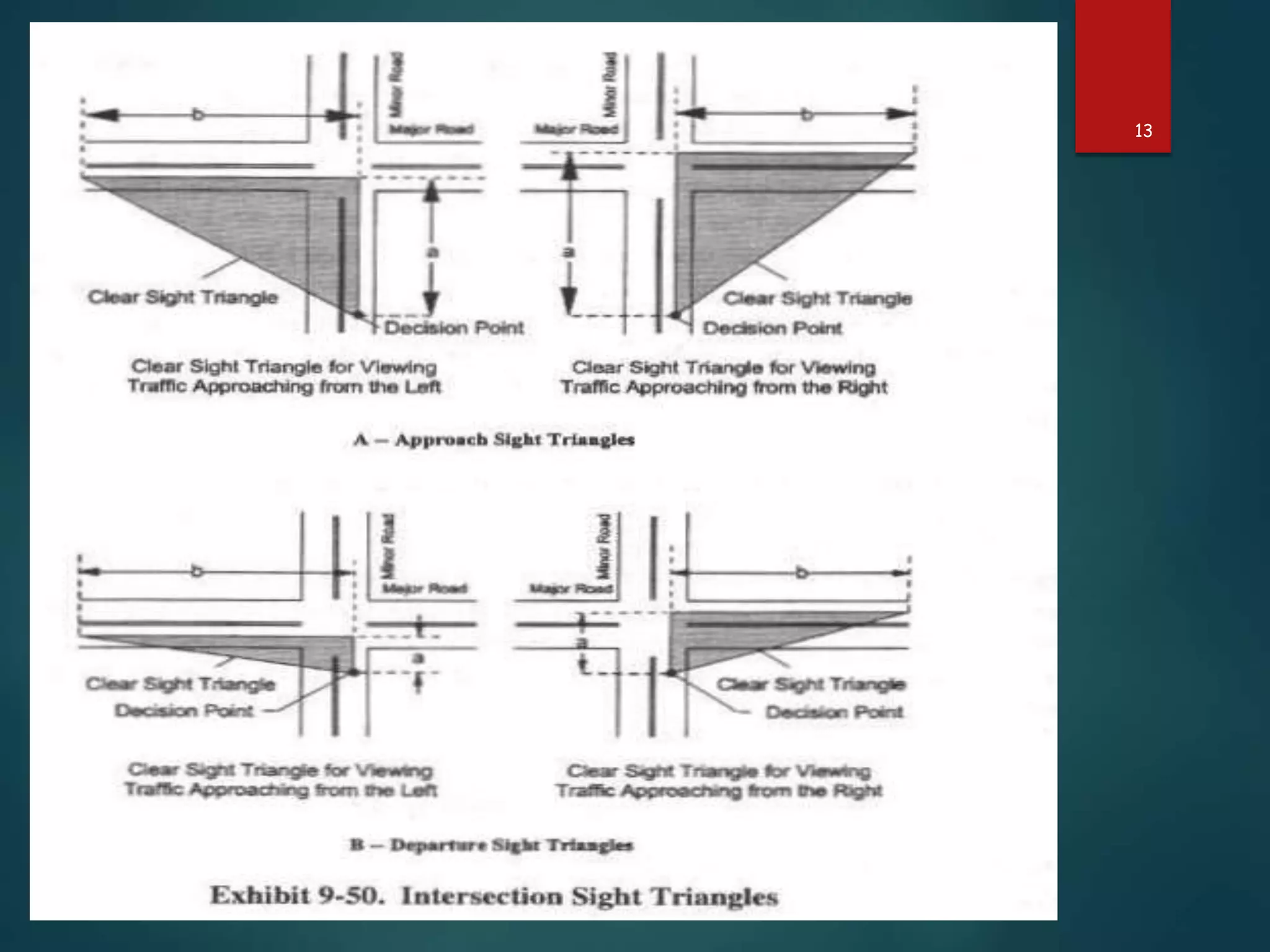
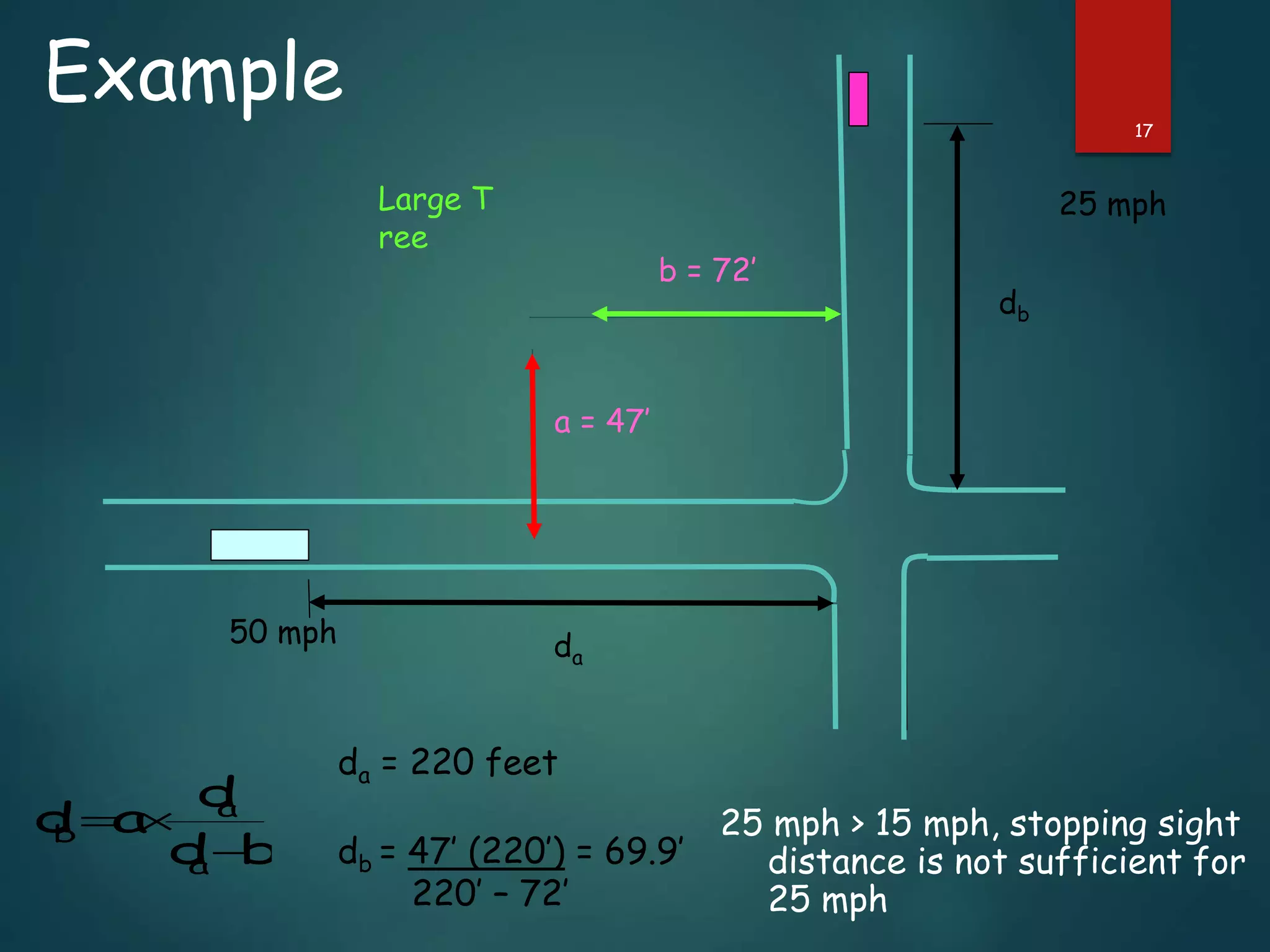
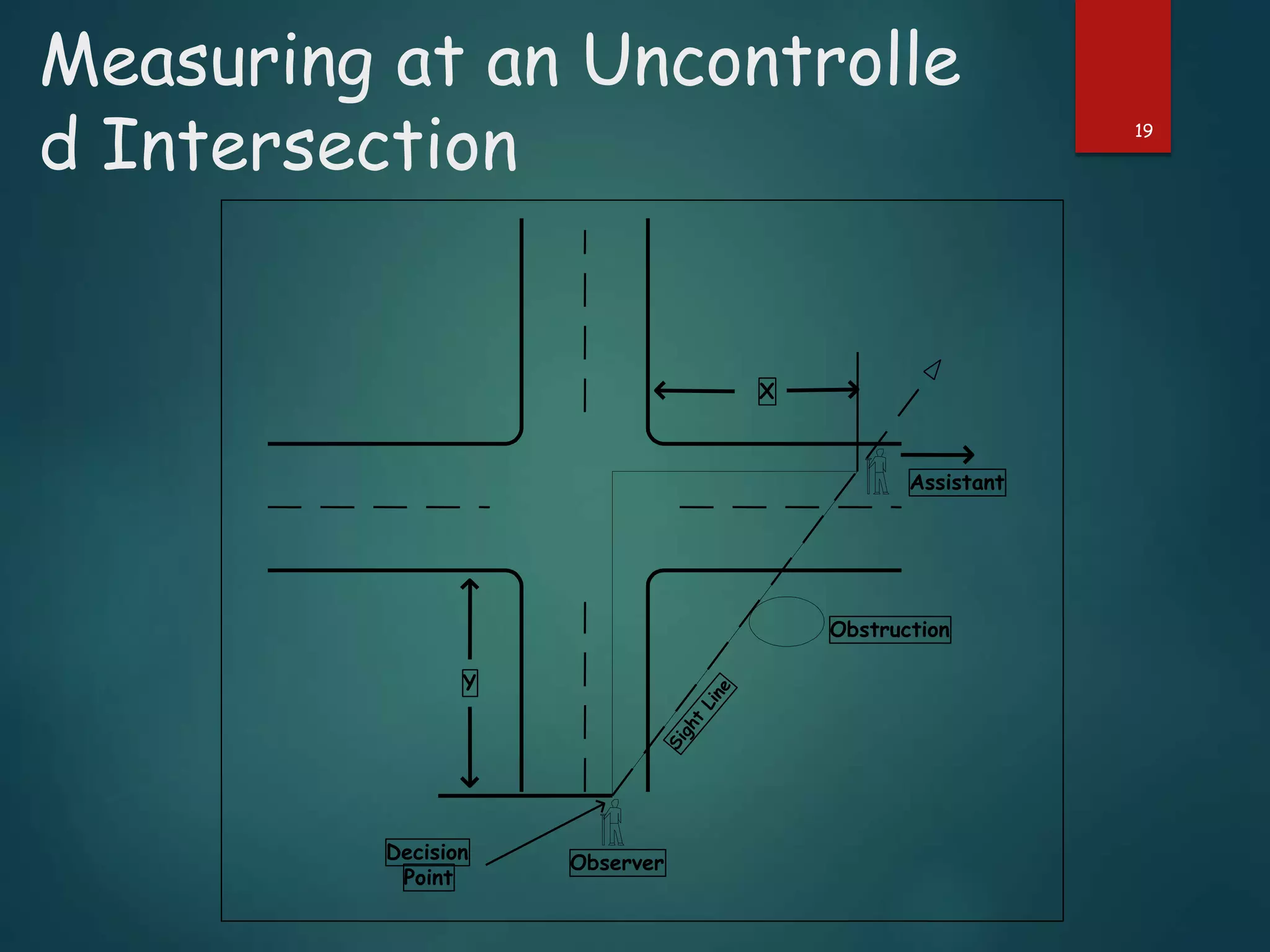
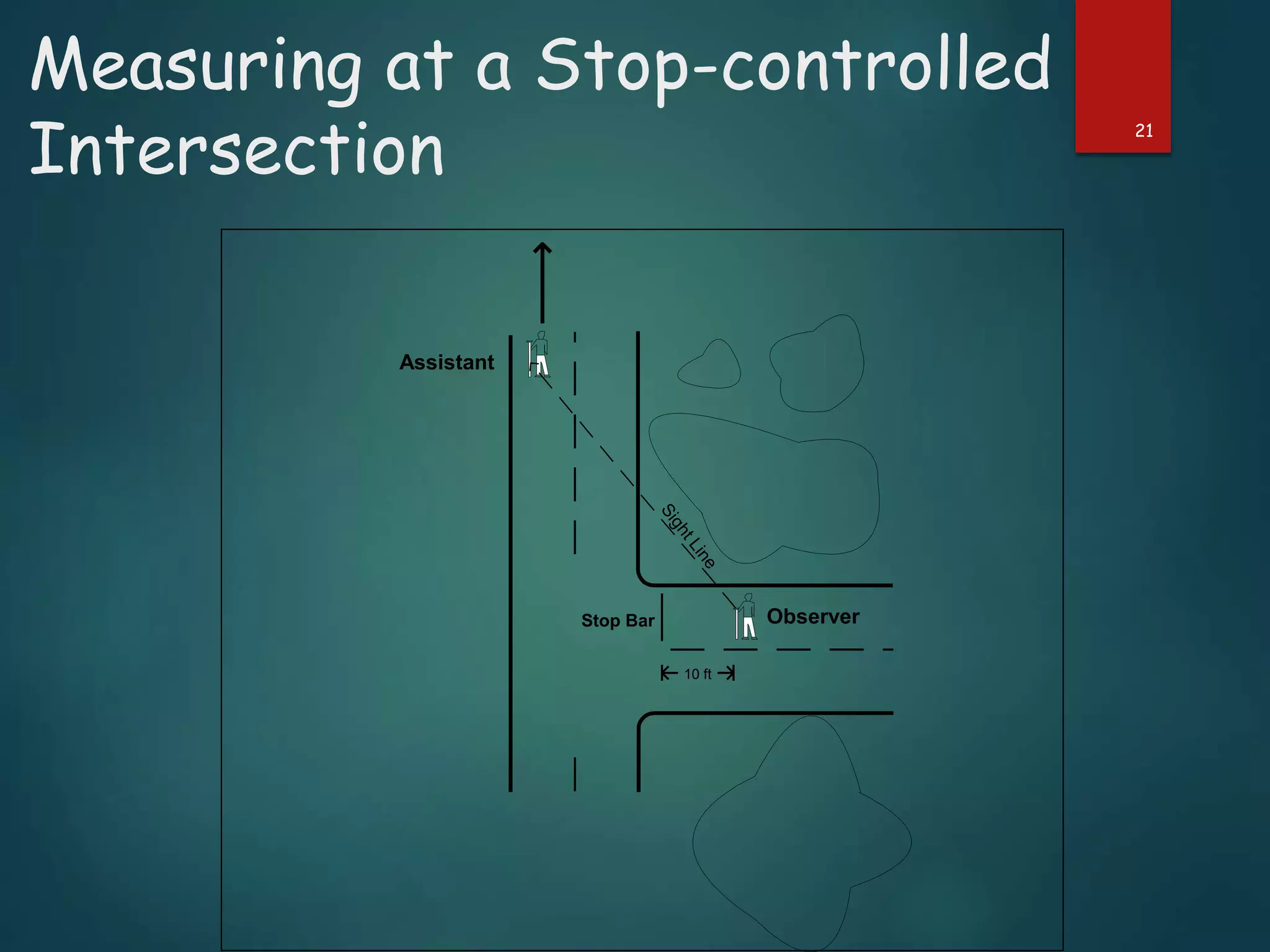
The document discusses the design of rotary intersections, highlighting their purpose in facilitating traffic movement in a clockwise direction while addressing safety concerns. It includes design objectives, specifications for width, capacity calculations, and operational requirements for effective functioning. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of adequate sight distance and unobstructed views at intersections to prevent conflicts and improve traffic flow.





![Capacity 7
Transportation road research lab (TRL) proposed the
following empirical formula to find the capacity of the
weaving section
𝑸𝒘 =
280𝑤 1 +
𝑒
𝑤
[1 −
𝑝
3
]
[1 +
𝑤
𝑙
]
where is the average entry and exit width, is the weaving
width, is the length of weaving, and is the proportion of
weaving traffic to the non-weaving traffic.
Four types of movements at a weaving section, and are the
non-weaving traffic and are the weaving traffic.
p =
𝒃+𝒄
𝒂+𝒃+𝒄+𝒅](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designofrotary-190509160707/75/Design-of-rotary-7-2048.jpg)