The document provides information about urinalysis including its purpose, regulation, volume, composition, laboratory tests, physical examination, chemical examination, and microscopic examination.
The key points are:
1. Urinalysis is performed to detect metabolic disturbances, intrinsic kidney conditions, and assess fluid and electrolyte balance.
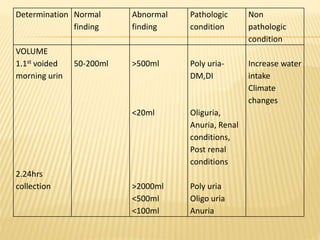
2. Urine is filtered from blood plasma and selectively reabsorbed and secreted by the kidneys to regulate volume and composition.
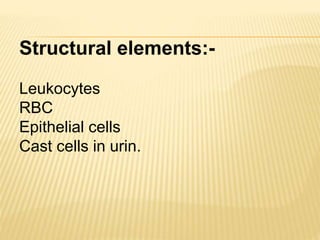
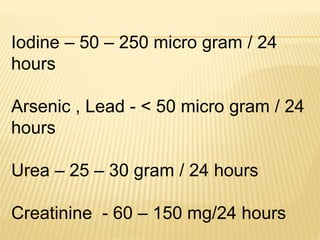
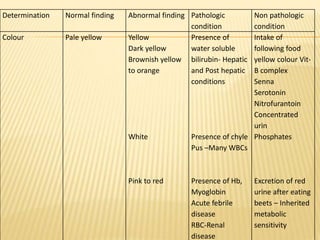
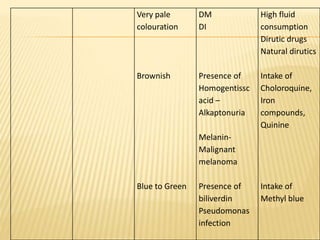
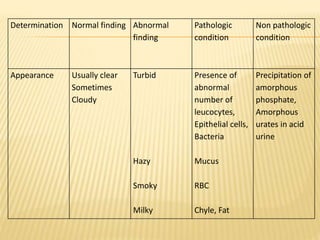
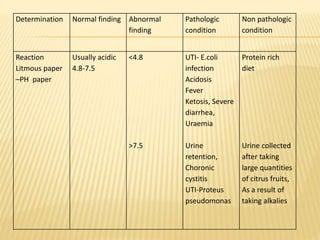
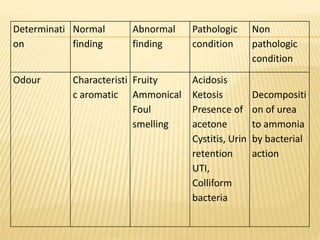
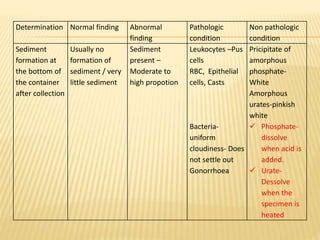
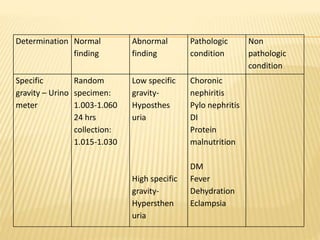
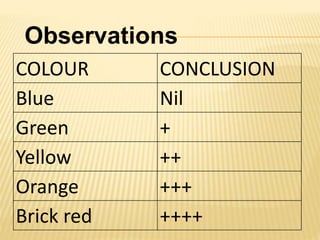
3. Laboratory tests include physical examination of urine properties, chemical tests to detect substances like glucose, protein, and ketones, and microscopic examination of the sediment.