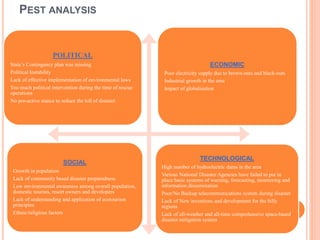
The case study on the Uttarakhand disaster covers the causes, impacts, and management principles related to the event, highlighting significant loss of life and economic damage due to natural calamities exacerbated by unplanned development and tourism. It emphasizes the need for improved disaster preparedness and management practices, including proactive community involvement and environmental protection measures. Recommendations include implementing better planning, reducing tourism impacts, and enhancing early warning systems.