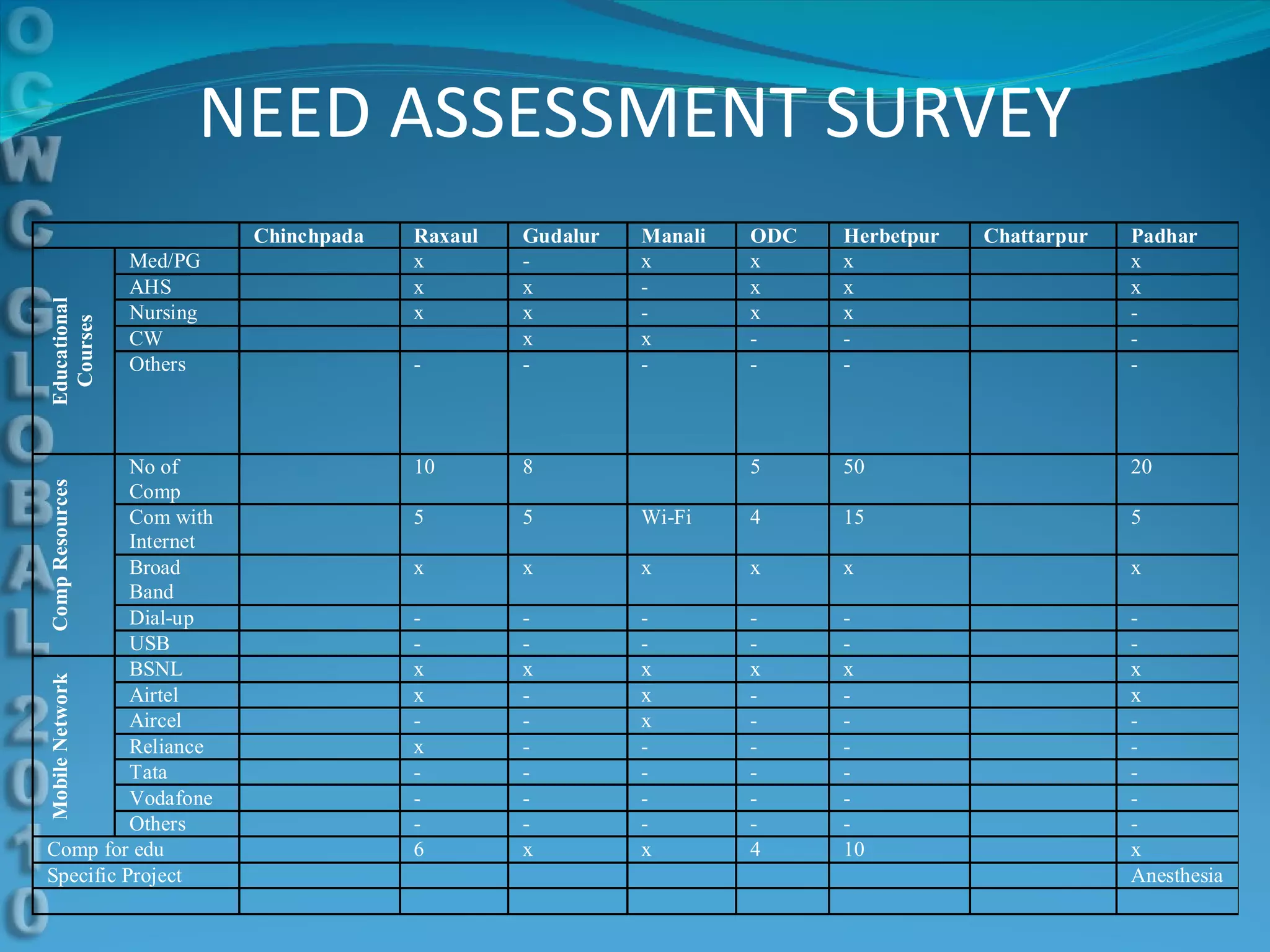
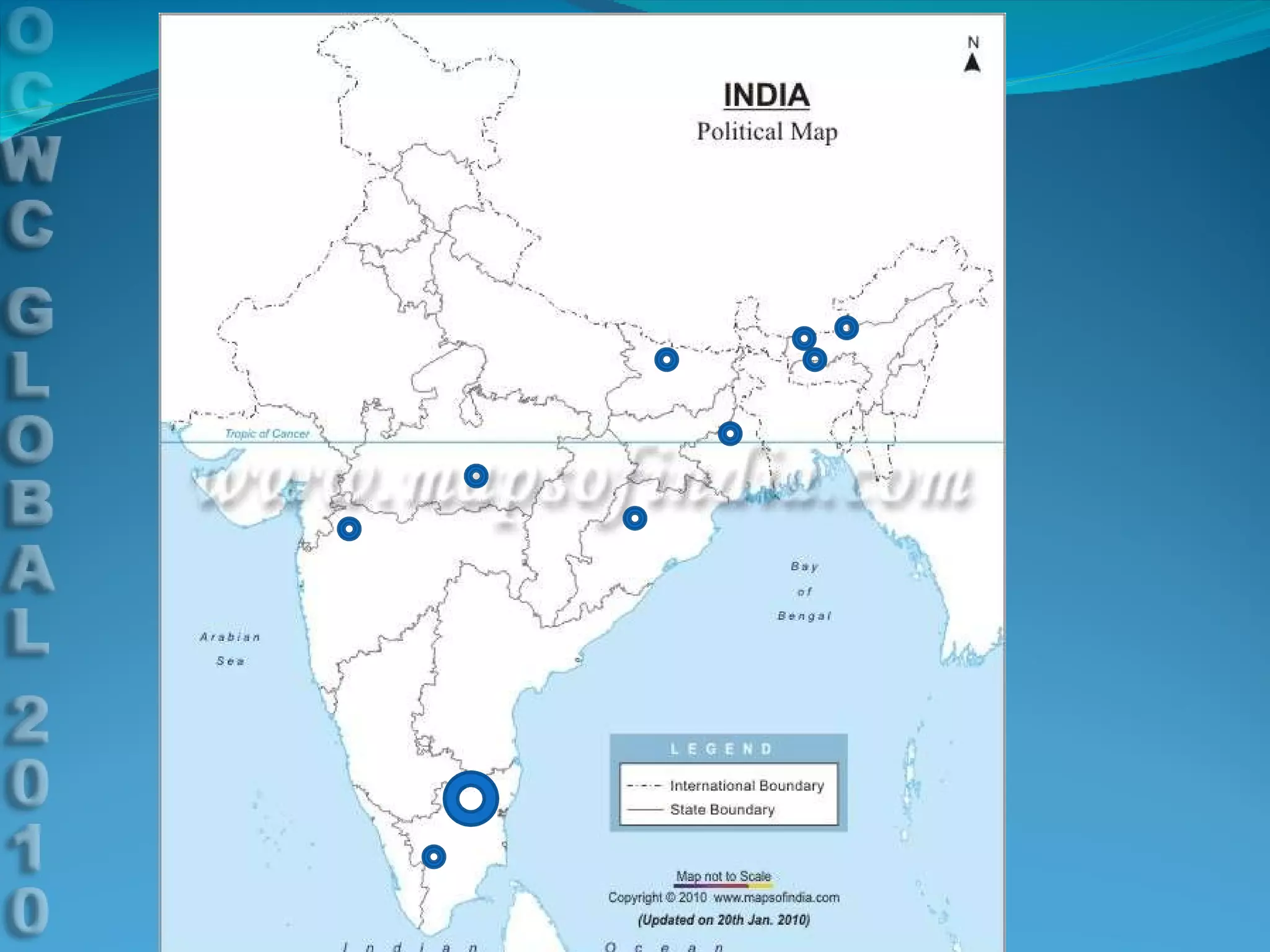
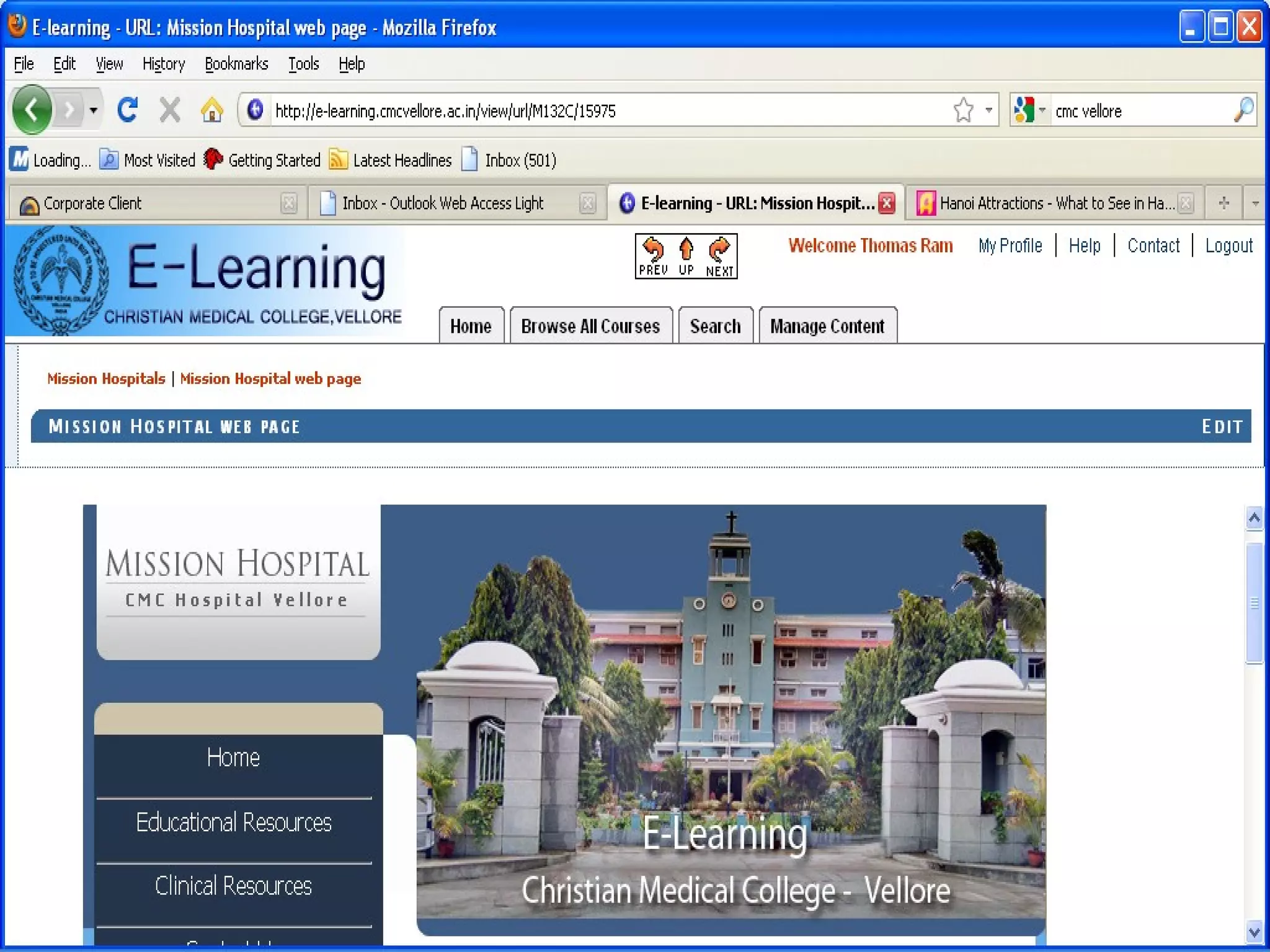
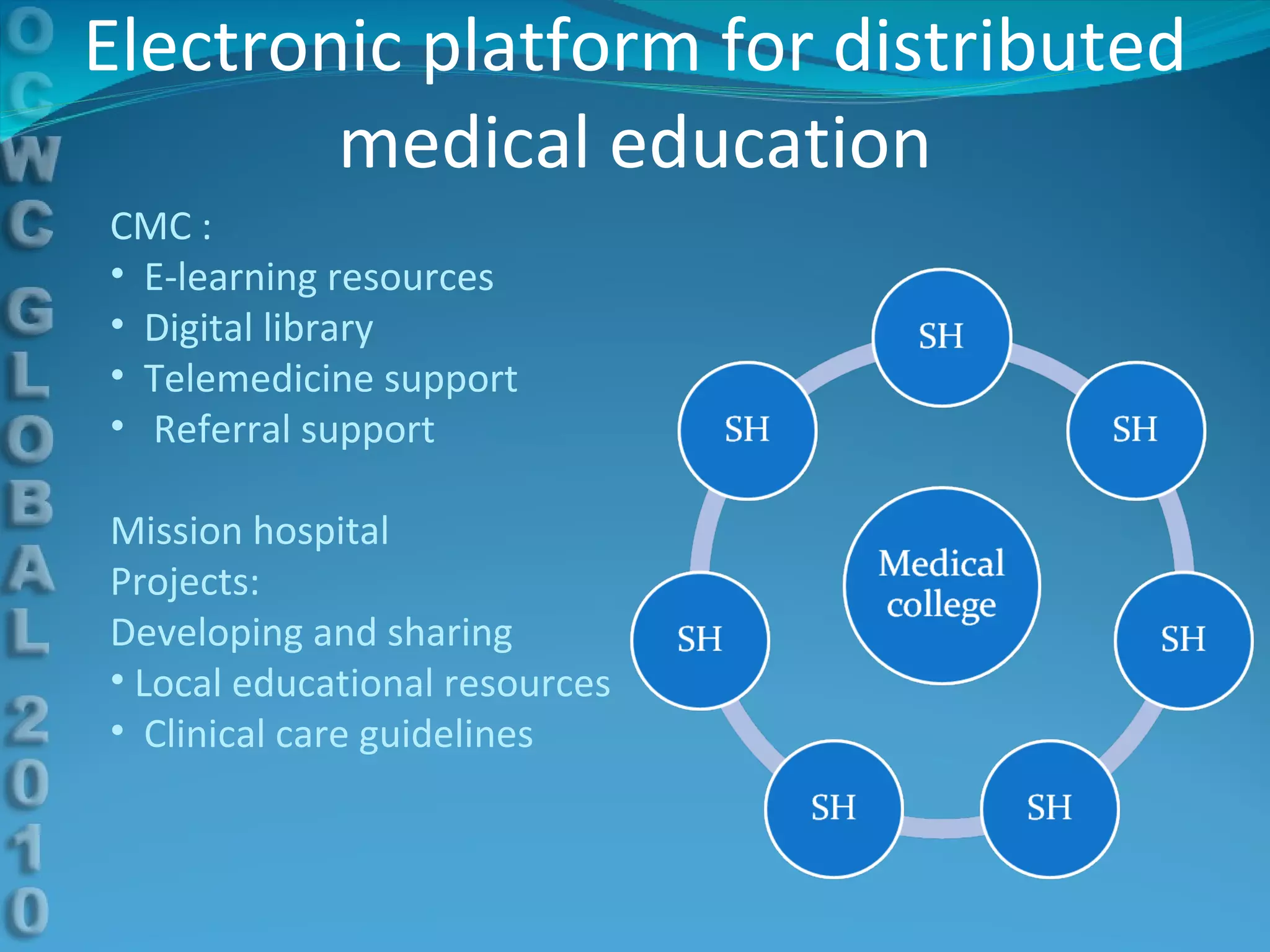
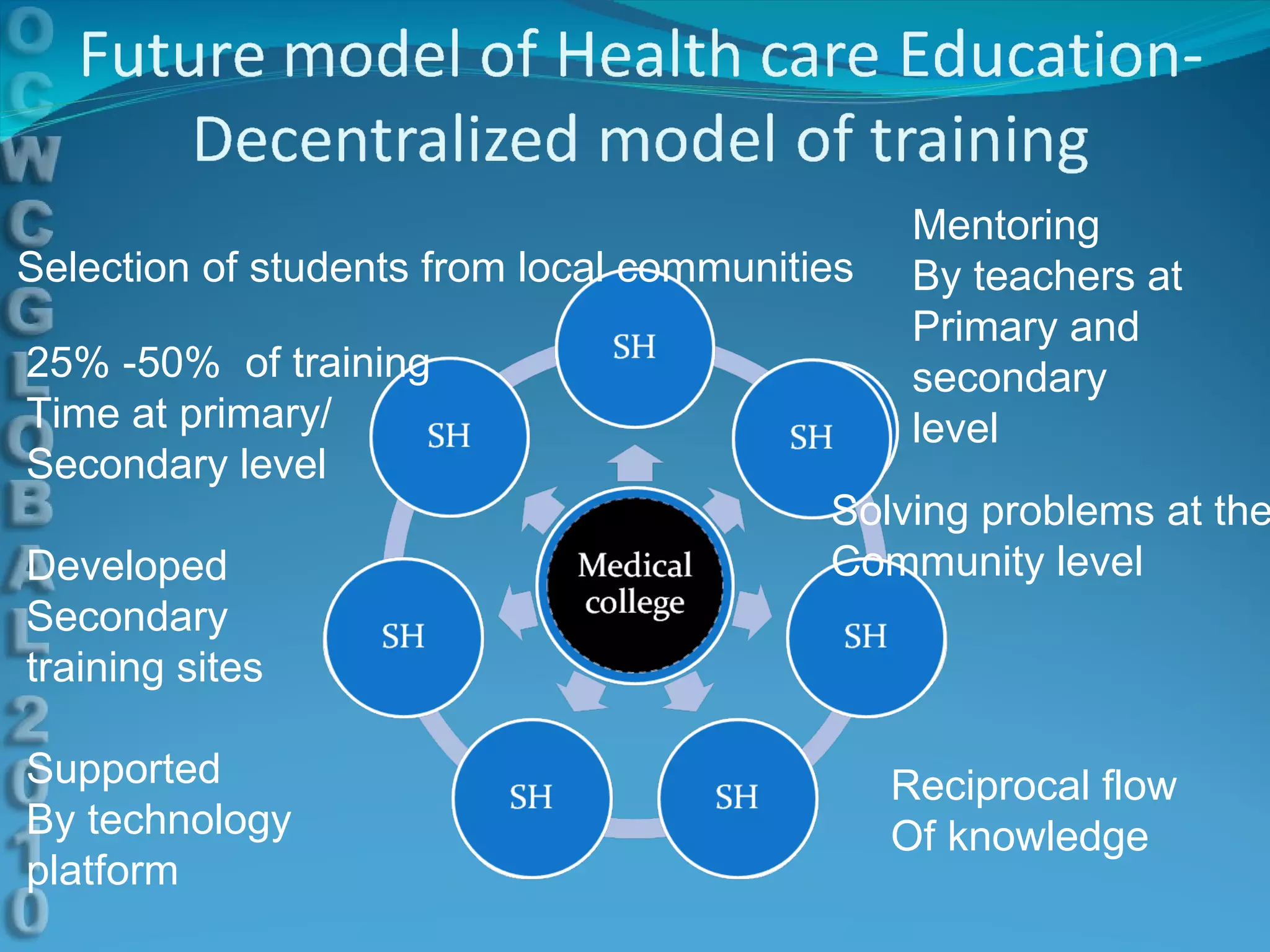
This document discusses using e-learning to support medical education and healthcare delivery at secondary hospitals in rural India. It outlines CMC Mission Hospitals' existing e-learning linkage and a needs assessment survey that found secondary hospitals have the infrastructure to access e-learning resources. The document proposes developing e-learning projects to provide clinical resources, guidelines, and networking opportunities to isolated hospitals. It envisions selecting some medical students from local communities and having them do part of their training at primary and secondary sites, with technology platforms and mentors supporting distributed education.





























![THANK YOU FOR YOUR KIND ATTENTION THANK YOU FOR YOUR KIND ATTENTION [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingoerforhealthcareeducationthomasram-100517004404-phpapp02/75/Using-OER-for-Health-Care-Education-39-2048.jpg)