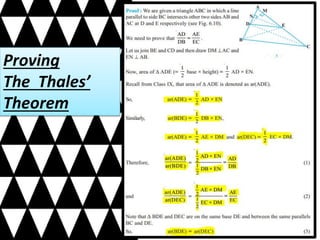
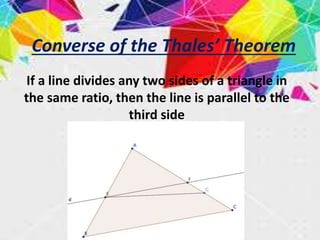
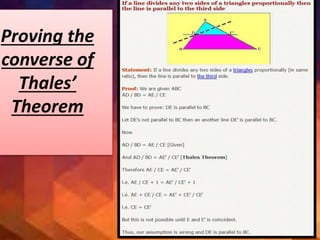
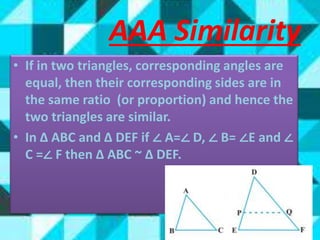
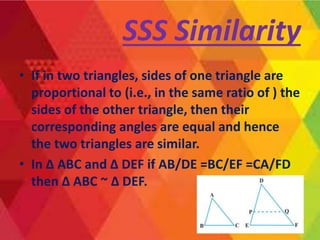
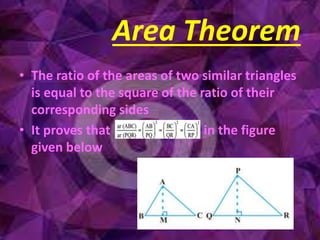
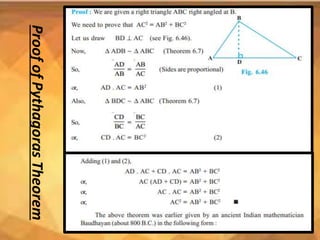
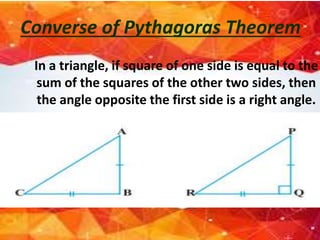
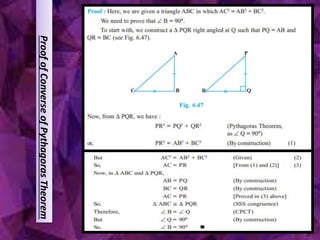
This document summarizes key concepts in geometry related to triangles. It discusses similarity criteria including AAA, SSA, and SSS. It also covers the area theorem, Pythagorean theorem, and its converse. The basic proportionality theorem and its converse are explained as well as how they relate to parallel lines. In summary, this document outlines important triangle properties and theorems for understanding similarity, area, right triangles, and parallel lines.