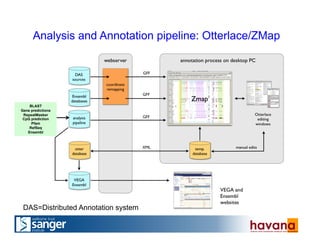
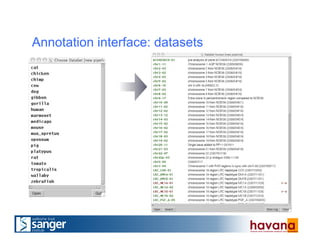
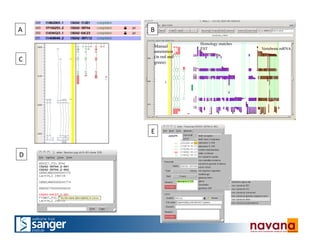
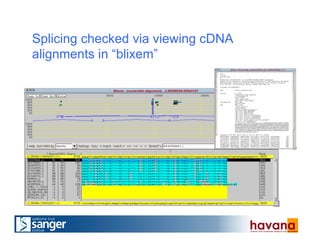
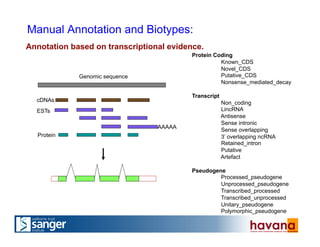
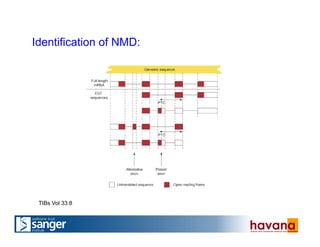
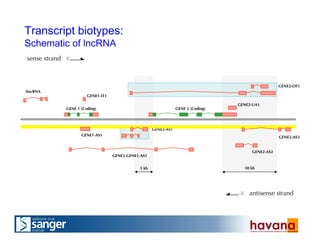
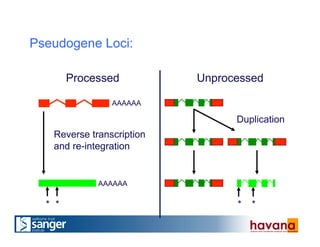
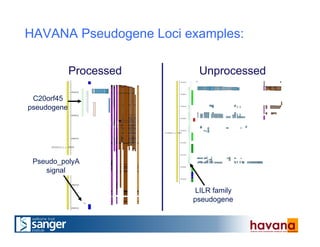
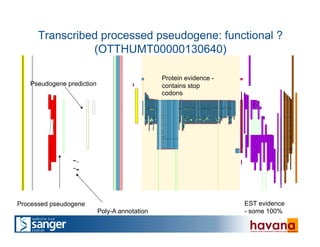
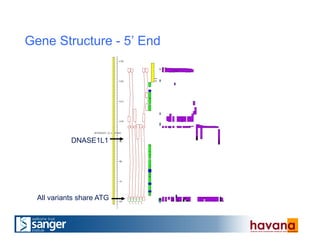
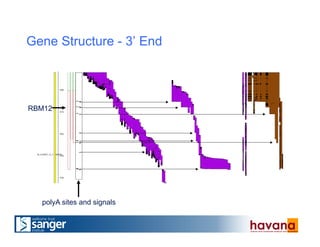
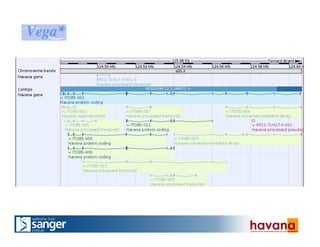
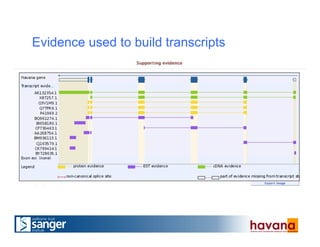
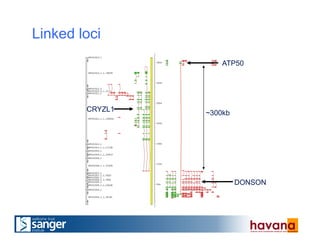
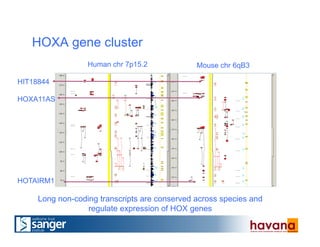
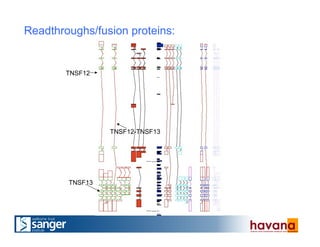
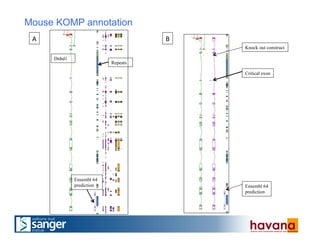
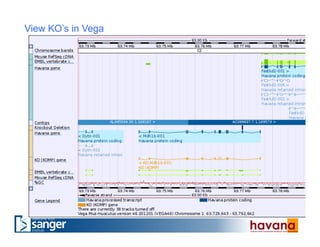
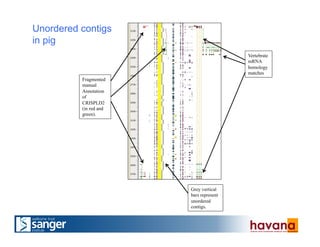
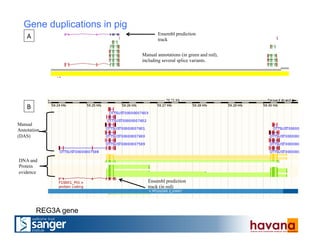
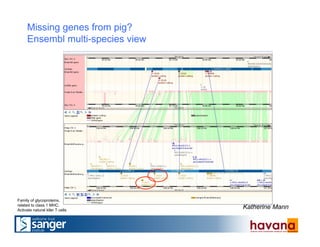
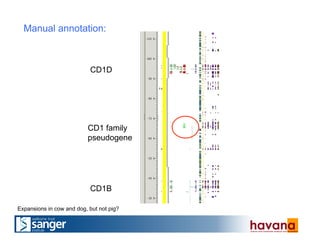
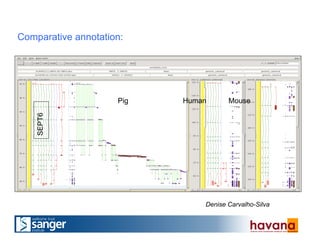
The document outlines the manual annotation processes for genomic data at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, focusing on human, mouse, and zebrafish species. It compares automatic and manual annotation, discussing the benefits and drawbacks of each method while describing the tools, community involvement, and training needed for effective annotation. The document highlights key projects, such as community annotations of swine and mouse genes, as well as ongoing challenges in maintaining high quality and consistency in genome annotations.