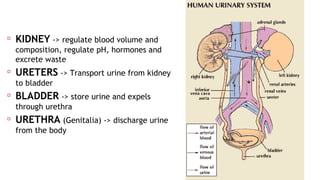
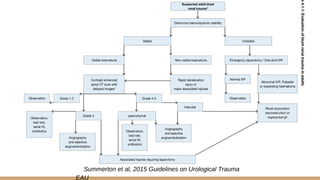
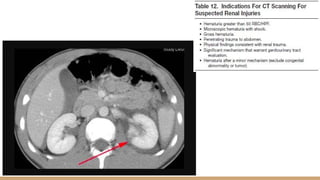
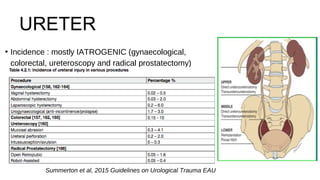
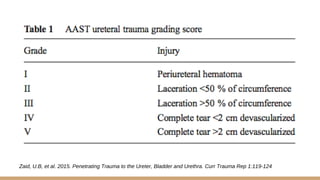
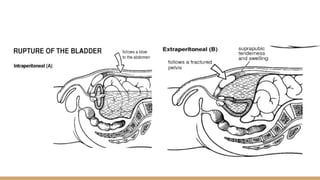
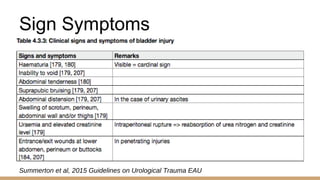
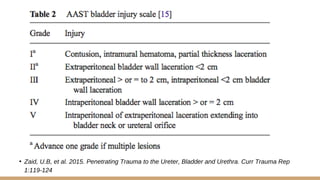
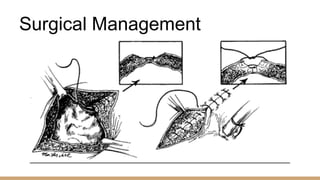
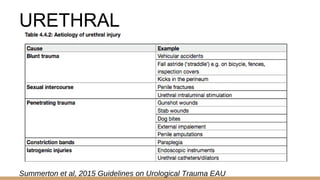
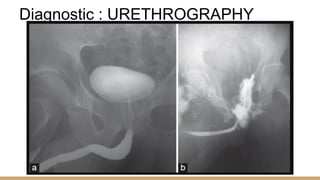
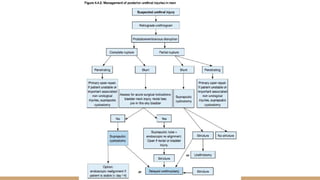
This document summarizes urogenital trauma, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It notes that the kidneys are most commonly injured in blunt trauma from impacts with seatbelts or steering wheels. Bladder and posterior urethra injuries are often associated with pelvic fractures from blunt trauma. Evaluation of trauma involves examination for bruising, hematuria, and penetrating objects. Imaging like ultrasound, IVP, CT and cystography are used for diagnosis. Surgical management depends on the specific organ injured and degree of trauma.