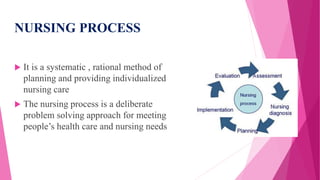
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various aspects of hospital care, including definitions, types, and roles of nurses across different hospital settings such as acute, critical, long-term, and home health care. It emphasizes concepts such as patient-centered care, interdisciplinary teamwork, and the characteristics of effective hospitals while detailing staff roles and training practices. Additionally, it discusses the impact of hospitalization on patients and their families, as well as the relationship between stress and health.