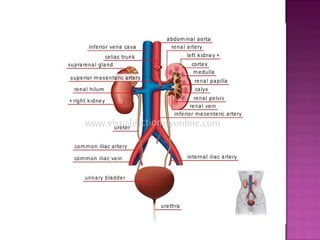
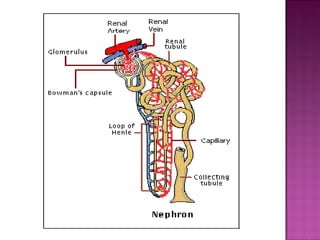
The document summarizes the anatomy and functions of the urinary and gastrointestinal systems. It describes the kidneys, nephrons, ureters, bladder, and urethra in urinary system. It then discusses factors that influence urination and various urinary conditions. For the gastrointestinal system, it outlines the structure of feces and factors affecting defecation. It concludes by describing common conditions like constipation, diarrhea, and incontinence.