Embed presentation
Download to read offline




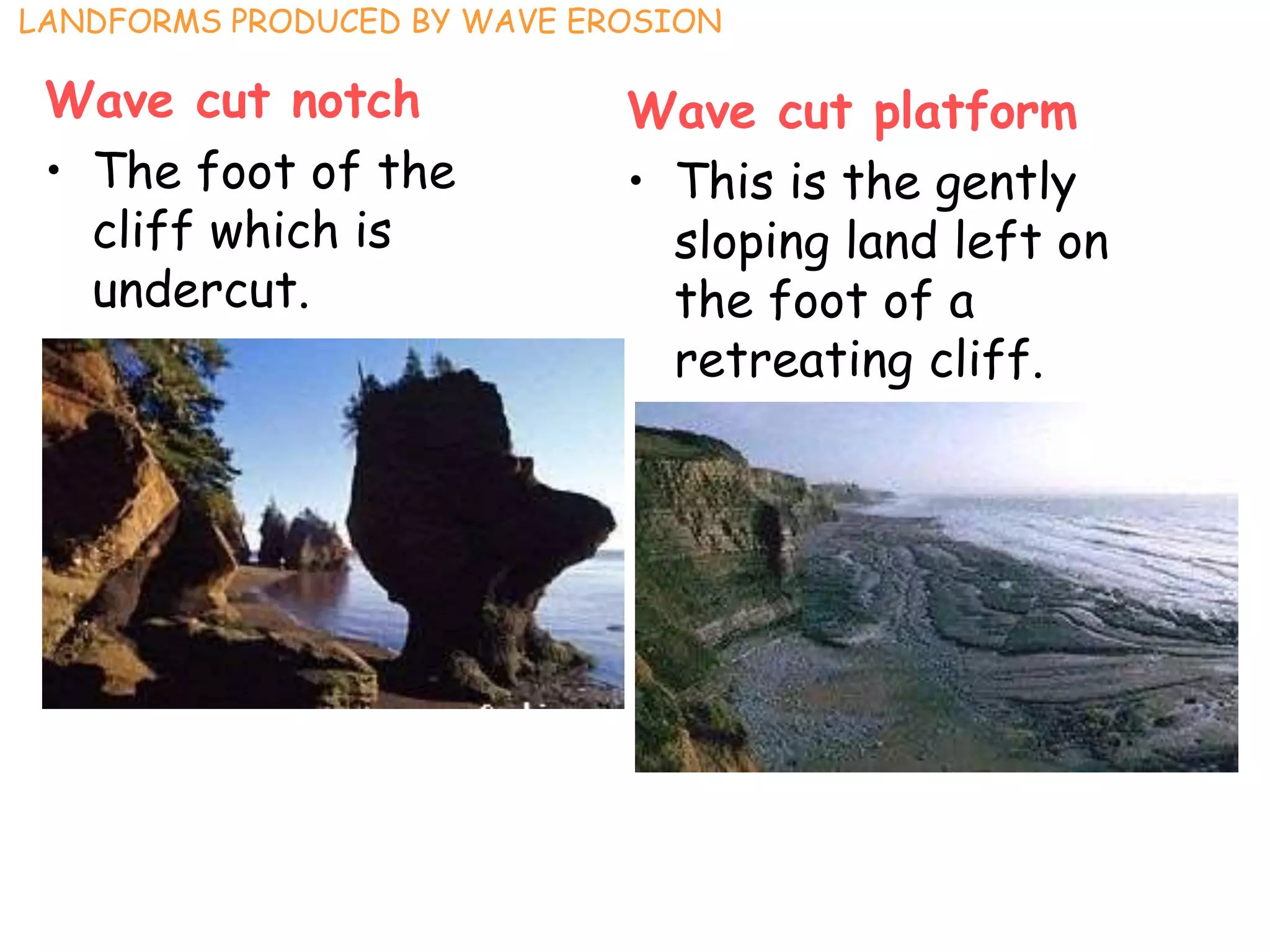
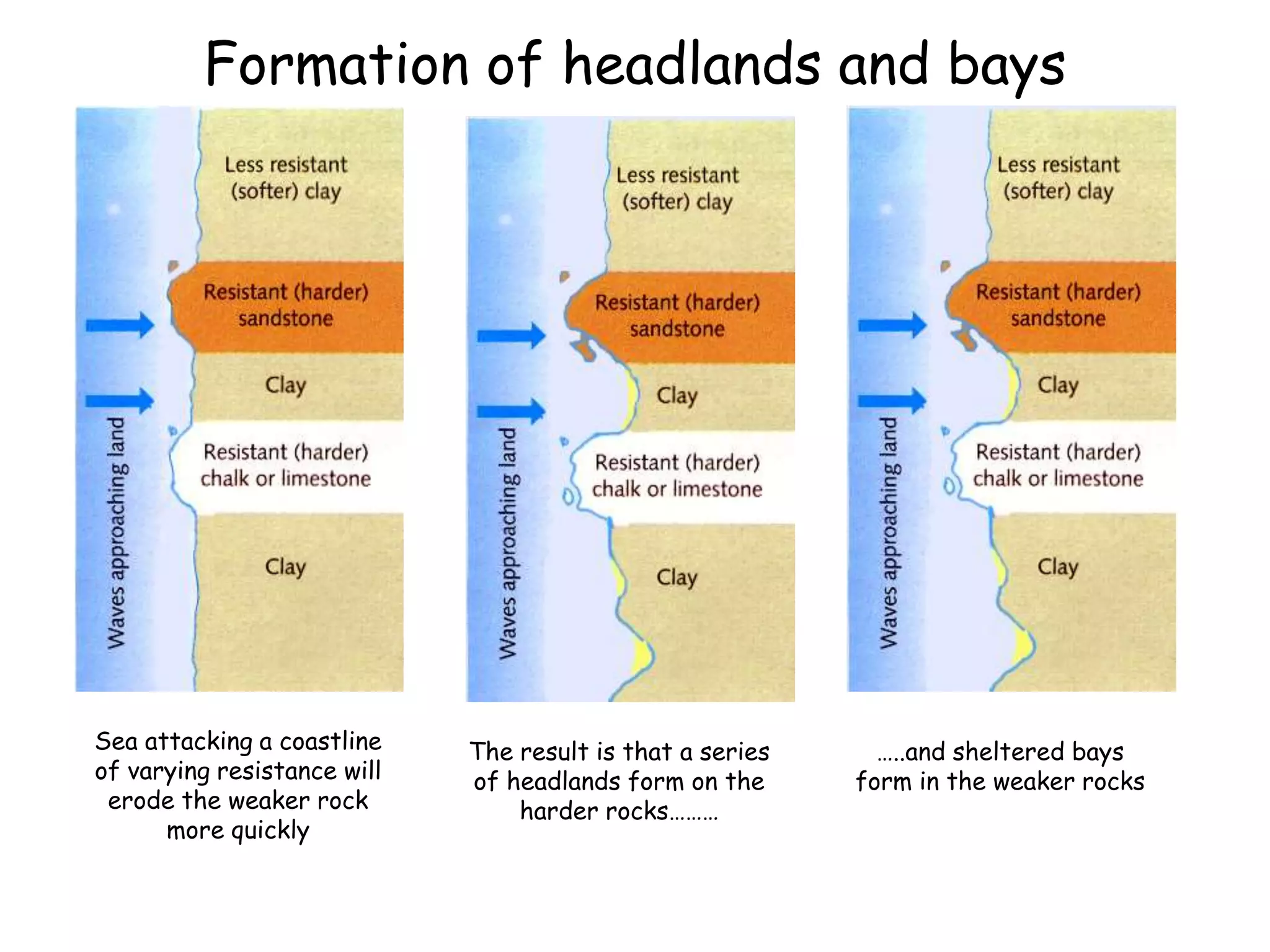
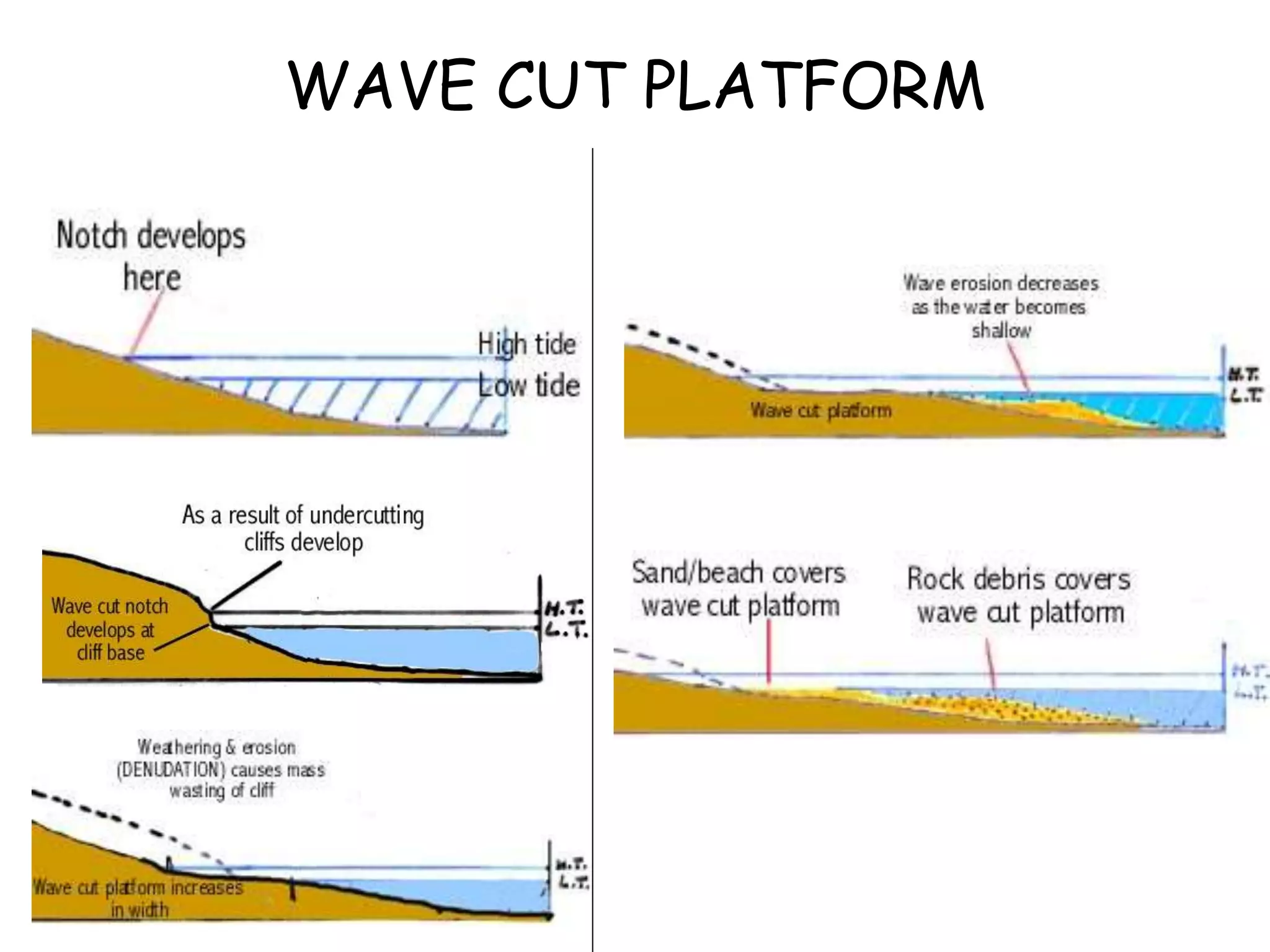
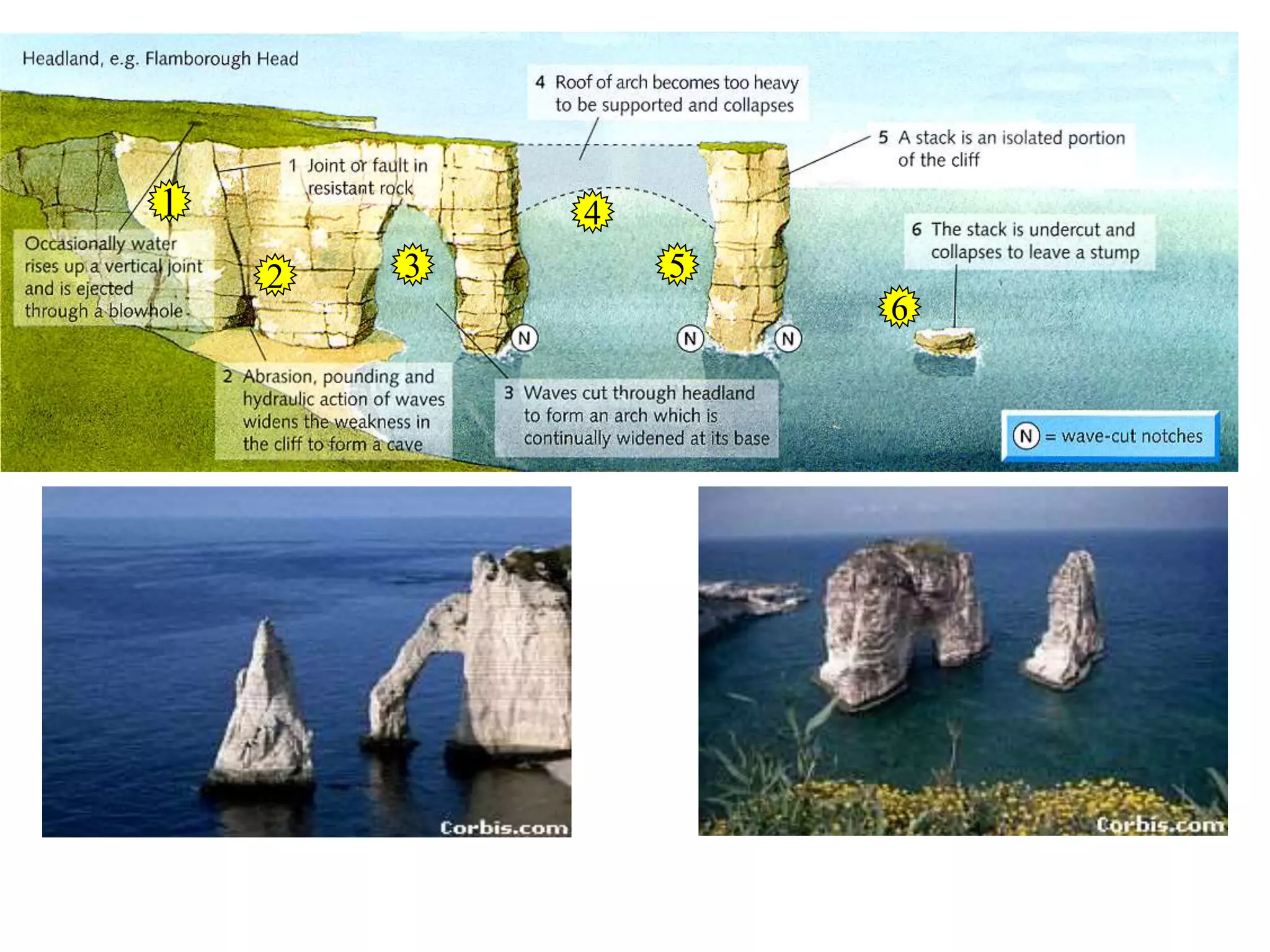




The document describes several landforms produced by wave erosion along coastlines including: - Stacks, which are pillars of rock isolated from the cliff due to wave erosion. - Headlands, which are parts of the coastline that jut out into the sea, often ending in cliffs. - Bays, which are wide curved inlets formed along coastlines with weaker, more erodible rock. - Arches and caves, which are openings formed when waves erode through headlands or into cliffs.











