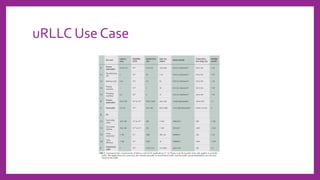
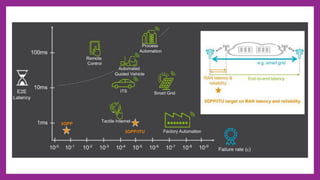
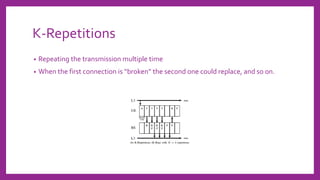
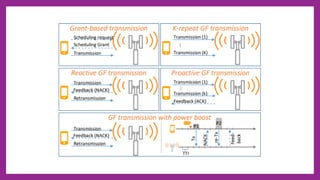
Ultra-reliable low latency communication (URLLC) aims to provide extremely reliable communication with very low latency for mission-critical applications. URLLC requires block error rates as low as 10^-9 and latencies in the order of milliseconds. Sources of delay and packet loss include transmission errors, coding delay, computing delay, propagation delay, backhaul delay, and transmission queueing violations. URLLC supports both scheduled and non-scheduled traffic using techniques like grant-free access, k-repetitions, and co-existence with enhanced mobile broadband scheduling through instant and reservation-based scheduling algorithms. Resource allocation problems can be modeled as knapsack problems to optimize metrics like throughput under constraints like available resource blocks.

![URLLC (Ultra-reliable low latency
communication)
• Ultra Reliable → BLERs as low as 10^-9 (10^-5 on [ITU-R M.2410.0])
• Ultra Low Latency →Very low latency
• Relate to mission-critical applications, where interrupted and robust exchange of
data is of outmost importance.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/urllc20190709-190709085857/85/Urllc-20190709-2-320.jpg)