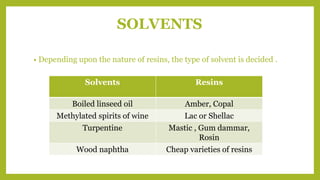
Varnishing is done to protect and beautify wooden surfaces. An ideal varnish forms a hard, durable protective film while maintaining an attractive gloss. Varnishes contain resins like copal or shellac, driers to accelerate drying, and solvents like linseed oil, turpentine or spirits of wine. Main types are oil, spirit, turpentine and water varnishes, which vary in drying time and durability. The varnishing process involves preparing the wood surface, treating knots, applying multiple thin coats until finished.