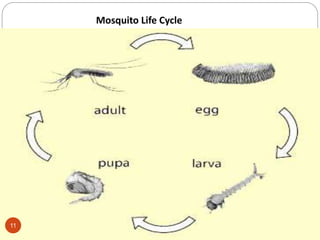
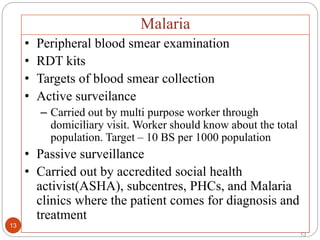
The document presents an overview of vector-borne diseases (VBDs) prevalent in India, focusing on malaria, dengue, chikungunya, and Japanese encephalitis. It highlights the causative agents, transmission methods, and typical symptoms of these illnesses, as well as preventive measures and the role of various departments in controlling VBDs. Effective surveillance, community awareness, and mosquito breeding source management are emphasized as crucial steps in reducing the incidence of these diseases.