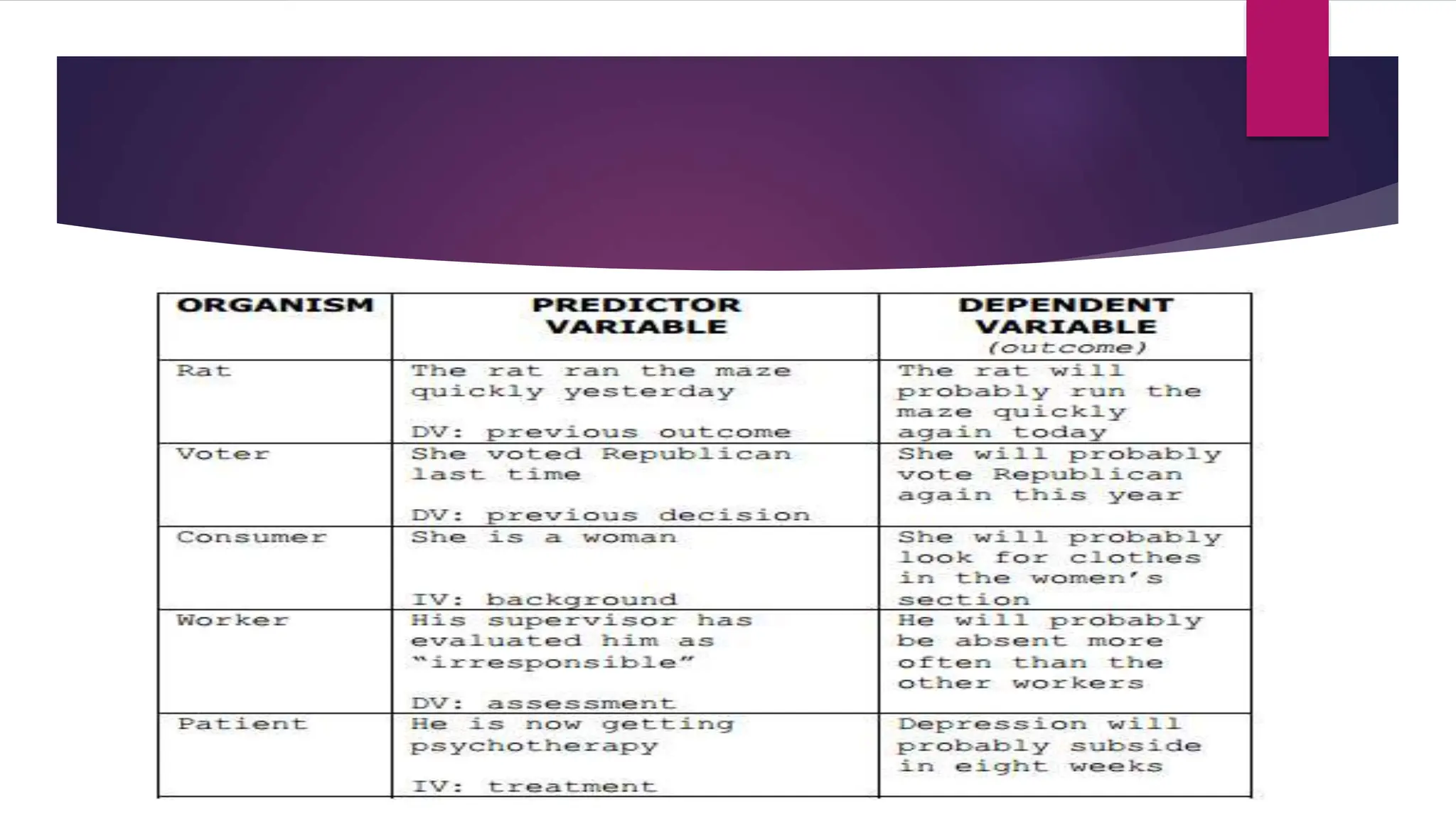
The document discusses the classification of variables in research, detailing types such as numeric, categorical, experimental, and non-experimental variables. It includes definitions and examples of continuous and discrete variables, as well as ordinal, nominal, dichotomous, and polychotomous variables. The significance of understanding these classifications is emphasized for effective research design and analysis.