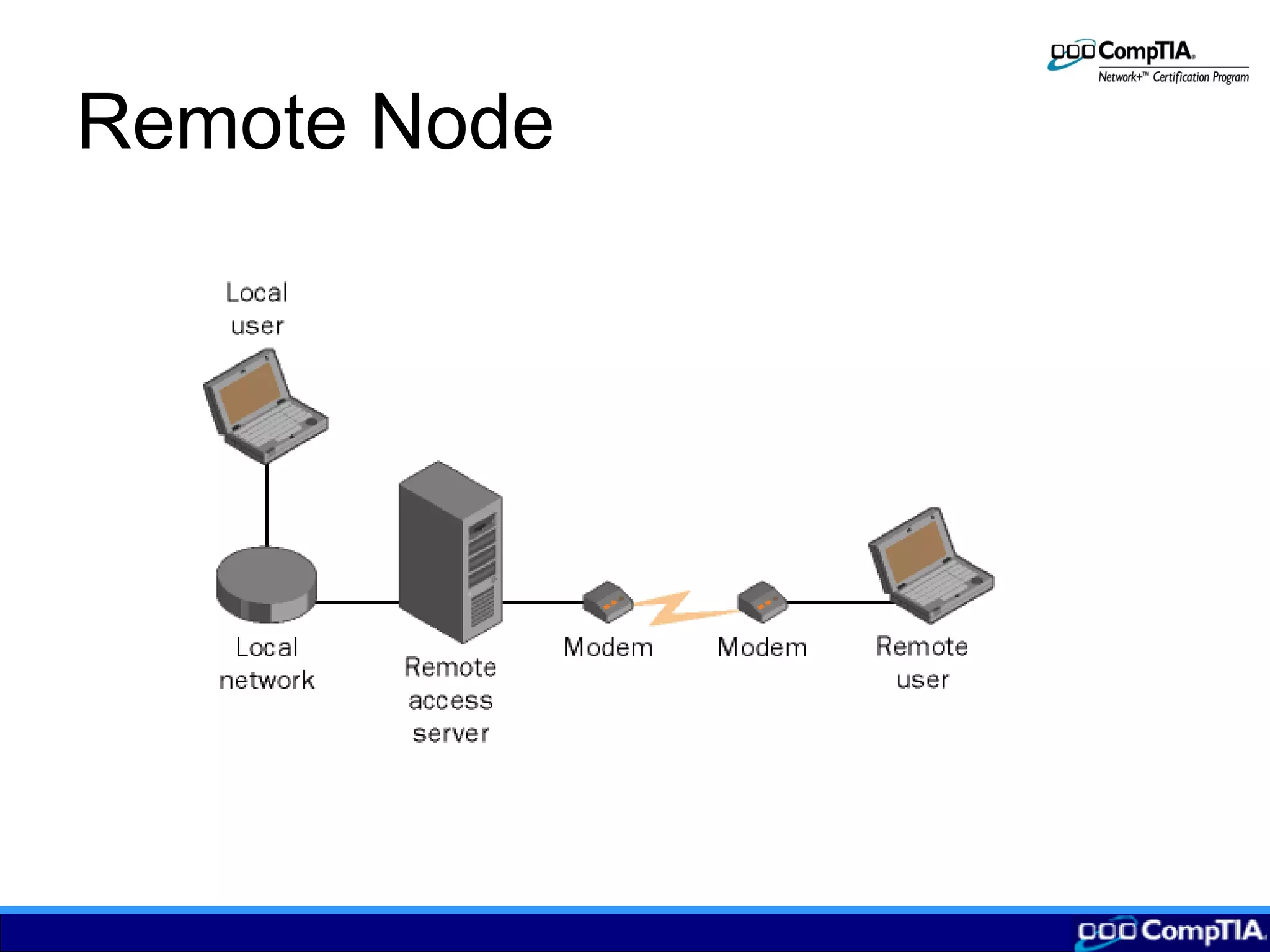
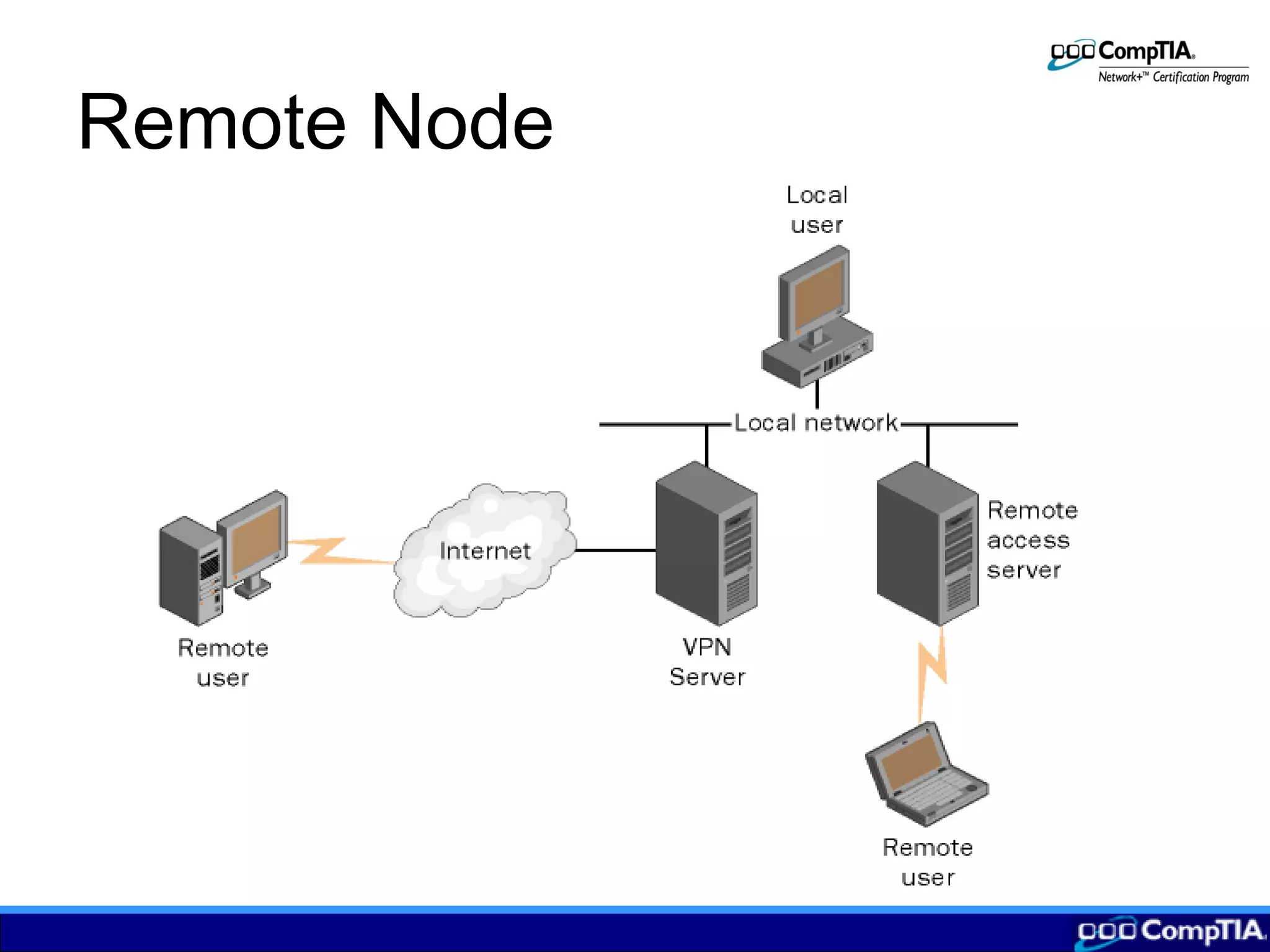
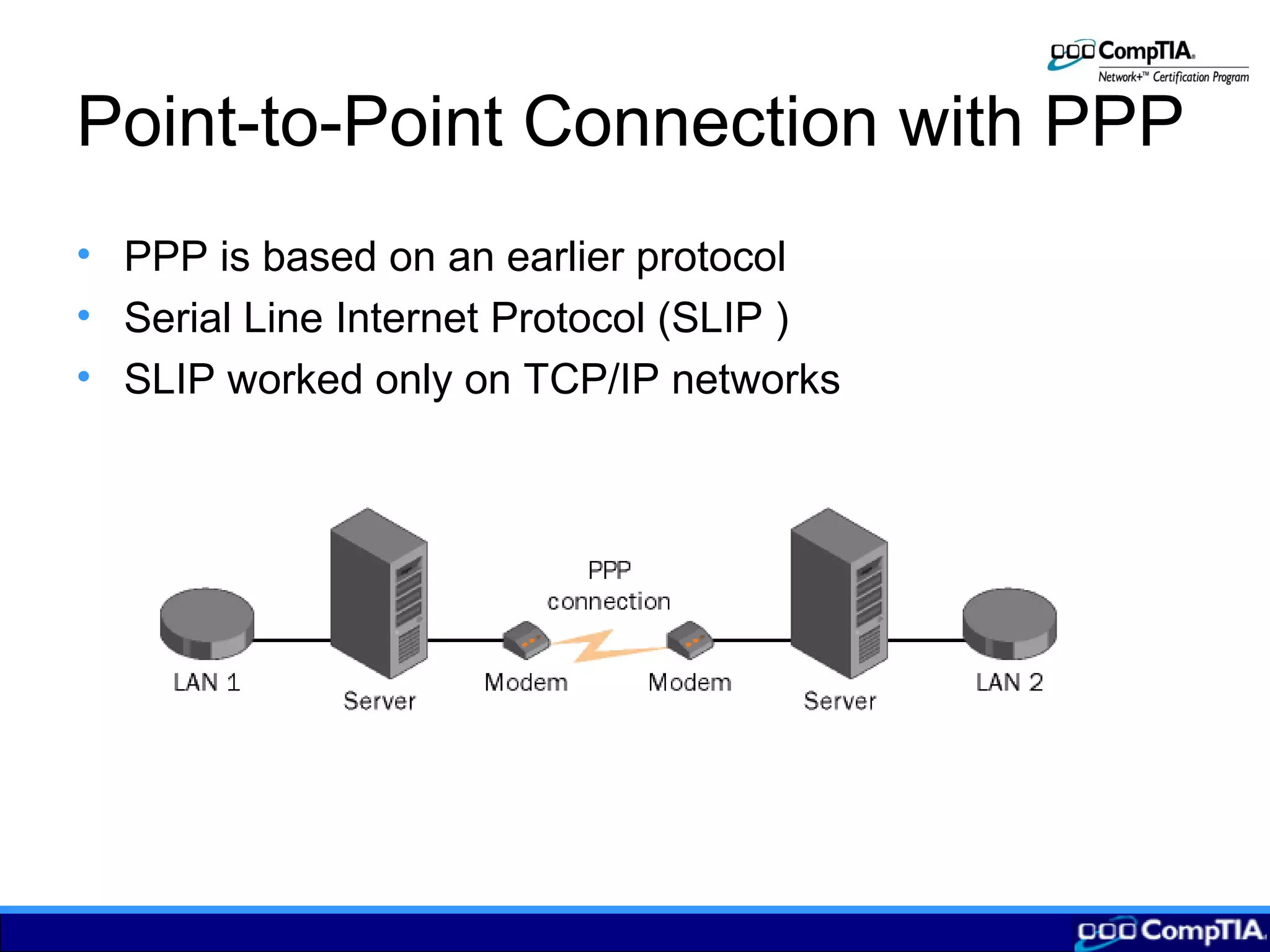
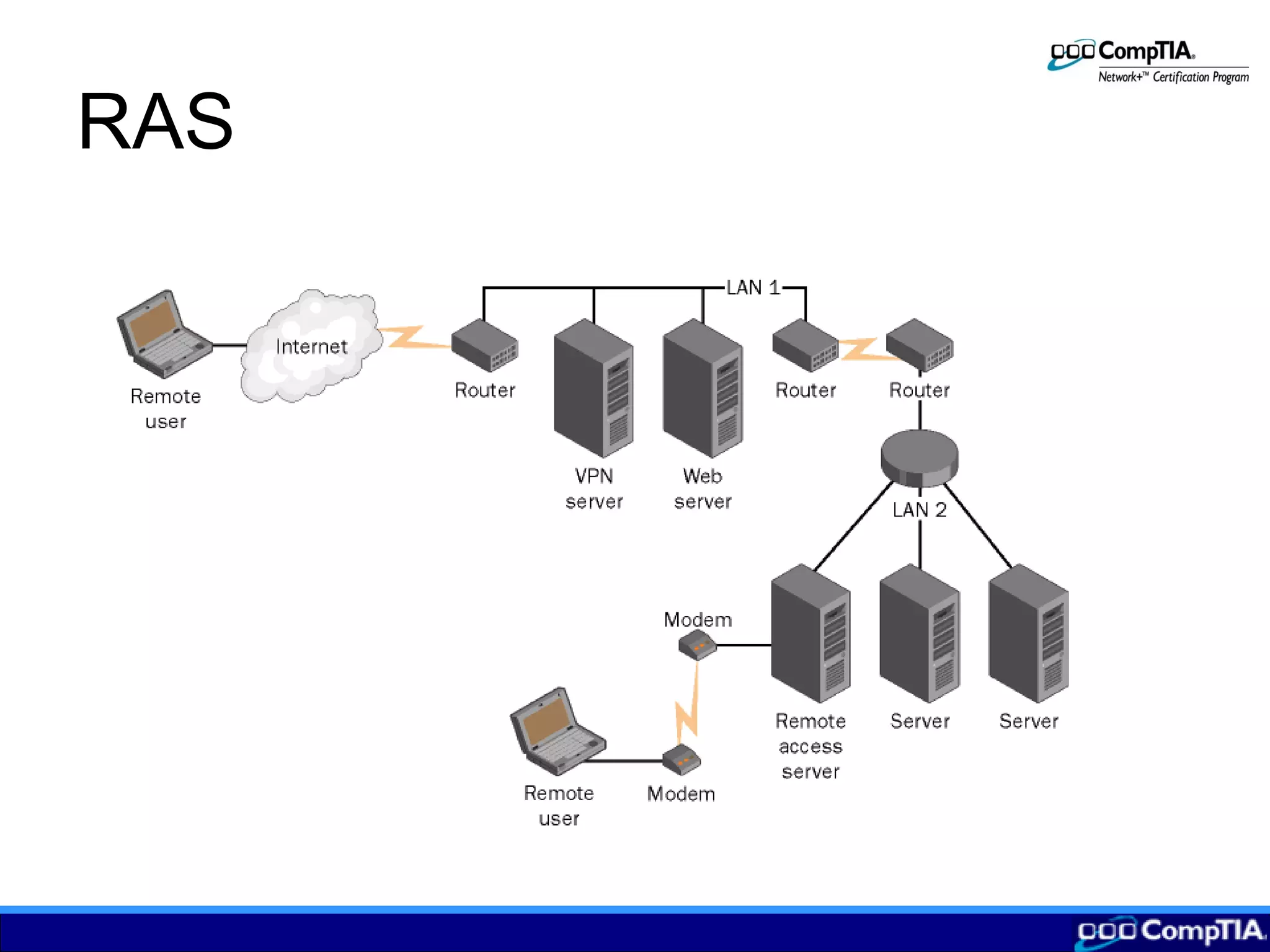
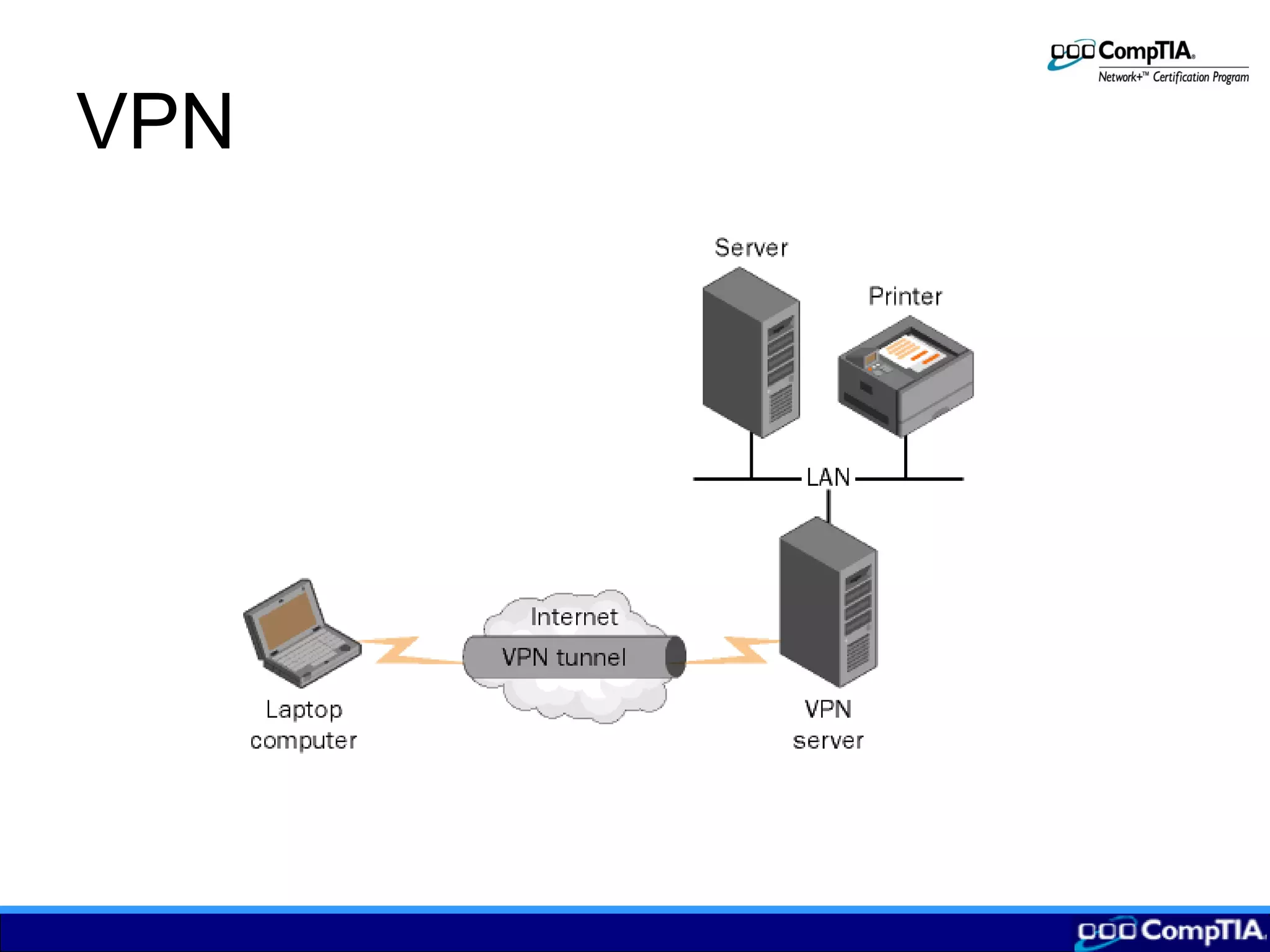
1) Remote nodes connect to networks via dial-up, DSL, cable or VPN and allow remote access but are slower than local connections.
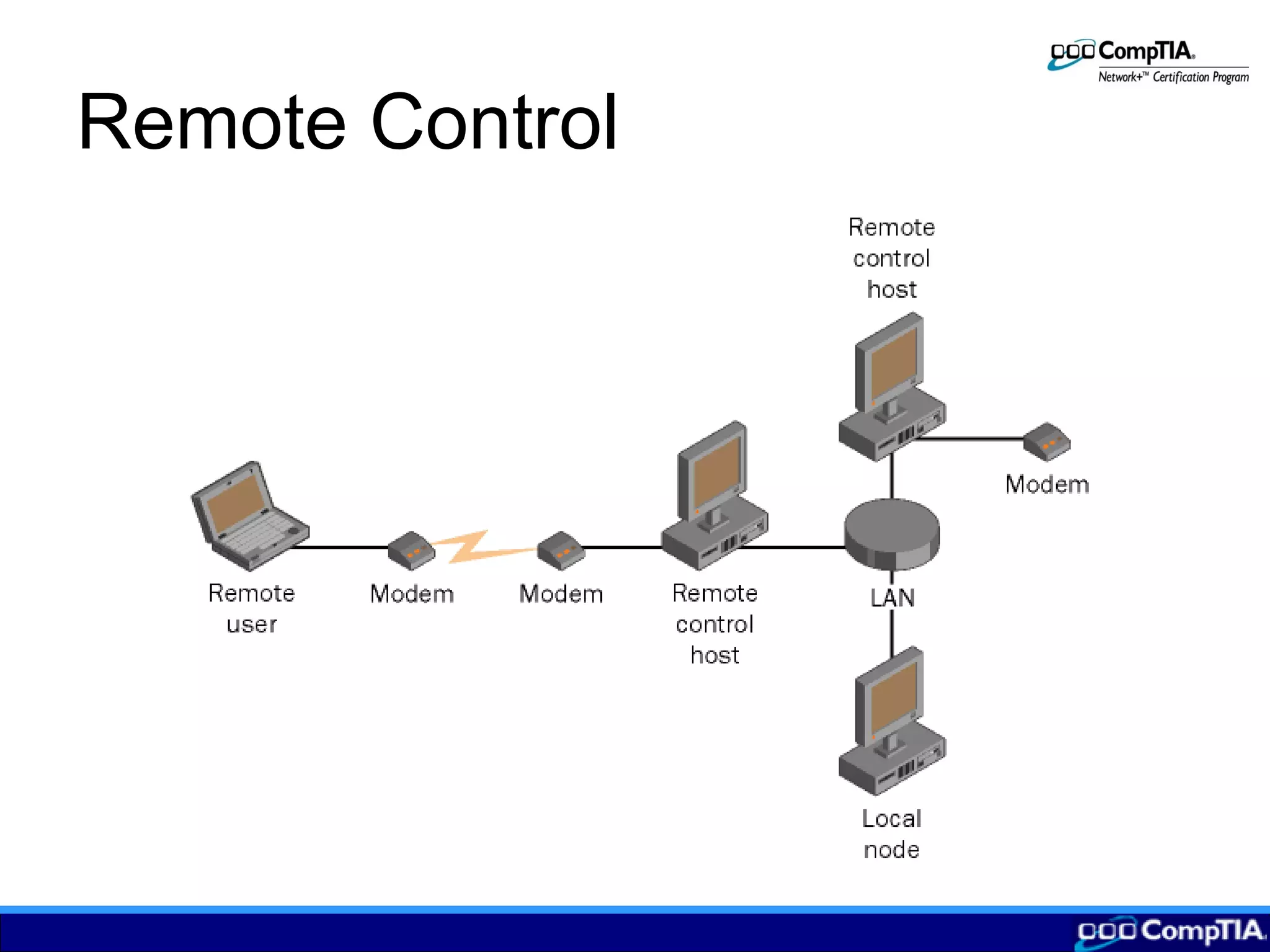
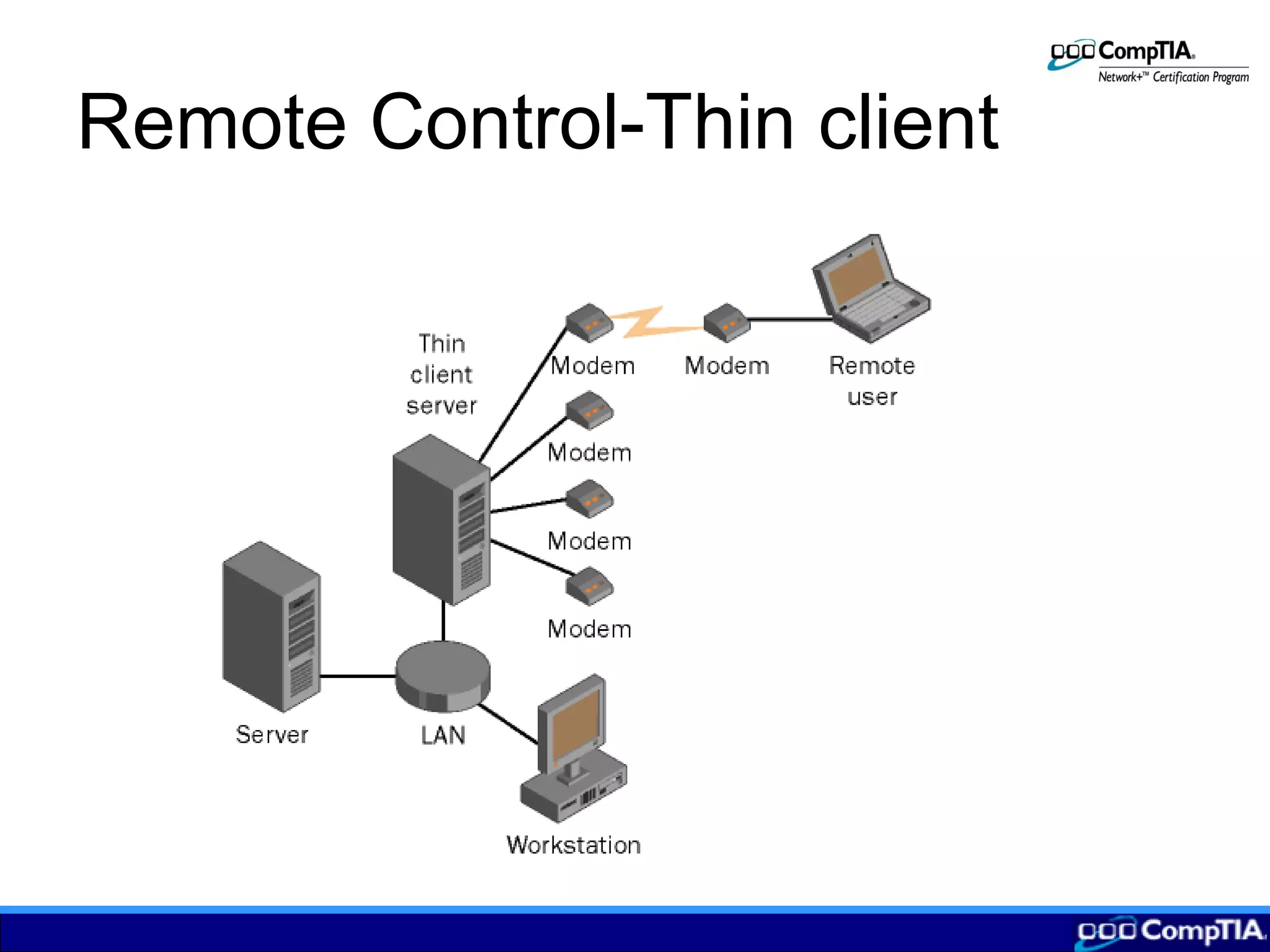
2) Remote control allows users to access applications on a local network node from a remote computer by transmitting keyboard/mouse inputs rather than processing data remotely.
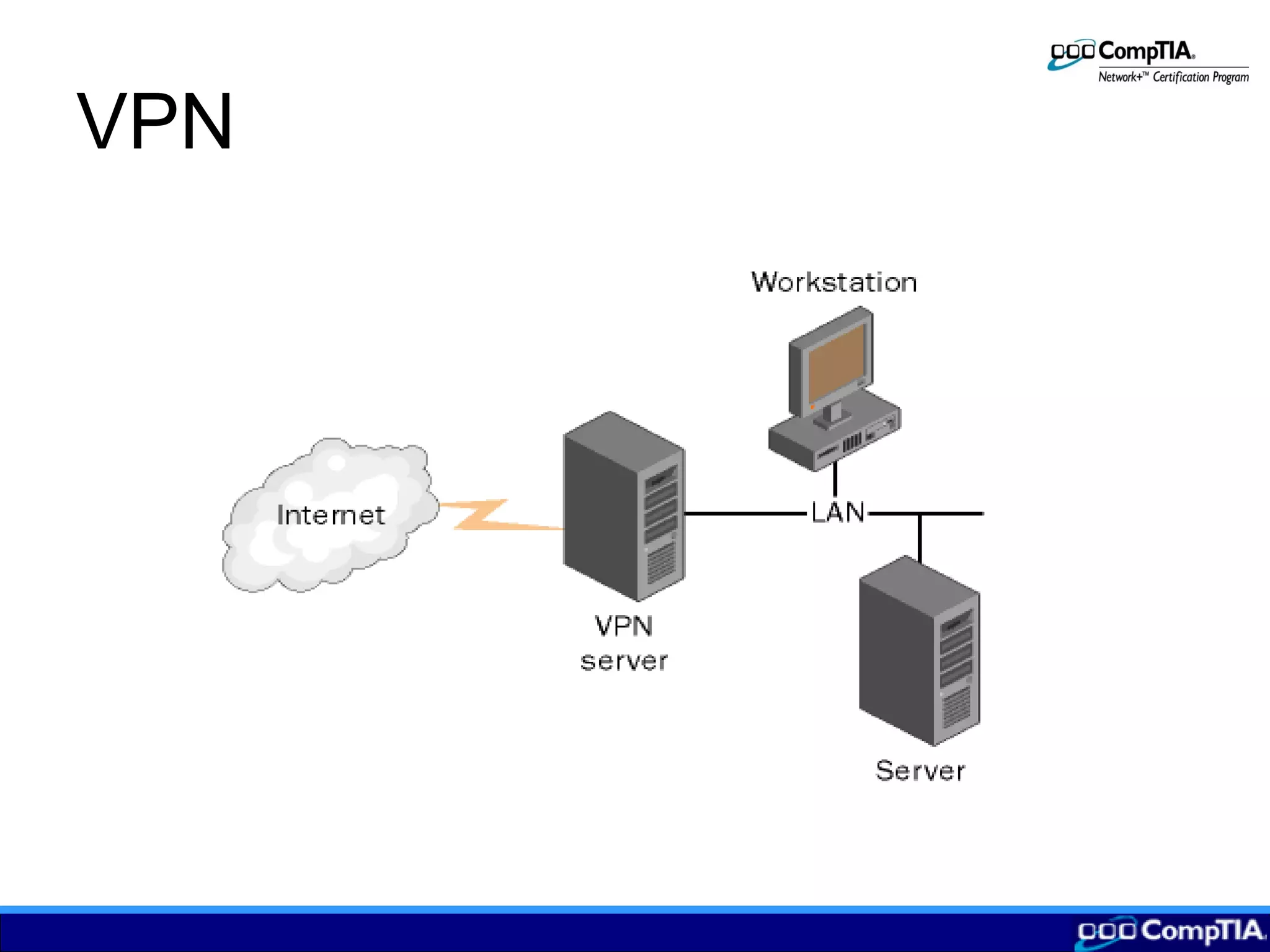
3) Configuring remote connections involves clients establishing tunnels via PPTP or L2TP to a remote access server providing VPN services to securely access the local network over the Internet.