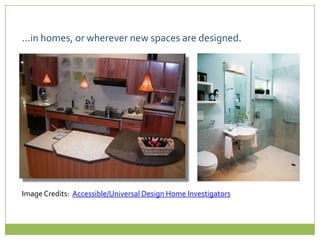
This document discusses the history and principles of Universal Design for Learning (UDL). [1] It describes how UDL originated from Ronald Mace's concept of universal design to create accessible architectural spaces. [2] UDL aims to design instruction that meets the needs of all students by providing multiple means of representation, action and expression, and engagement. [3] The three principles of UDL are guided by research on the three networks in the brain that influence how we recognize, strategize, and feel about our experiences. Technology can support implementing UDL principles in various ways.