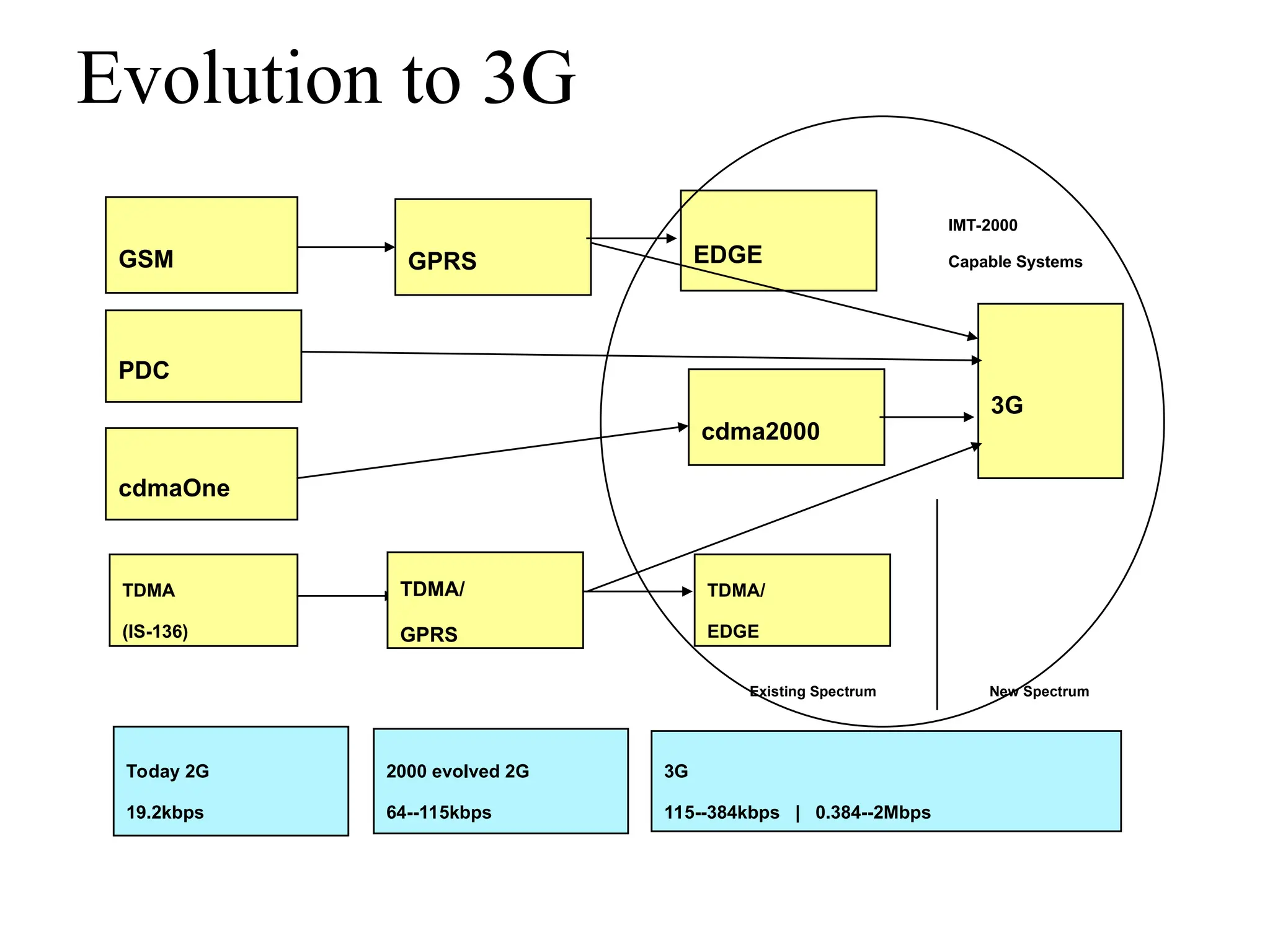
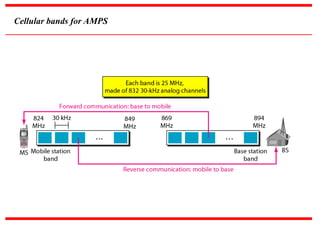
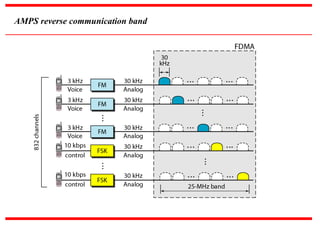
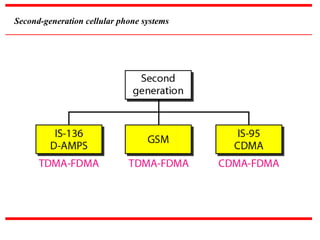
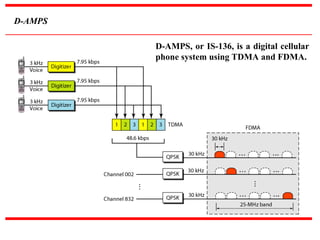
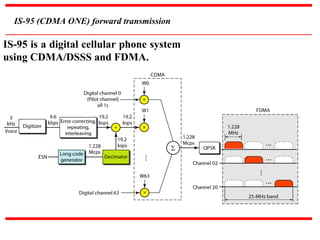
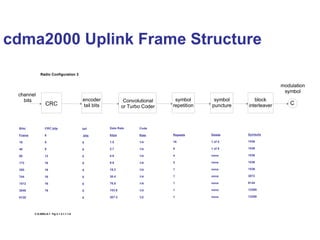
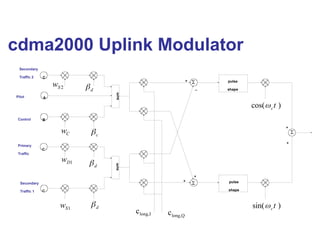
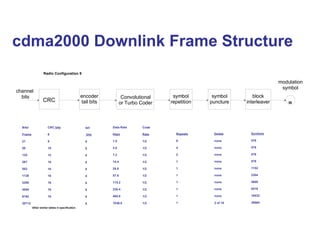
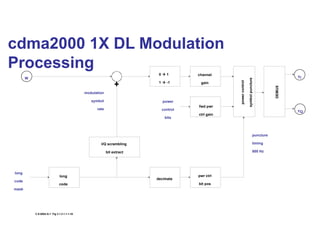
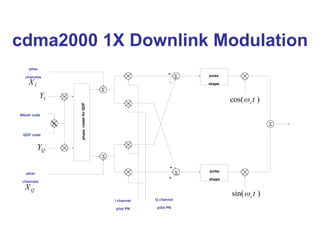
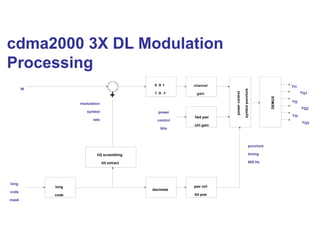
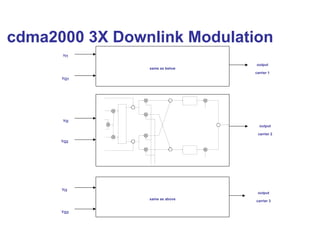
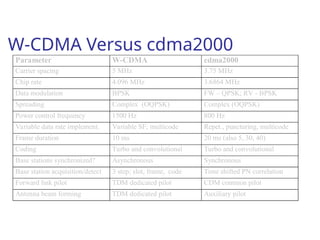
The document discusses various cellular communication systems, including advanced mobile phone systems (AMPS), digital AMPS (D-AMPS), and CDMA technologies. It explains the evolution from 2G to 3G technology, detailing the characteristics, data rates, and operational frameworks of different standards like IS-95 and CDMA2000. Additionally, it contrasts CDMA2000 with WCDMA, focusing on parameters such as power control and base station synchronization.