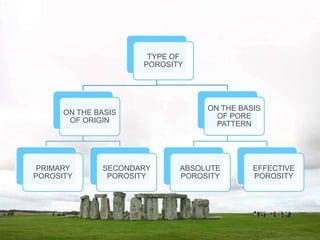
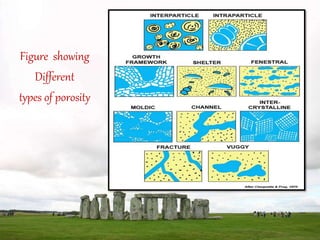
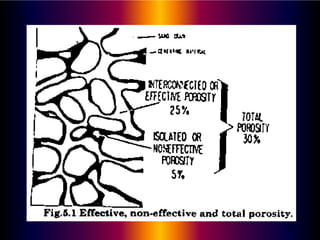
This document discusses key petrophysical properties of hydrocarbon-bearing reservoir rocks including porosity, permeability, saturation, and capillarity. It defines porosity as the ratio of pore space to total volume, permeability as the ability of rocks to allow fluid flow through interconnected pores, saturation as the volume of pore space occupied by a fluid, and capillarity as the pressure difference between fluids across curved interfaces in rock pores. Accurate analysis and modeling of these petrophysical properties is important for estimating petroleum reserves and recovery efficiency from reservoirs.