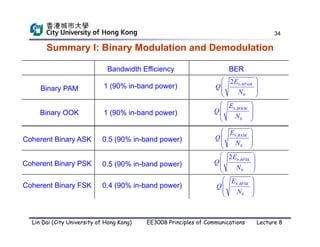
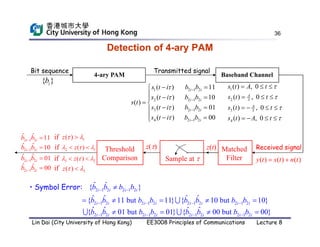
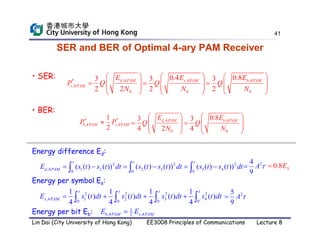
This document discusses digital demodulation techniques. It begins by introducing sources of signal corruption like thermal noise. Thermal noise is modeled as additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN). Digital demodulation involves filtering, sampling, and threshold comparison to detect transmitted bits. The optimal receiver design minimizes the bit error rate (BER) by choosing the optimal filter, sampling point, and threshold. BER is calculated based on the probability of detecting 1 given a 0 was sent and vice versa. The threshold that minimizes BER is derived by equating these two error probabilities.