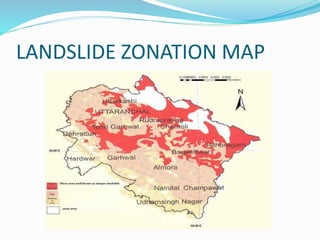
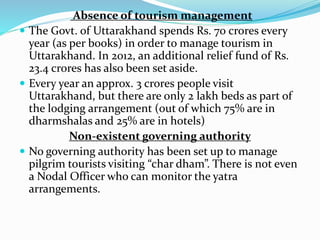
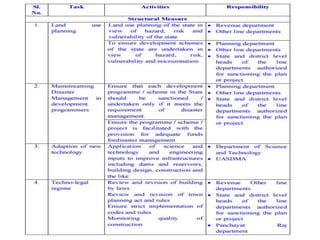
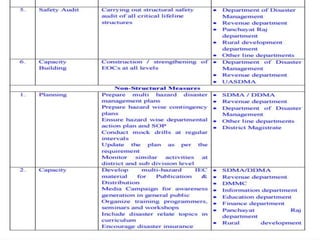
The document summarizes a case study on the 2013 Uttarakhand floods in India. It describes how heavy rainfall from June 14-17, over 375% of the average, caused devastating floods and landslides. The melting of the Chorabari Glacier triggered flooding of the Mandakini River. Over 800 people died and infrastructure like roads and buildings were damaged. Both natural factors like heavy rainfall and landslides, as well as man-made factors like deforestation, construction of hydroelectric projects, and lack of disaster management planning, contributed to the severe impacts of the floods.
![CASE STUDY ON
UTTARAKHAND FLOOD
DISASTER
SUBMITTED BY:
VISHNU DUA [12MEU095]
VINEET KUMAR [12MEU093]
SIDDHARTH SOOD [12MEU084]
MOHIT VIJ [12MEU056]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ukflooddisaster2013-150423104458-conversion-gate01/75/uttarakhand-flood-disaster-2013-1-2048.jpg)