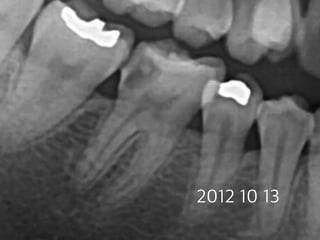
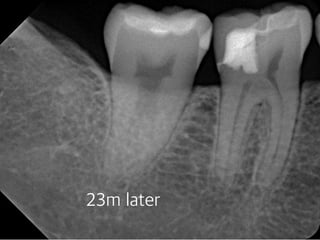
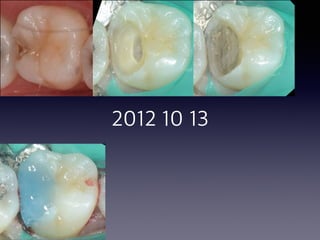
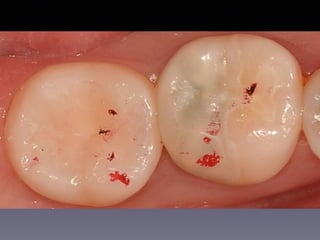
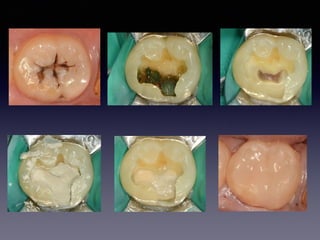
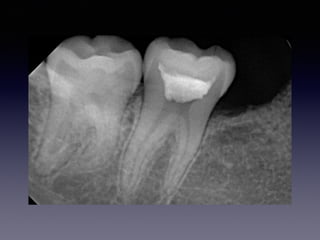
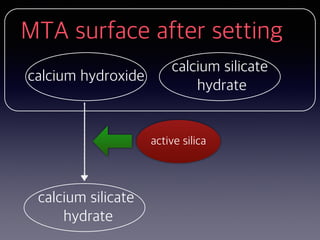
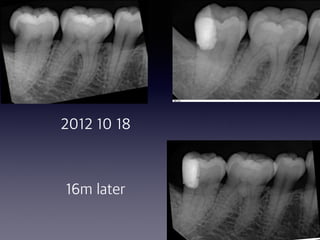
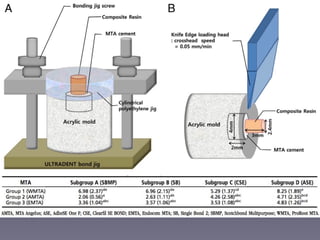
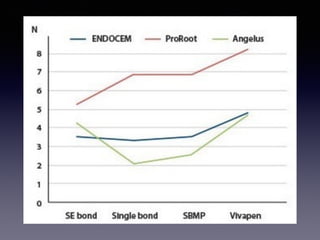
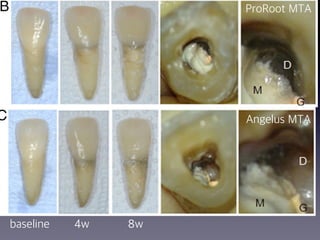
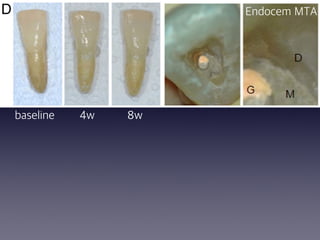
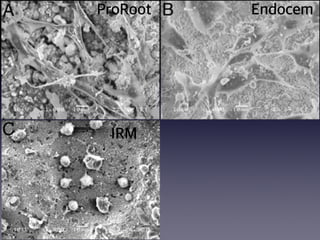
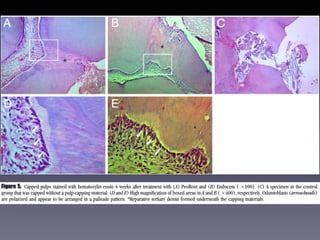
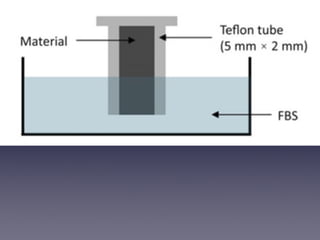
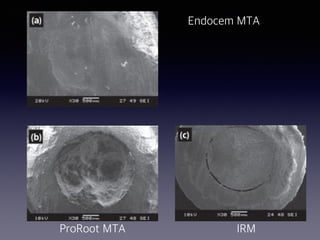
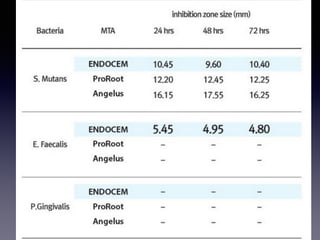
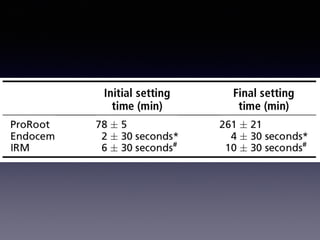
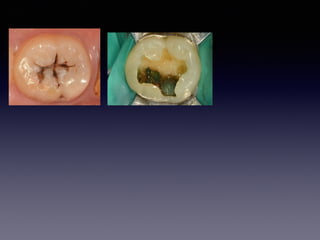
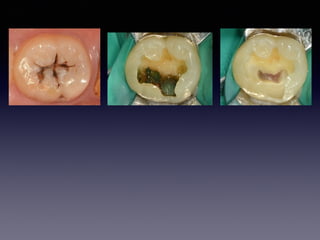
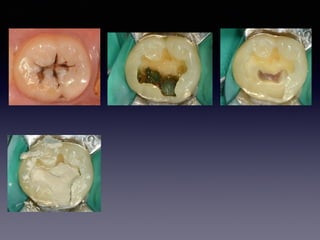
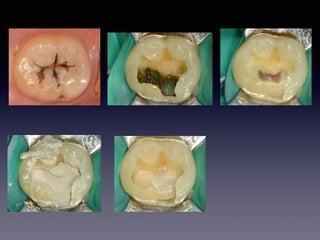
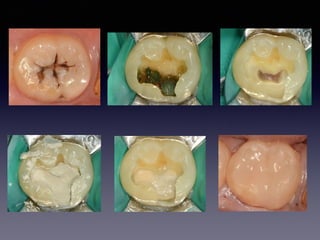
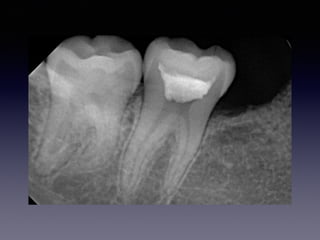
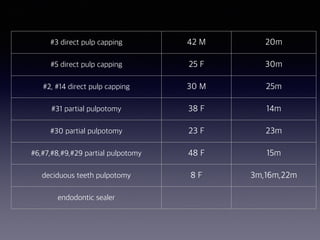
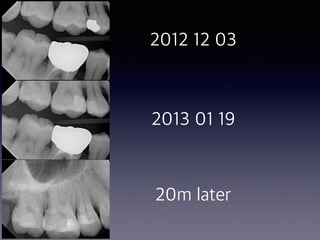
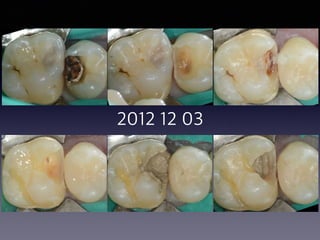
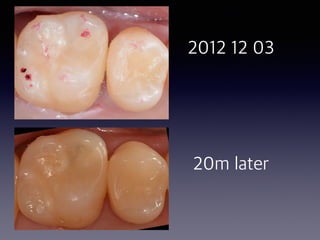
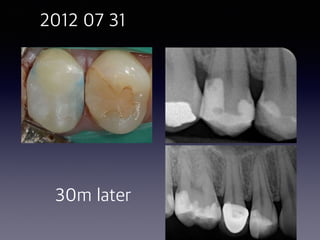
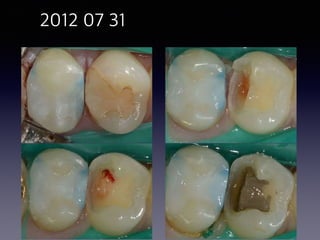
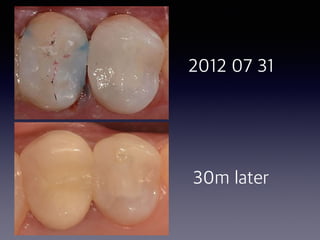
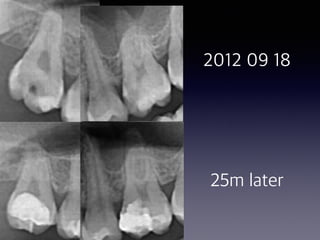
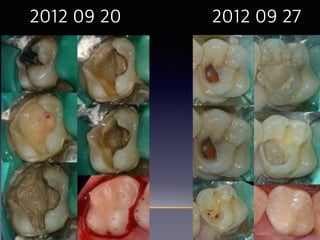
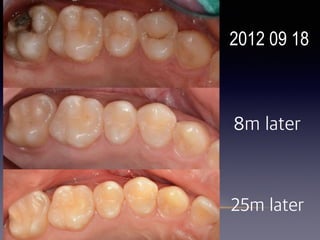
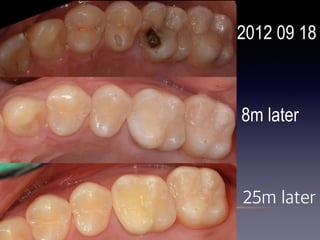
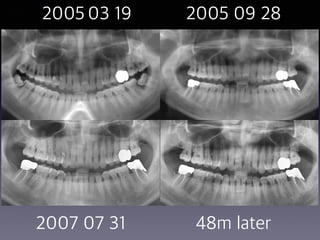
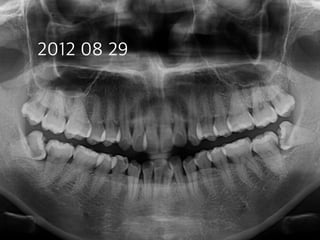
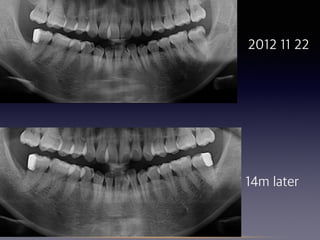
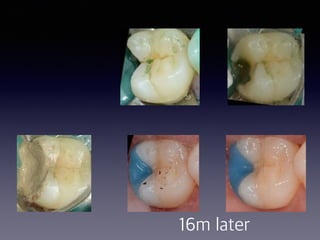
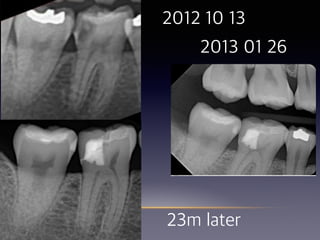
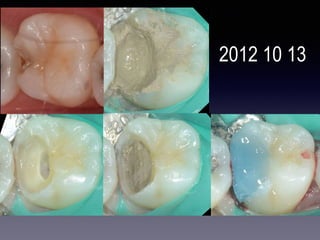
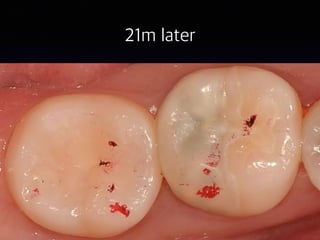
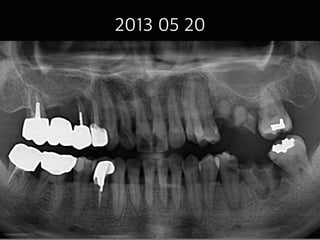
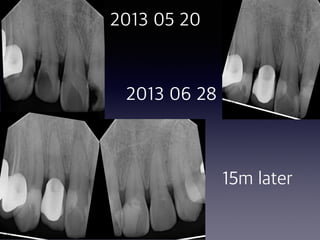
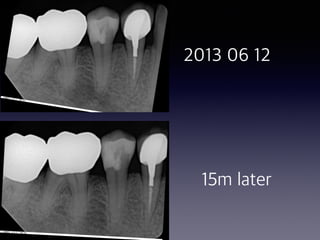
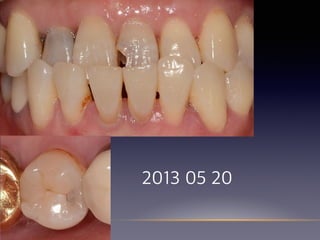
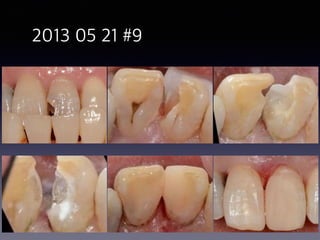
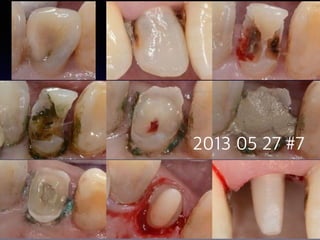
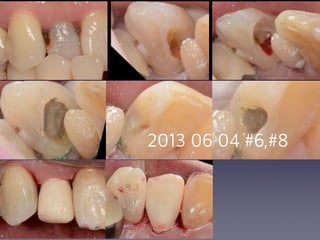
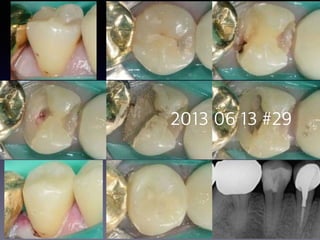
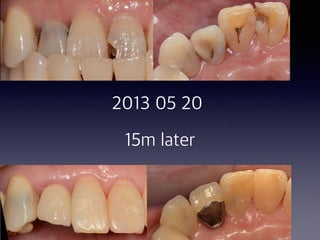
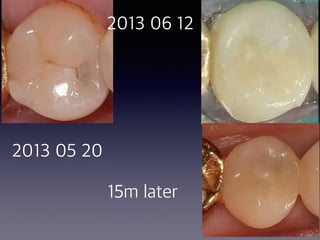
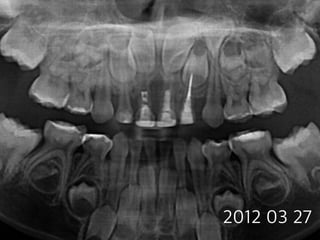
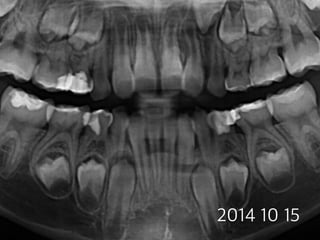
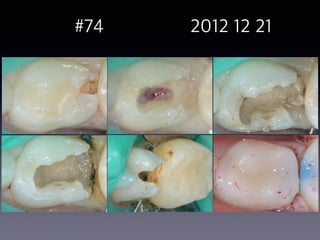
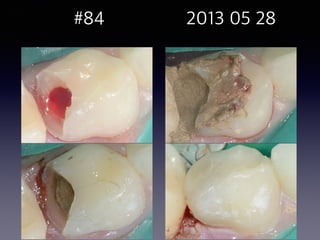
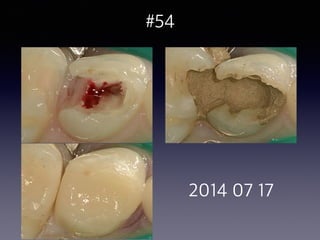
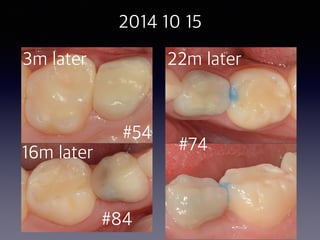
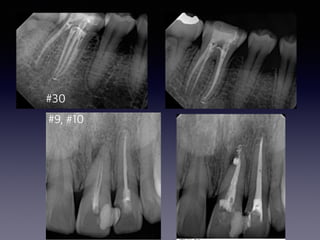
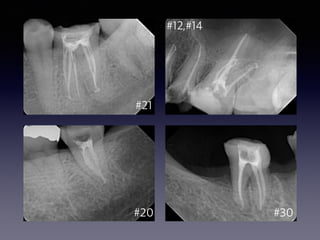
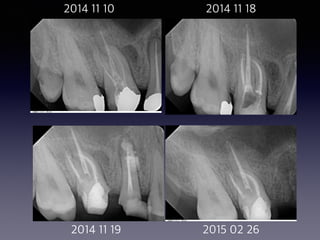
This document summarizes research on the use of Endocem MTA for vital pulp therapies like direct pulp capping, partial pulpotomy, and pulpotomy. It finds that Endocem MTA has biocompatibility, odontogenic effects, sealing ability, lacks discoloration, and antibacterial effects similar to ProRoot MTA. Case studies show high success rates for these treatments over periods of up to 3 years. While long term studies are still needed, Endocem MTA appears to be an effective and safer alternative to calcium hydroxide for vital pulp therapies.