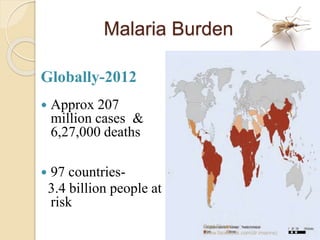
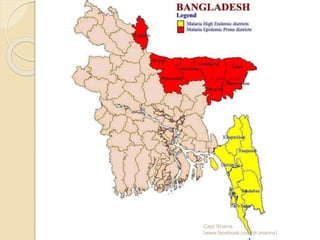
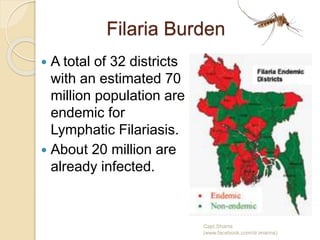
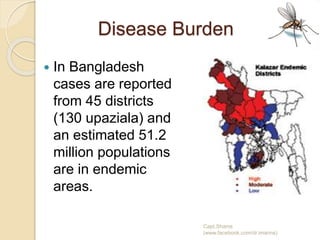
The document discusses vector borne diseases in Bangladesh. It begins by defining vectors and common vector borne diseases globally and in Bangladesh, including malaria, filariasis, dengue, and leishmaniasis. It then covers the prevalence and burden of these key diseases. The final sections discuss prevention and control strategies like integrated vector management, environmental control, chemical and biological control, and recommendations to apply multiple approaches to strengthen control through collaboration between government and organizations.