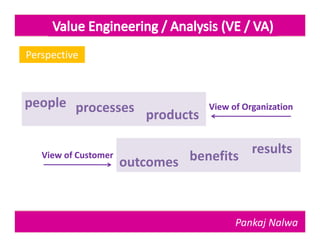
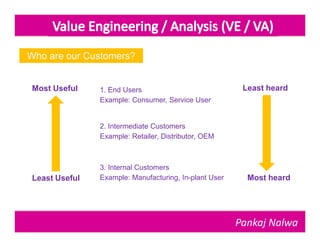
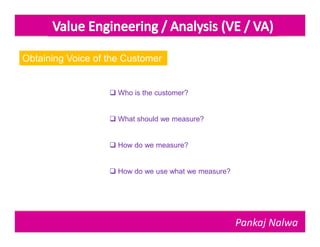
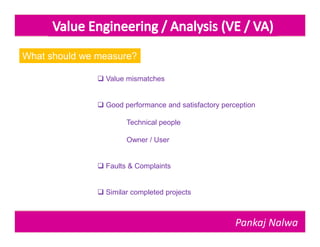
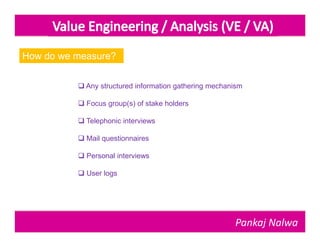
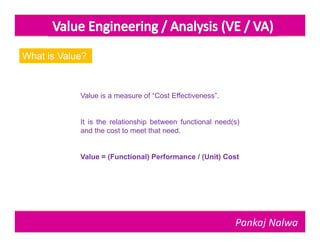
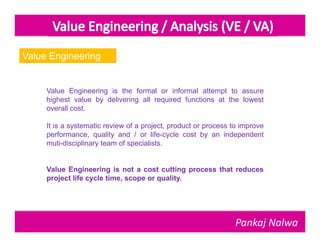
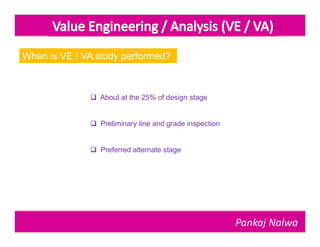
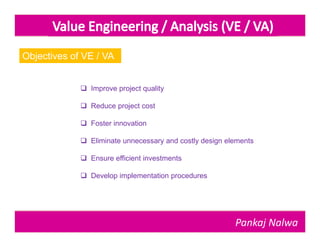
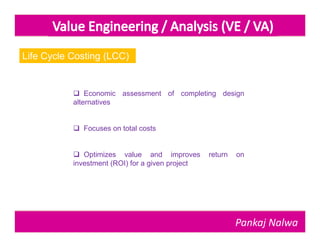
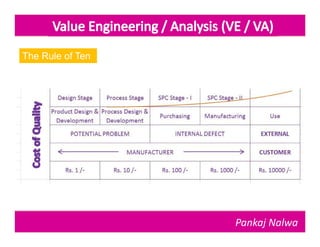
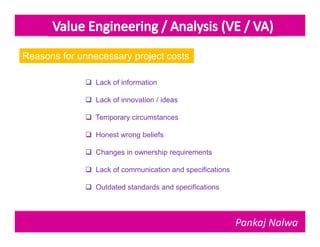
Pankaj Nalwa has over 16 years of industrial experience and specialized training in tooling and product development. He holds an MBA in International Business and has led training programs in quality practices, tool room management, product development, and more. As a trainer, he emphasizes viewing organizations from the perspectives of customers, products, processes, and results. He teaches methods for capturing the voice of customers, including focus groups, interviews, and surveys to understand value mismatches and customer satisfaction. Nalwa promotes value engineering to deliver required functions at the lowest cost through a multi-disciplinary team review of projects, products, and processes.