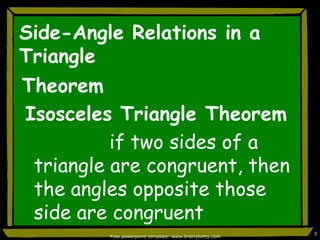
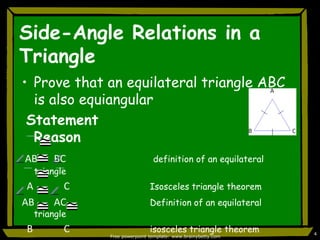
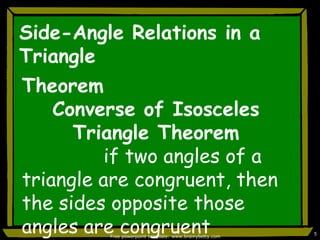
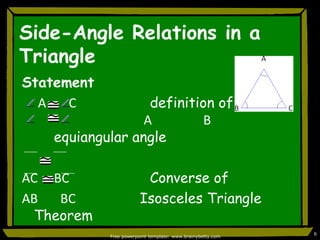
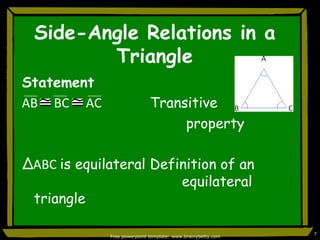
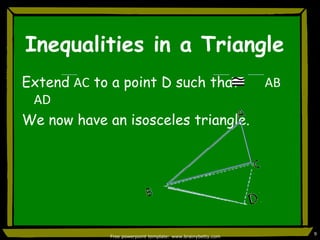
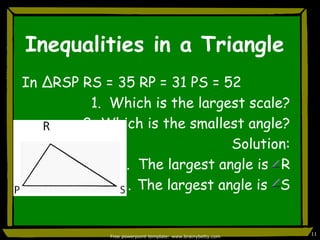
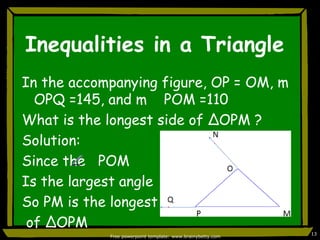
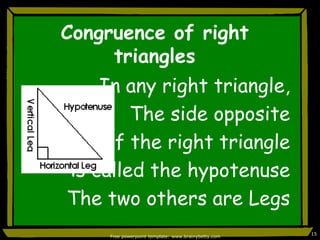
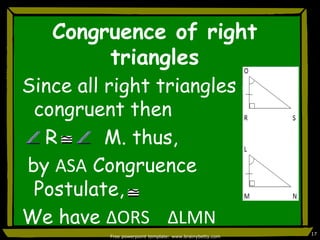
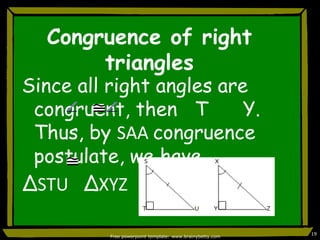
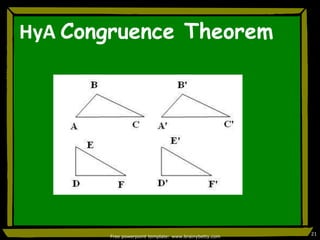
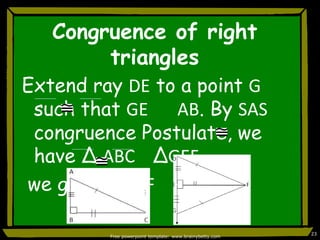
This document discusses triangle congruence and relationships between sides and angles of triangles. It introduces several theorems regarding isosceles, equilateral, and right triangles including: if two sides of a triangle are congruent, the angles opposite them are also congruent; if two angles of a triangle are congruent, the sides opposite them are also congruent; and if corresponding parts of two right triangles are congruent, the triangles are congruent. Examples are provided to demonstrate applying these theorems.