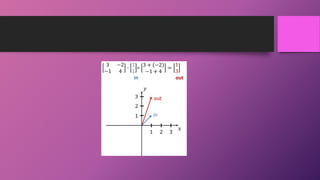
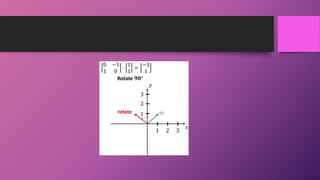
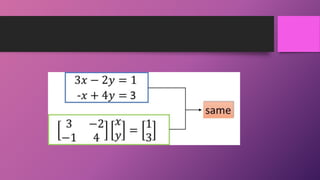
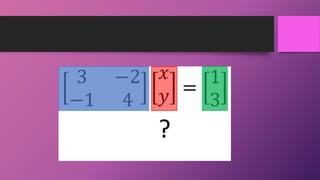
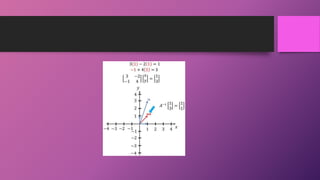
Linear algebra is the foundation of machine learning. Most machine learning data is represented as vectors, matrices, or tensors, so linear algebra is heavily relied upon. Vectors are 1D arrays that represent points with magnitude and direction. Matrices are 2D arrays of numbers with fixed rows and columns. Tensors generalize vectors and matrices by allowing more than two dimensions, such as 3D images with RGB values. Key concepts in linear algebra include eigenvectors, which are vectors only scaled by a matrix, and eigenvalues, which are the scaling factors.




![A matrix
• A matrix is a two-dimensional array of numbers, that has a fixed
number of rows and columns. It contains a number at the
intersection of each row and each column. A matrix is usually
denoted by square brackets [].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linearalgebra-230123035038-d23f7133/85/linear_algebra-pptx-5-320.jpg)