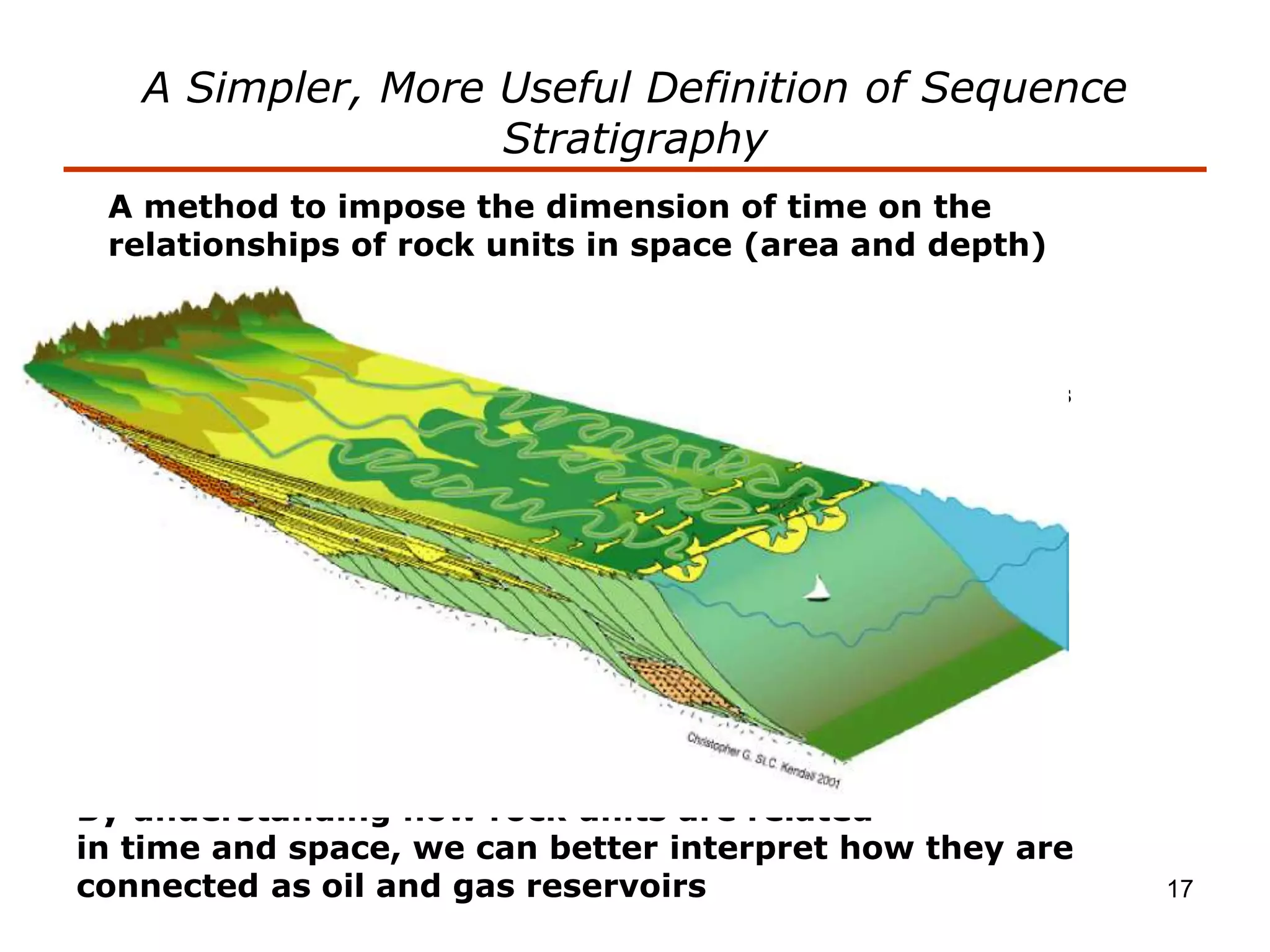
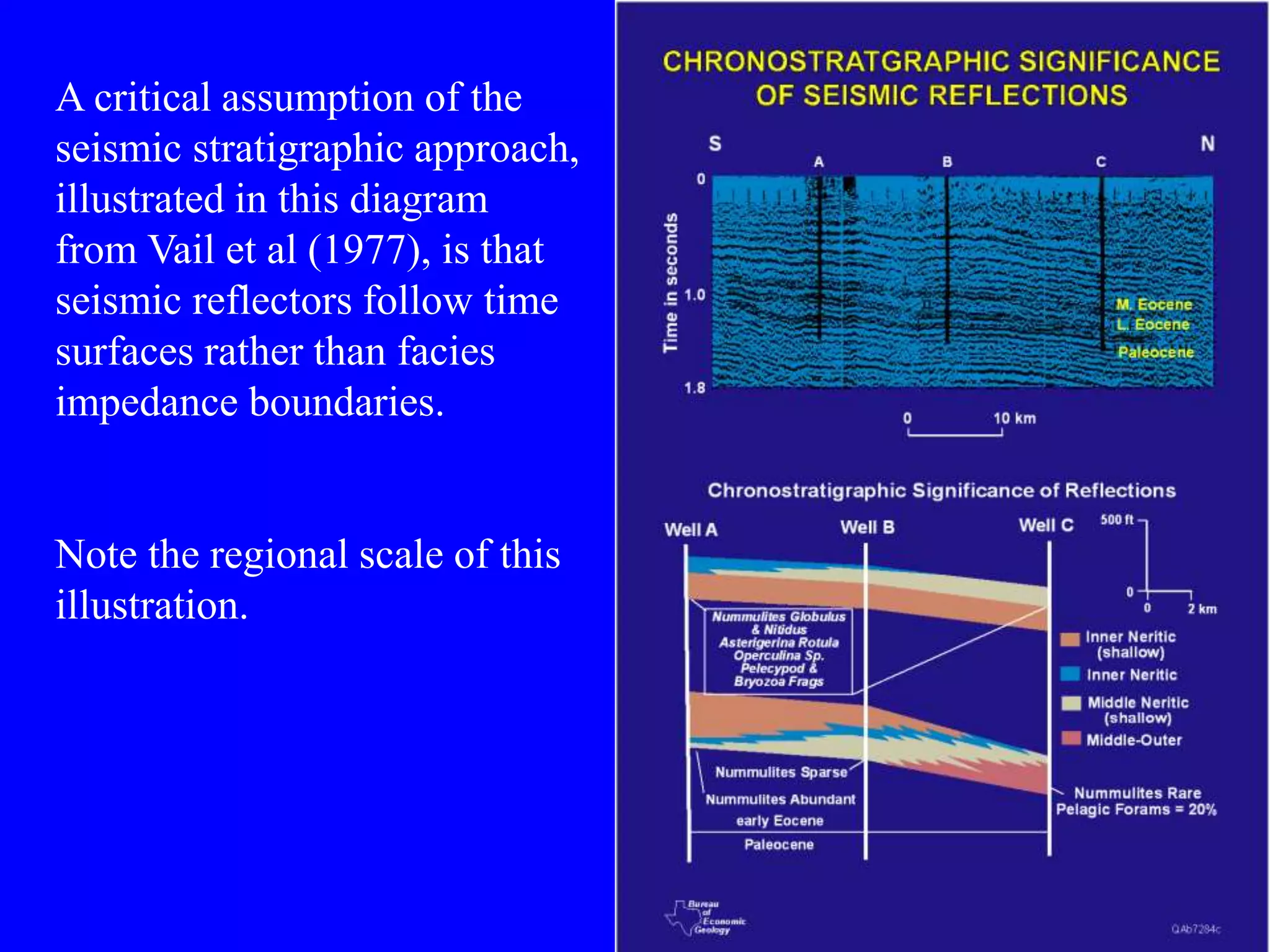
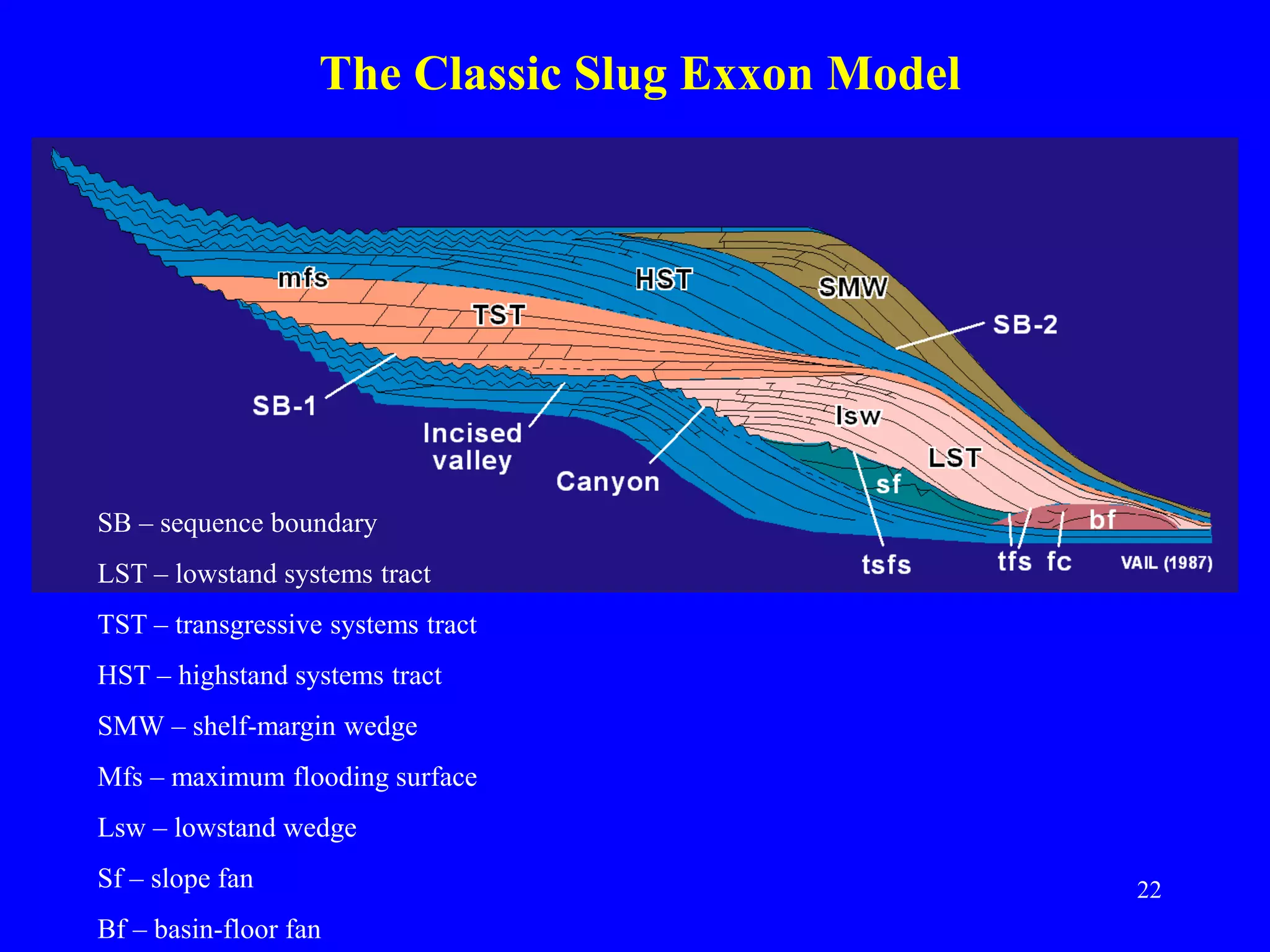
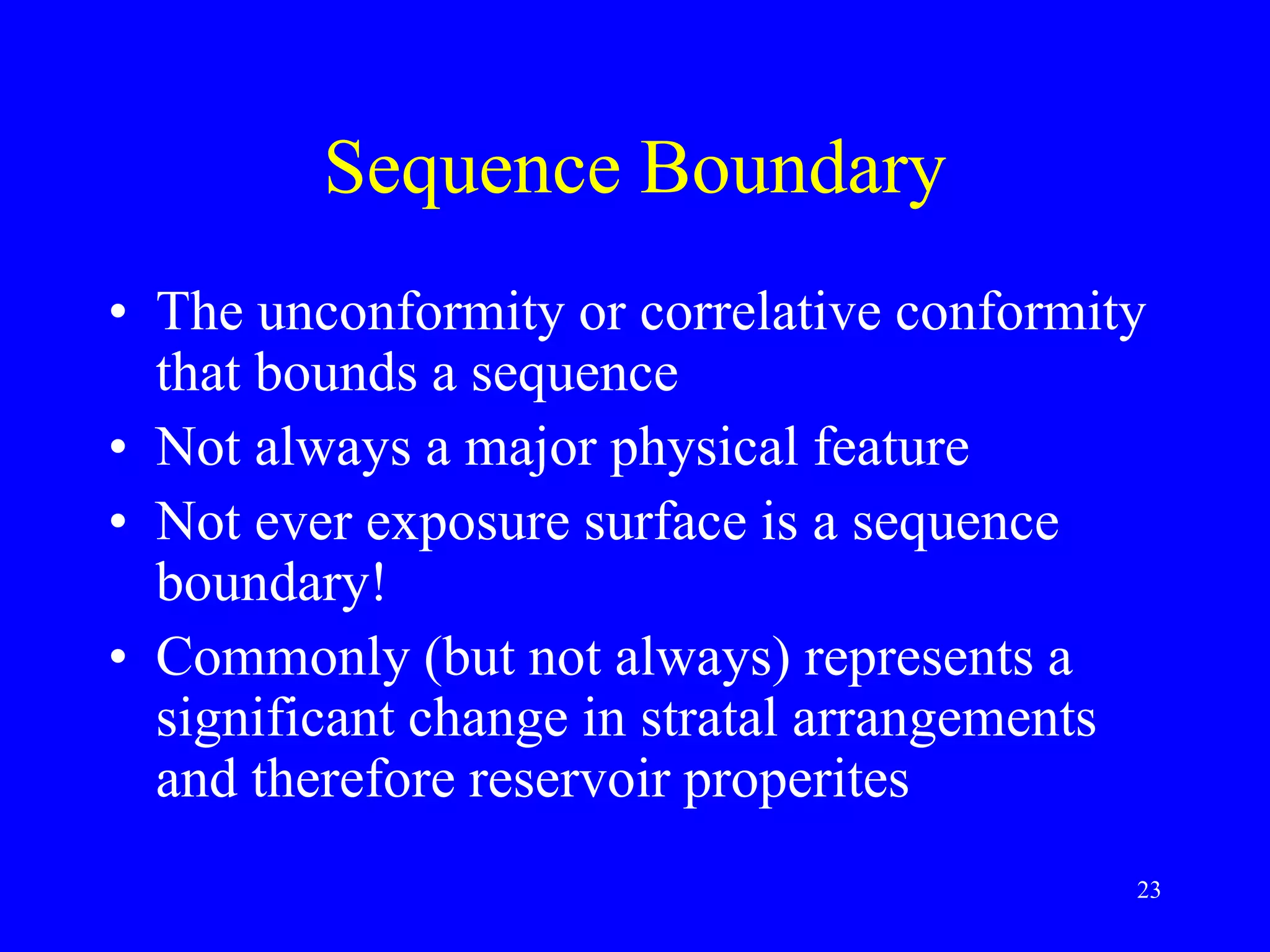
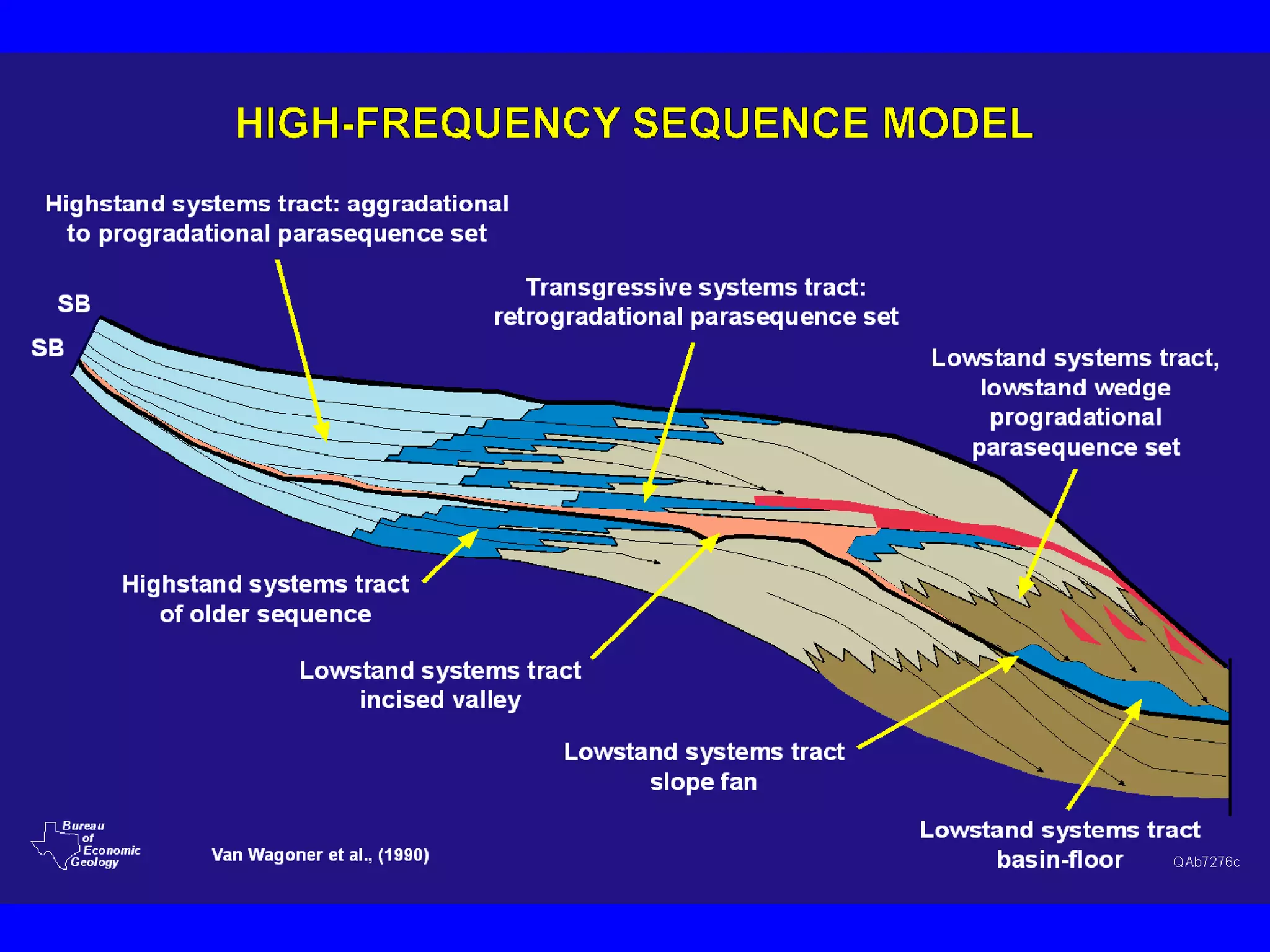
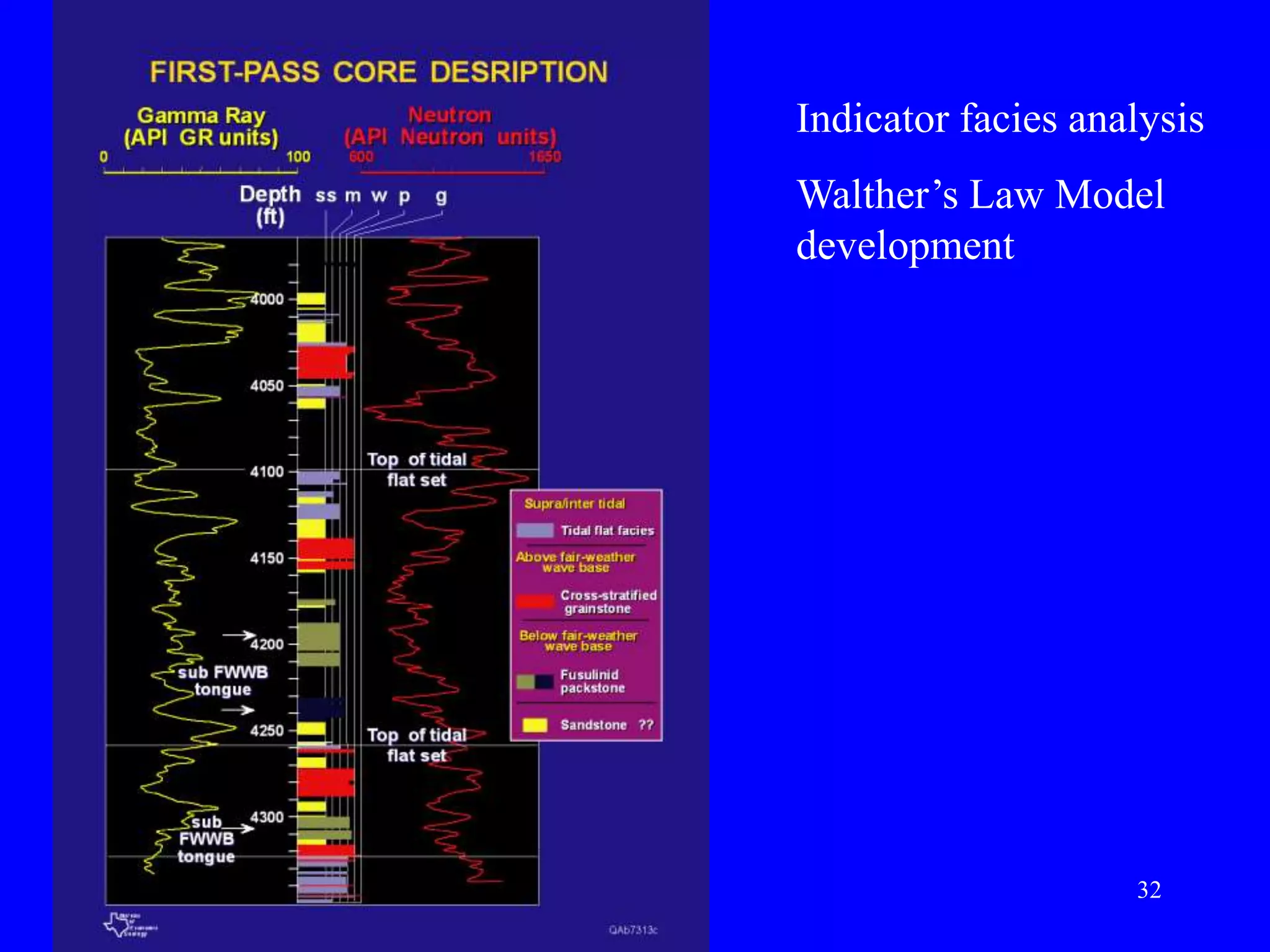
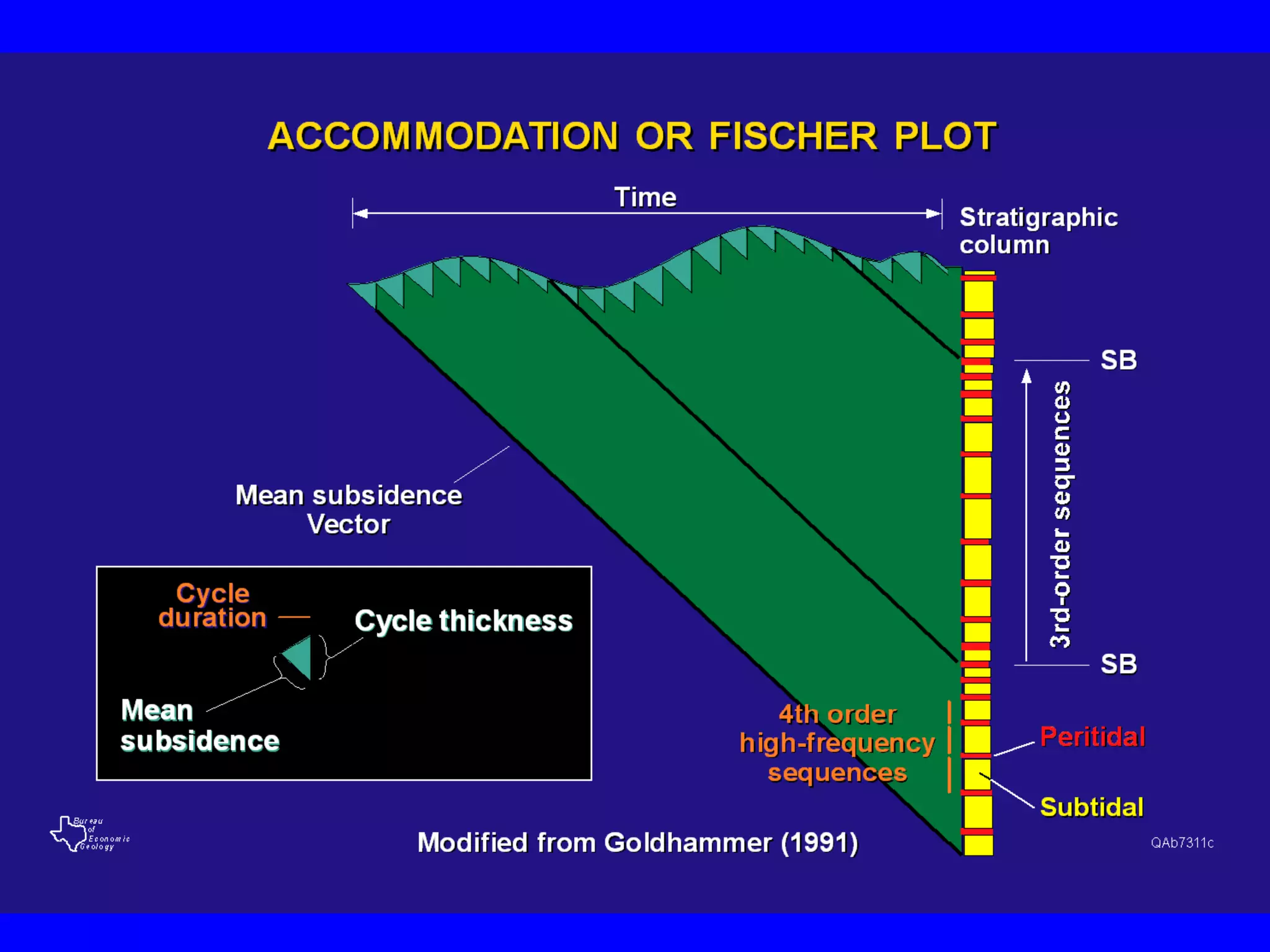
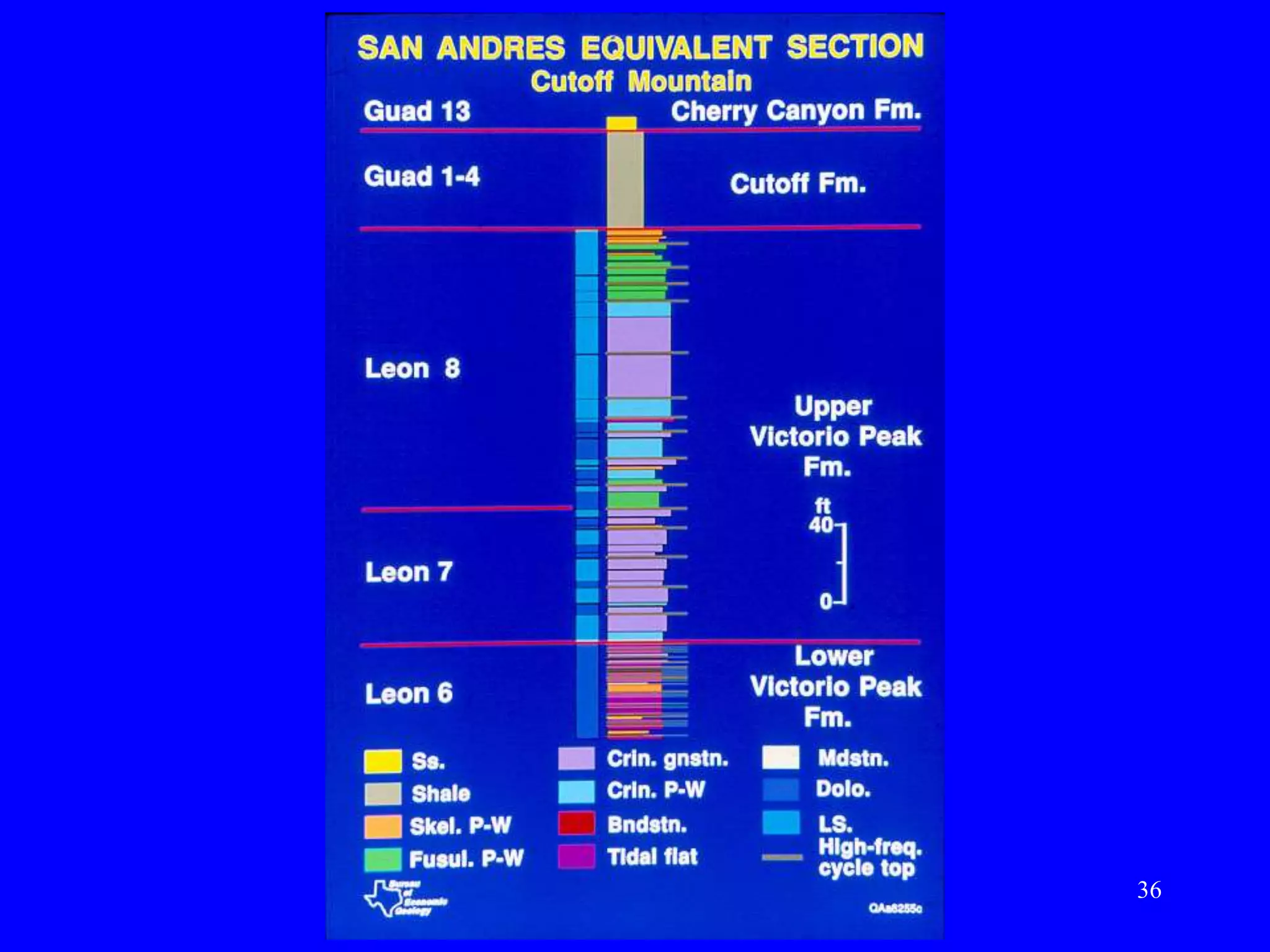
Stratigraphic principles and sequence stratigraphy are methods used to analyze sedimentary rock layers and impose a temporal dimension. Key concepts include:
- Steno's laws of superposition, original horizontality, and lateral continuity which describe how sedimentary layers are deposited.
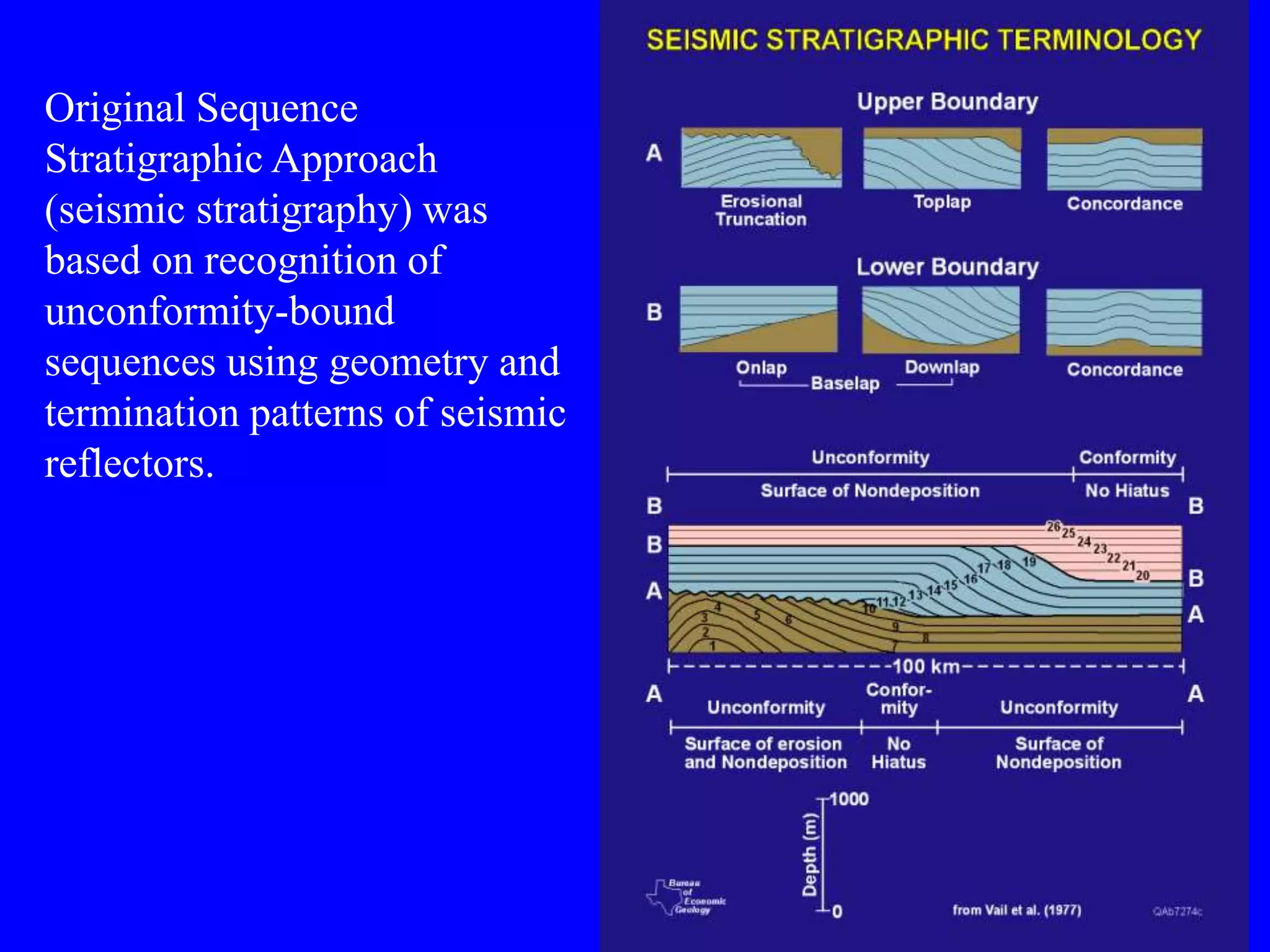
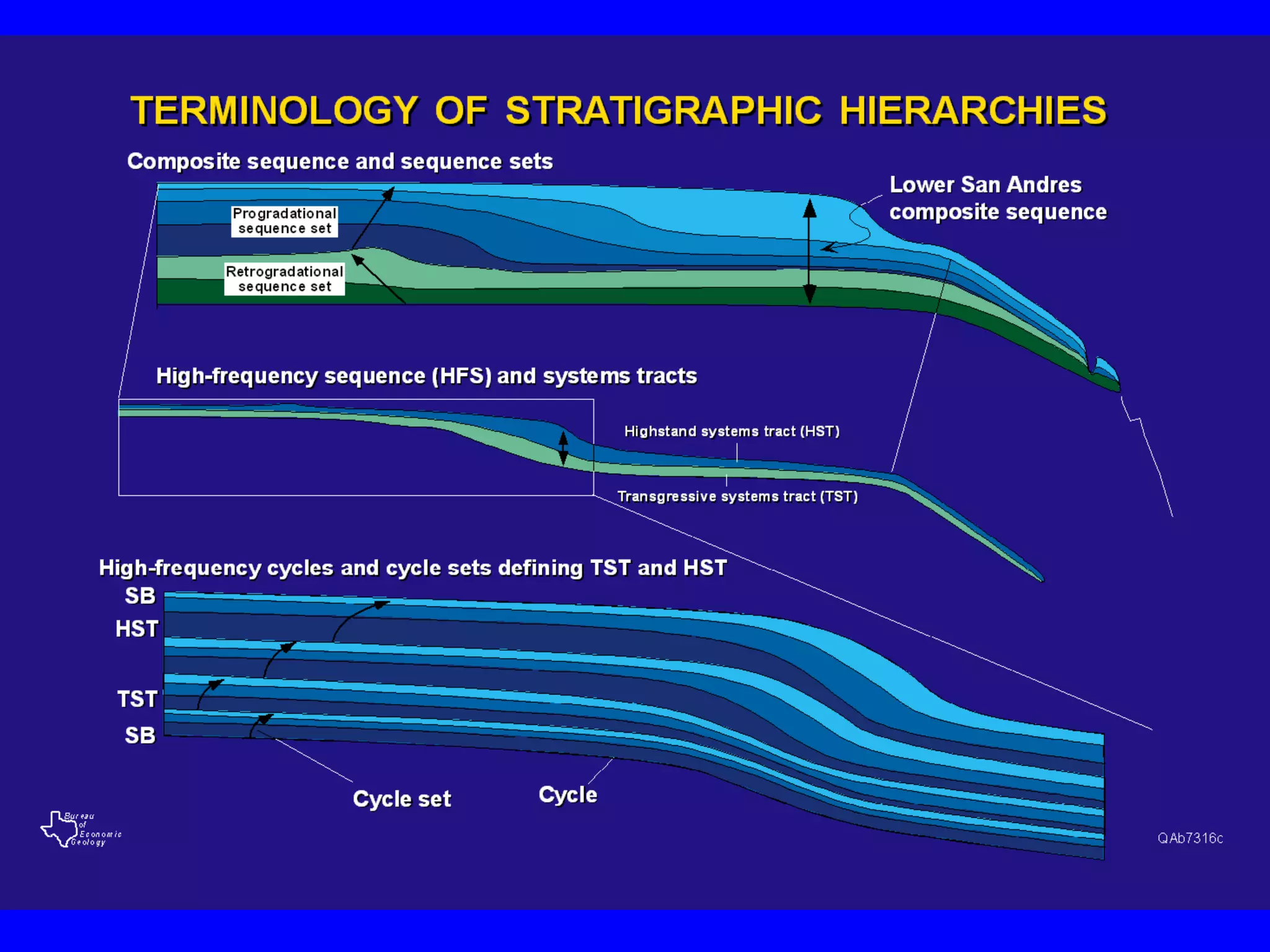
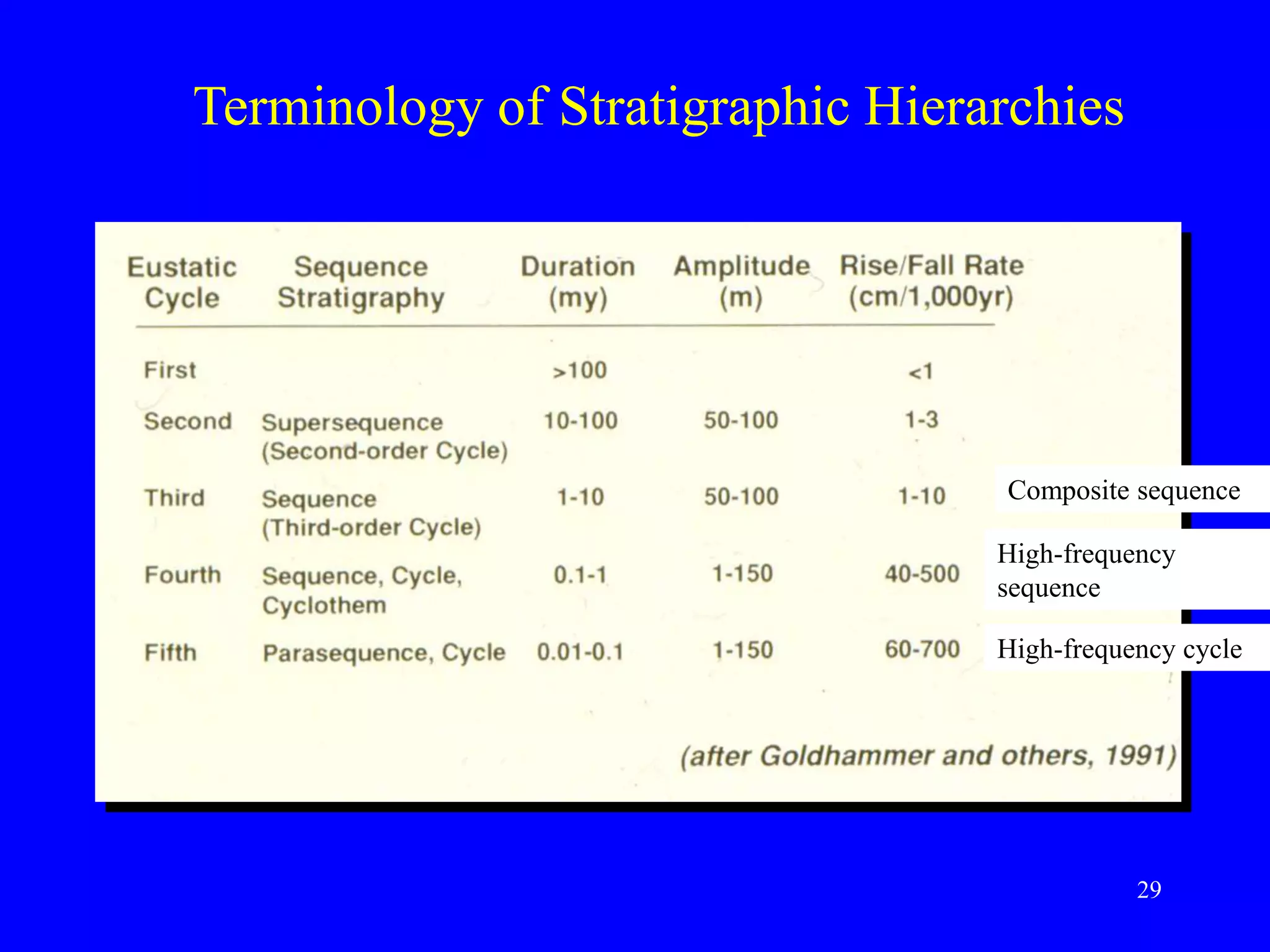
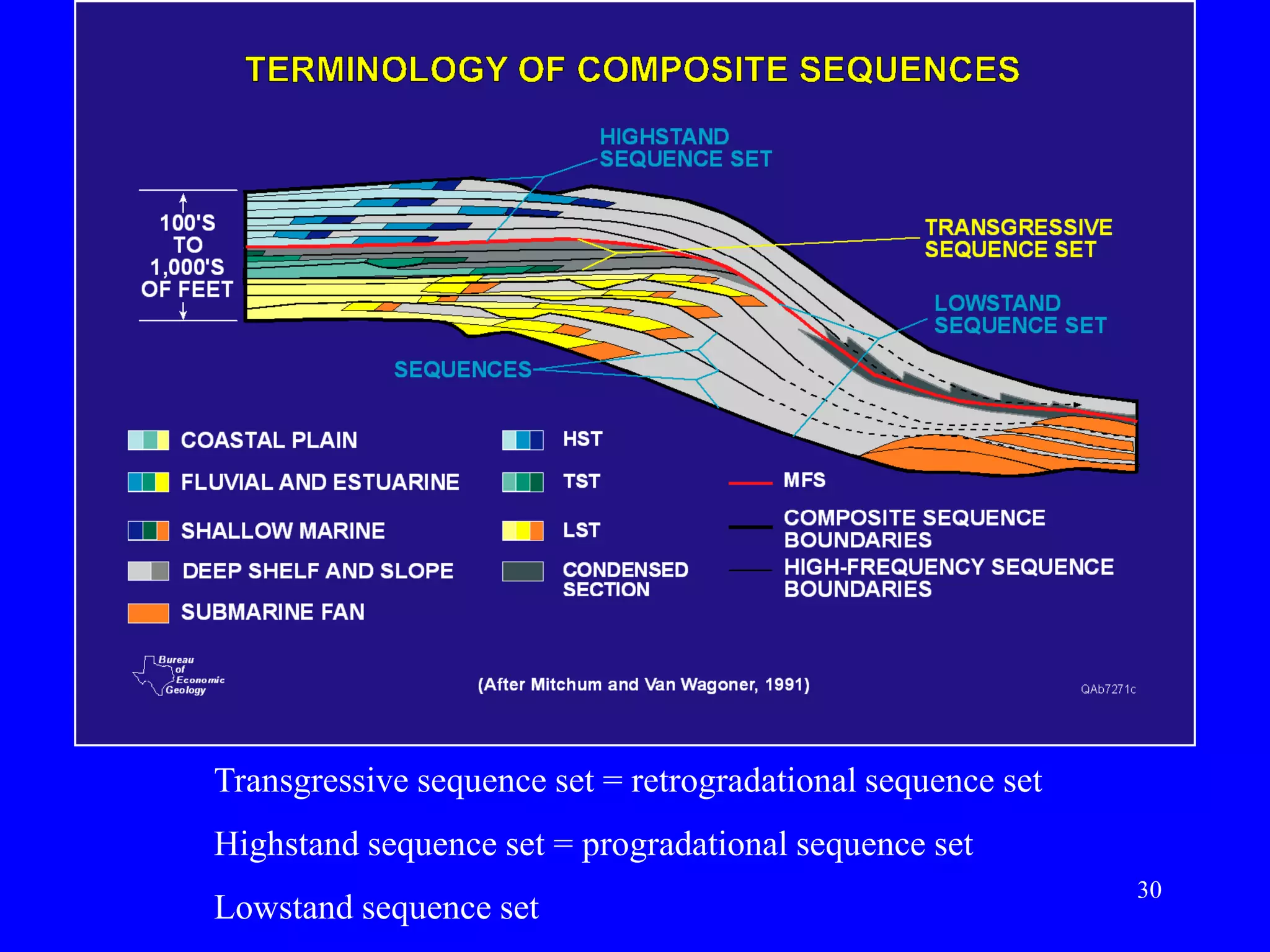
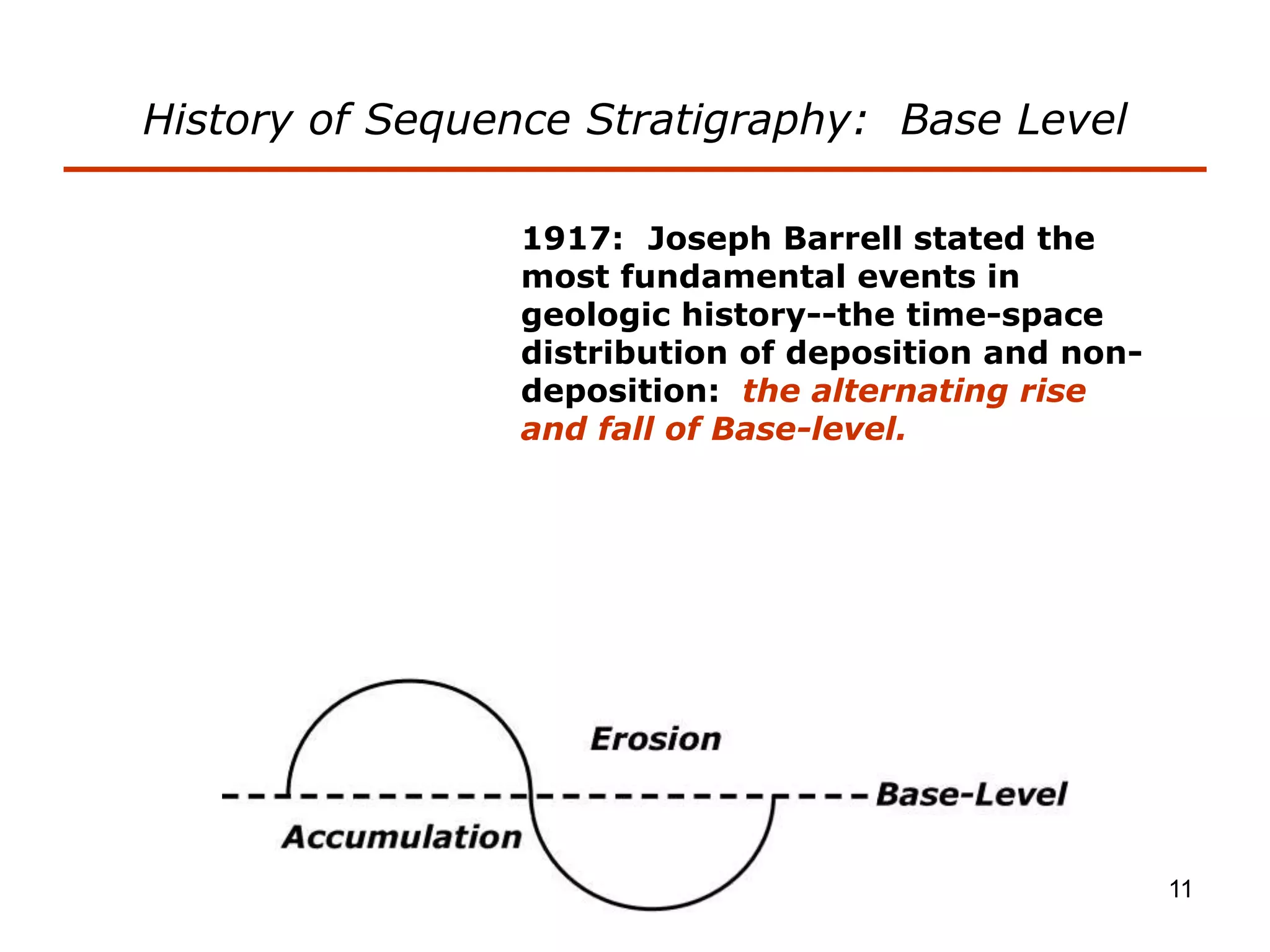
- Sequence stratigraphy subdivides strata using surfaces that represent changes in relative sea level, including sequence boundaries, maximum flooding surfaces, and systems tracts like transgressive and highstand.
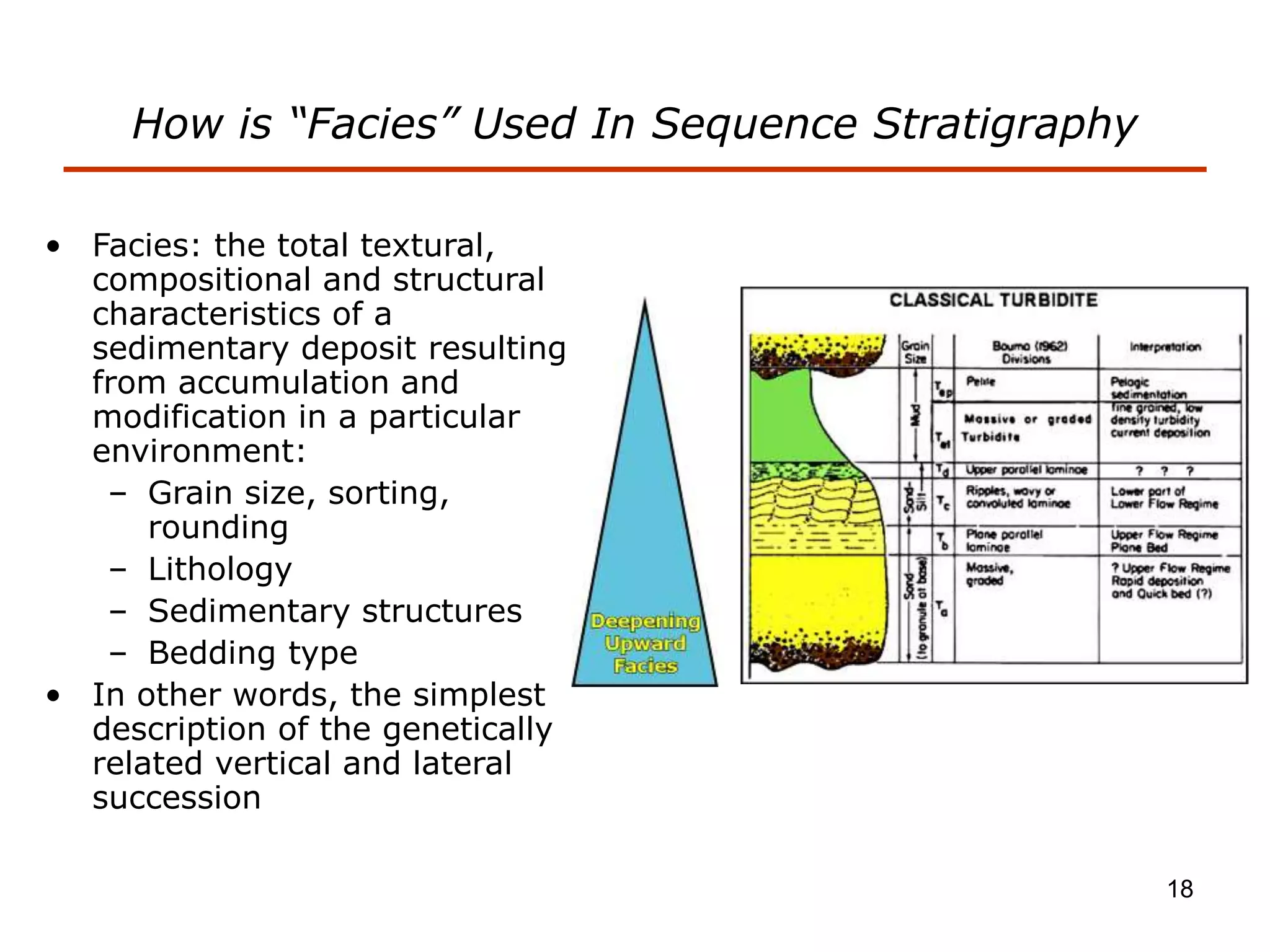
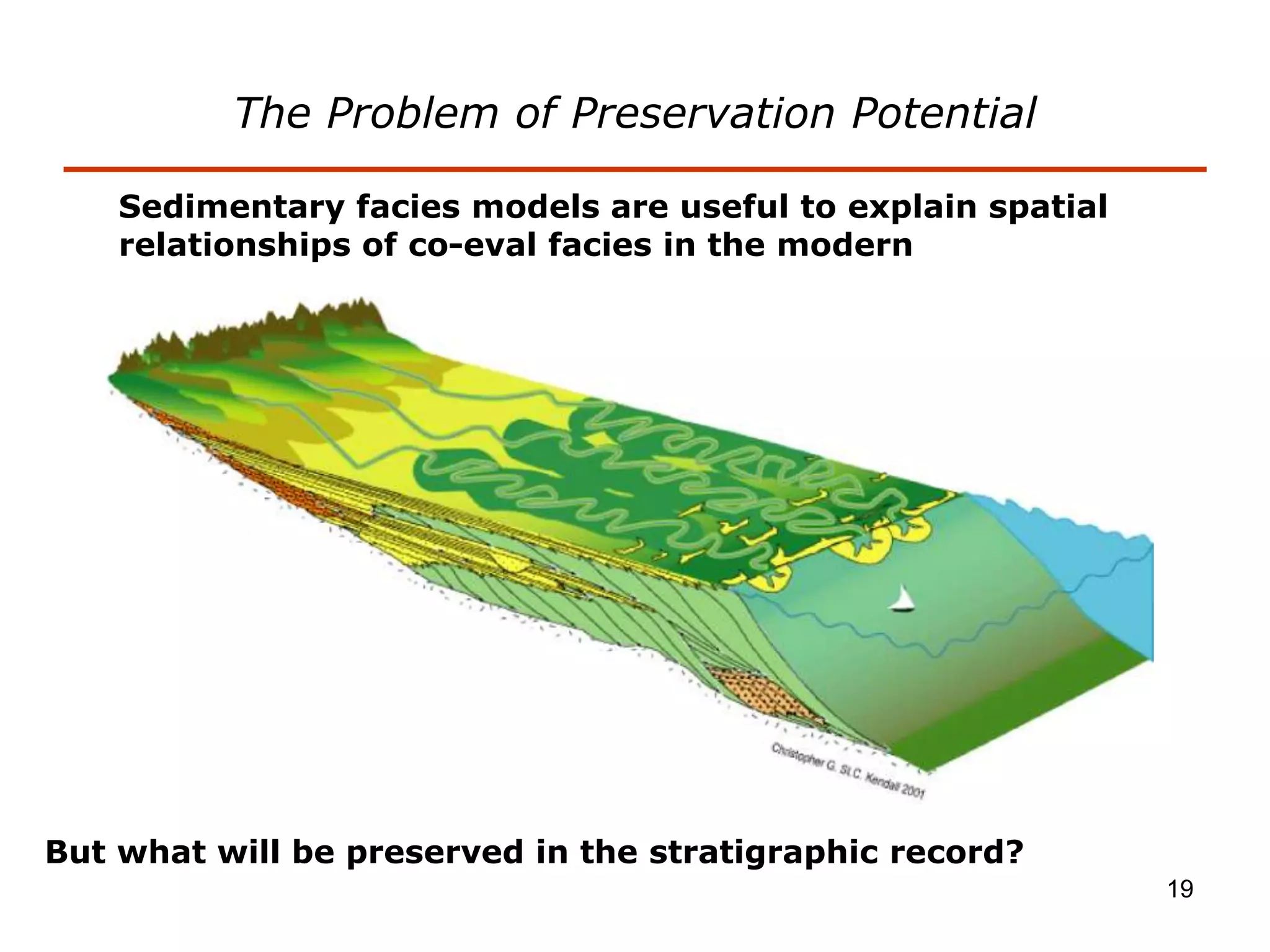
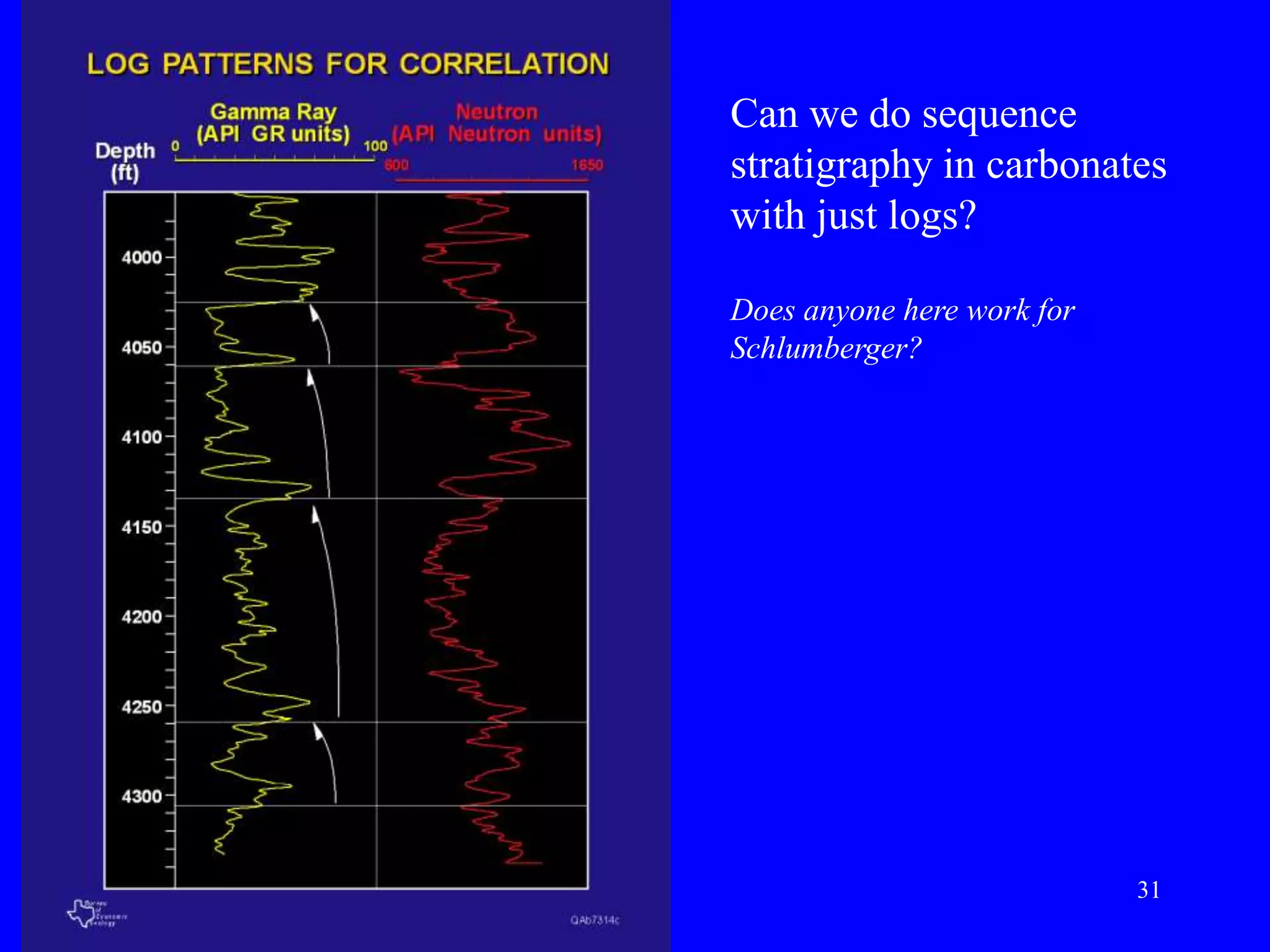
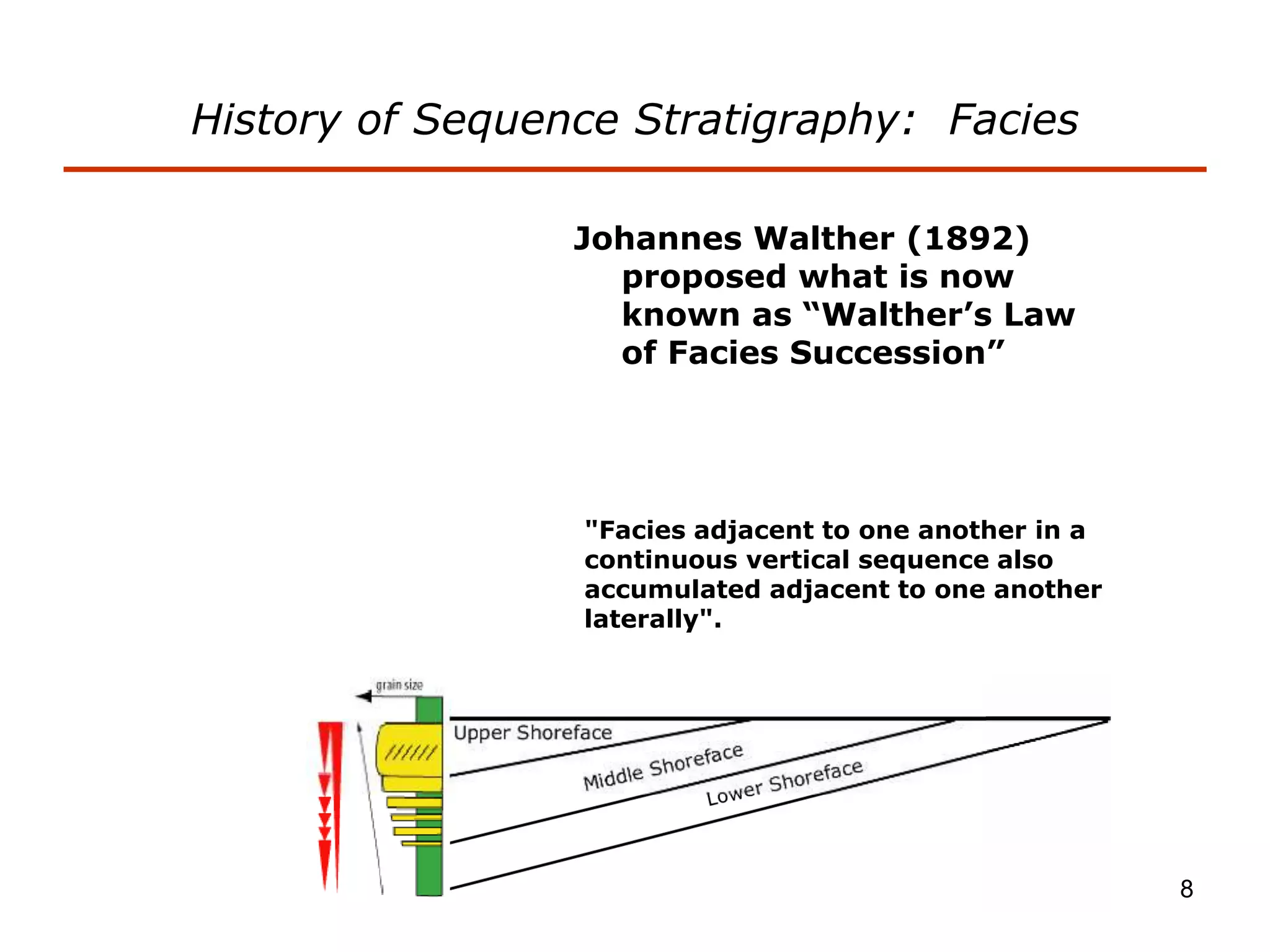
- Facies describe the characteristics of sediment deposited in different environments, and sequence stratigraphy studies the geometric relationships between facies belts to interpret depositional history.






![16
•A framework of genetically related stratigraphic facies
geometries and their bounding surfaces used to determine
depositional setting
•Subdivision & interpretation of sedimentary record using a
framework surfaces seen in outcrops, well logs, & 2-D and
3-D seismic.
•Include: Surfaces of erosion & non-deposition (sequence
boundaries), systems tracts
•Flooding (trangressive surfaces [TS] &/or maximum
flooding surfaces [mfs]); require that relative sea-level is
known
•This framework used to predict the extent of sedimentary
facies geometry, lithologic character, grain size, sorting &
reservoir quality
A Definition of Sequence Stratigraphy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vdocument-230115124817-7c863f8e/75/vdocument-in_pptintroduction-to-sequence-stratigraphy-jackson-viewstratigraphic-principles-ppt-16-2048.jpg)