Embed presentation
Downloaded 15 times

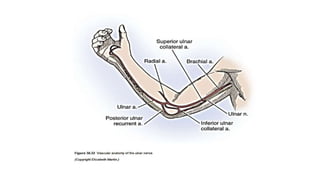

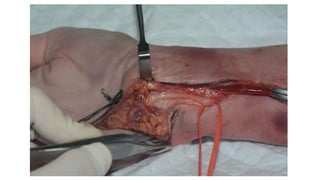

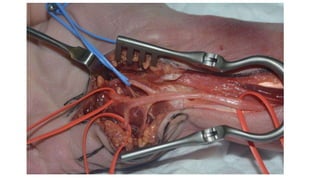

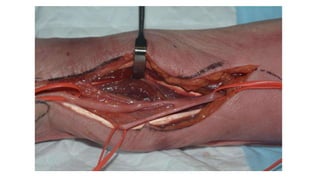

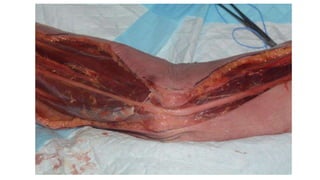



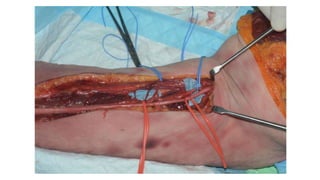
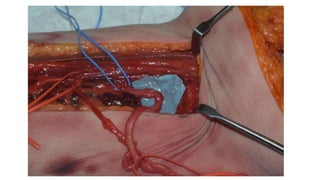


The document describes the surgical technique for harvesting a vascularised ulnar nerve graft. The dissection begins by incising over the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon proximal to the wrist. The nerve is identified and followed distally into the Guyon canal between the pisiform bone and hook of the hamate. Proximally, the nerve is followed into the olecranon notch and divided above the superficial ulnar collateral artery, ensuring a vascularized graft. The harvested ulnar nerve with vascular supply is then ready to be coapted to the target nerve.















