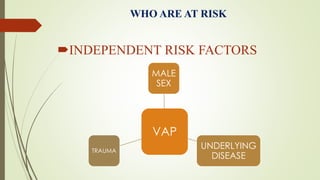
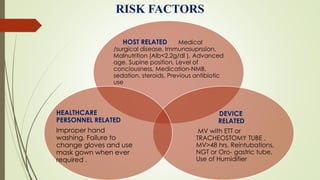
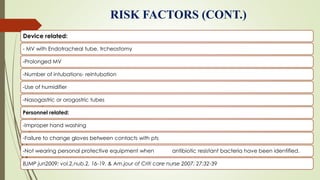
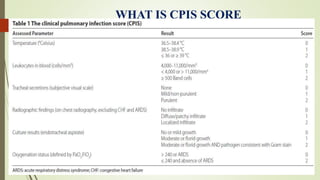
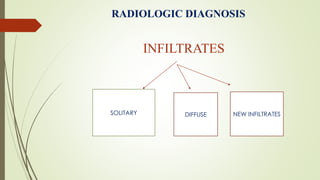
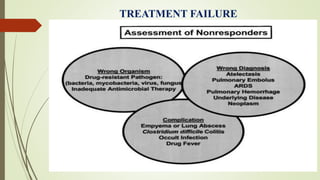
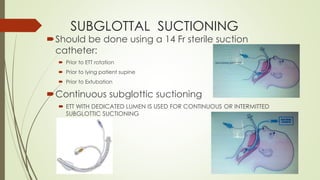
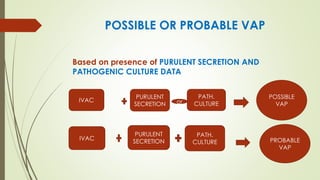
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a common nosocomial infection that occurs in patients on mechanical ventilation. It can develop within the first 5 days of intubation or later after the 10th day. Risk factors include prolonged mechanical ventilation, comorbidities, and improper infection control practices. Common causative organisms include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus for early-onset VAP and Pseudomonas, MRSA, and drug-resistant Gram-negative rods for late-onset VAP. Diagnosis is based on clinical, microbiological, and radiological criteria though there is no gold standard. Treatment involves administering appropriate