1. The cross product of two vectors gives a vector perpendicular to both vectors, with magnitude equal to the area of the parallelogram formed by the two vectors.
2. If two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are given by vectors a and b, the area of the parallelogram is |a x b|.
3. If the position vectors of three vertices of a triangle are given, the area of the triangle can be found as 1/2 times the magnitude of the cross product of any two sides of the triangle.










































![Properties of Dot Product
a . b =
5
➝ ➝
+
-
0
If θ ∈ [0, 𝝿/2)
If θ ∈ (𝝿/2, 𝝿]
If θ = 𝝿/2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-49-320.jpg)






![Let a, b, c be three mutually perpendicular vectors of the same
magnitude and equally inclined at an angle θ, with the vector
a + b + c. Then 36 cos2 2θ is equal to _________.
[JEE Main 2021]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-58-320.jpg)

![Let a, b & c be three unit vectors such that |a - b|2 + |a - c|2 = 8. Then
|a + 2b|2 + |a + 2c|2 is equal to ________.
[JEE Main 2021]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-60-320.jpg)
![If a, b and c are unit vectors satisfying
|a - b|2 + |b - c|2 + |c - a|2 = 9, then |2a + 5b + 5c| is
➝➝ ➝
➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝
[JEE Adv. 2012]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-61-320.jpg)







![[JEE Main 2020]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-70-320.jpg)


![[JEE Main 2021]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-73-320.jpg)

![[JEE Adv. 2015]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-75-320.jpg)





![Let a = î + ĵ + k
̂ , b = î - ĵ + k
̂ and c = î - ĵ - k
̂ be there vectors. A vector
v in the plane of a and b, whose projection on c is 1/√3, is given by
➝ ➝ ➝
➝
A. î - 3ĵ + 3k
̂ B. -3î - 3ĵ - k
̂
C. 3î - ĵ + 3k
̂ D. î + ĵ - 3k
̂ [JEE 2011]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-81-320.jpg)
![[JEE Main 2021]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-82-320.jpg)






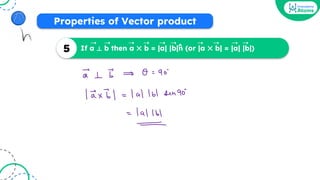






![[JEE Main 2021]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-98-320.jpg)
![[JEE Adv. 2011]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-99-320.jpg)
![[JEE Adv. 2020]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-100-320.jpg)

![Let △PQr be a triangle. Let a = QR, b = RP and c = PQ. if |a| = 12, |b|
= 4√3, b.c = 24, then which of the following is are) true?
A. B.
C. |a x b + c x a | = 48√3 D. a . b = -72
➝
➝
➝ __ __ __
➝ ➝ ➝
➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝
[JEE Adv. 2015]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-102-320.jpg)









![[JEE Adv. 2020]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-112-320.jpg)





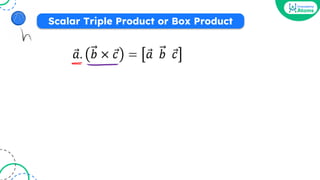








![[a b c] = -[a c b]
2
➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝➝
Properties of Box Product (STP)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-127-320.jpg)

![[a b b] = [a b a] = 0
4
➝➝➝ ➝➝➝
Properties of Box Product (STP)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-129-320.jpg)
![The scalar triple product of three mutually perpendicular unit
vectors is ± 1. Thus [î ĵ k
̂ ] = 1, [î ĵ k
̂ ] = -1
5
Properties of Box Product (STP)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-130-320.jpg)
![If two of the three vectors a, b, c are parallel then
[a b c] = 0
6 ➝ ➝ ➝
Properties of Box Product (STP)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-131-320.jpg)
![Three non-zero non-collinear vectors are coplanar if
[a b c] = 0
7 ➝ ➝ ➝
Properties of Box Product (STP)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-132-320.jpg)
![[a + b c d] = [a c d] + [b c d]
8
➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝
Properties of Box Product (STP)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-133-320.jpg)
![[a + b b + c c + a] = 2[a b c]
9
➝
[a - b b - c c - a] = 0
10
[a ⨉ b b ⨉ c c ⨉ a] = [a b c]2
11
➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝
➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝
➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝
➝
Properties of Box Product (STP)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-134-320.jpg)

![For any three vectors a, b, c [a + b, b + c, c + a] equals
A. [a b c] B. 2 [a b c]
C. [a b c]2 D. 0
➝➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝➝ ➝
➝➝➝
➝➝➝
➝➝➝](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-136-320.jpg)
![Let a, b and c be distinct positive numbers. If the vectors
then c is equal to
A. B.
C. D.
[JEE Main 2021]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-137-320.jpg)


![For 3 non zero Vectors
If [a b c] ≠ 0 ⇒ Linearly Independent
If [a b c] = 0 ⇒ Linearly Dependent
➝➝➝
➝ ➝➝
Linearly Dependent v/s Independent Vectors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-140-320.jpg)







![[a ⨉ b b ⨉ c c ⨉ a] = [a b c]2
4
➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝
Vector Triple Product (VTP) - Properties](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-148-320.jpg)
![[JEE Main 2021]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-149-320.jpg)

![[JEE Main 2021]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-151-320.jpg)

![[JEE Adv. 2010]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-153-320.jpg)


![Vector Product of Four Vectors
V = (a ⨉ b) ⨉ (c ⨉ d) = [a b d]c - [a b c]d
➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-156-320.jpg)
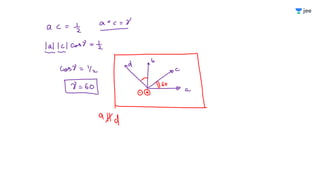
![If a, b, c and d are unit vectors such that (a x b) . (c x d) = 1 and
a . c = 1/ 2, then
➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝ ➝
➝ ➝
A. a, b, c are non - coplanar
B. b, c, d are non - coplanar
C. b, d are non - parallel
D. a, d are parallel and b, c are parallel
➝ ➝ ➝
➝
➝
➝
➝ ➝
➝
➝
[JEE Adv. 2009]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoralgebraoneshotbounceback-240207124248-aa784c0d/85/Vector-Algebra-One-Shot-BounceBack-pdf-157-320.jpg)