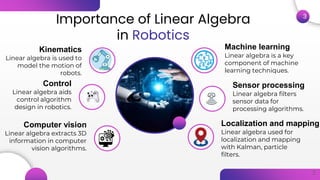
Linear algebra plays a crucial role in various aspects of robotics by providing mathematical tools to represent, analyze, and control robotic systems. It is used for robot kinematics to model motion, control algorithms, computer vision algorithms, machine learning techniques, localization and mapping with filters, and processing sensor data. Specifically, it enables representation of robot poses with homogeneous transformations, solving forward and inverse kinematics with matrices, control of robot motion with Jacobian matrices, fusing sensor measurements with Kalman filters, rectifying images and reconstructing 3D scenes with transformation matrices, and building accurate maps through sparse matrices and linear systems.