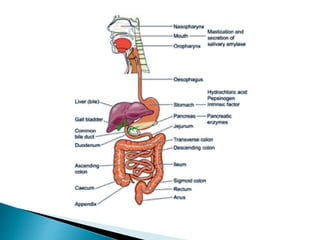
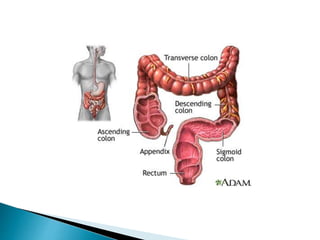
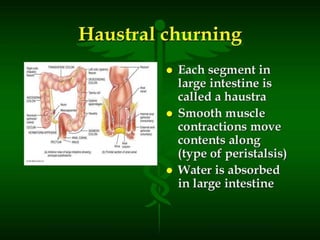
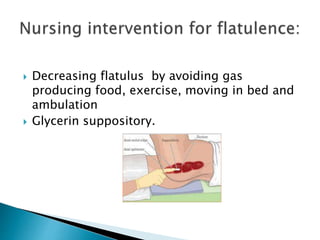
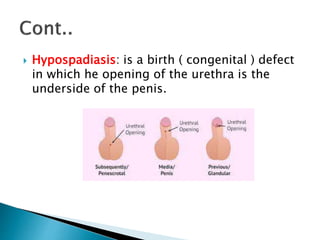
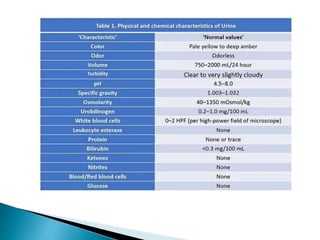
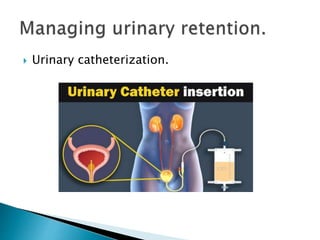
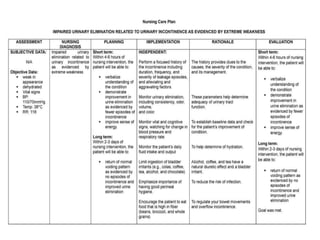
This document defines elimination patterns and discusses fecal and urinary elimination. It describes the structures involved in defecation and factors that can affect stool appearance. Common problems with elimination like diarrhea, constipation and incontinence are outlined. Nursing assessments and interventions for both urinary and bowel issues are provided, including bladder training, diet modifications, and exercise.