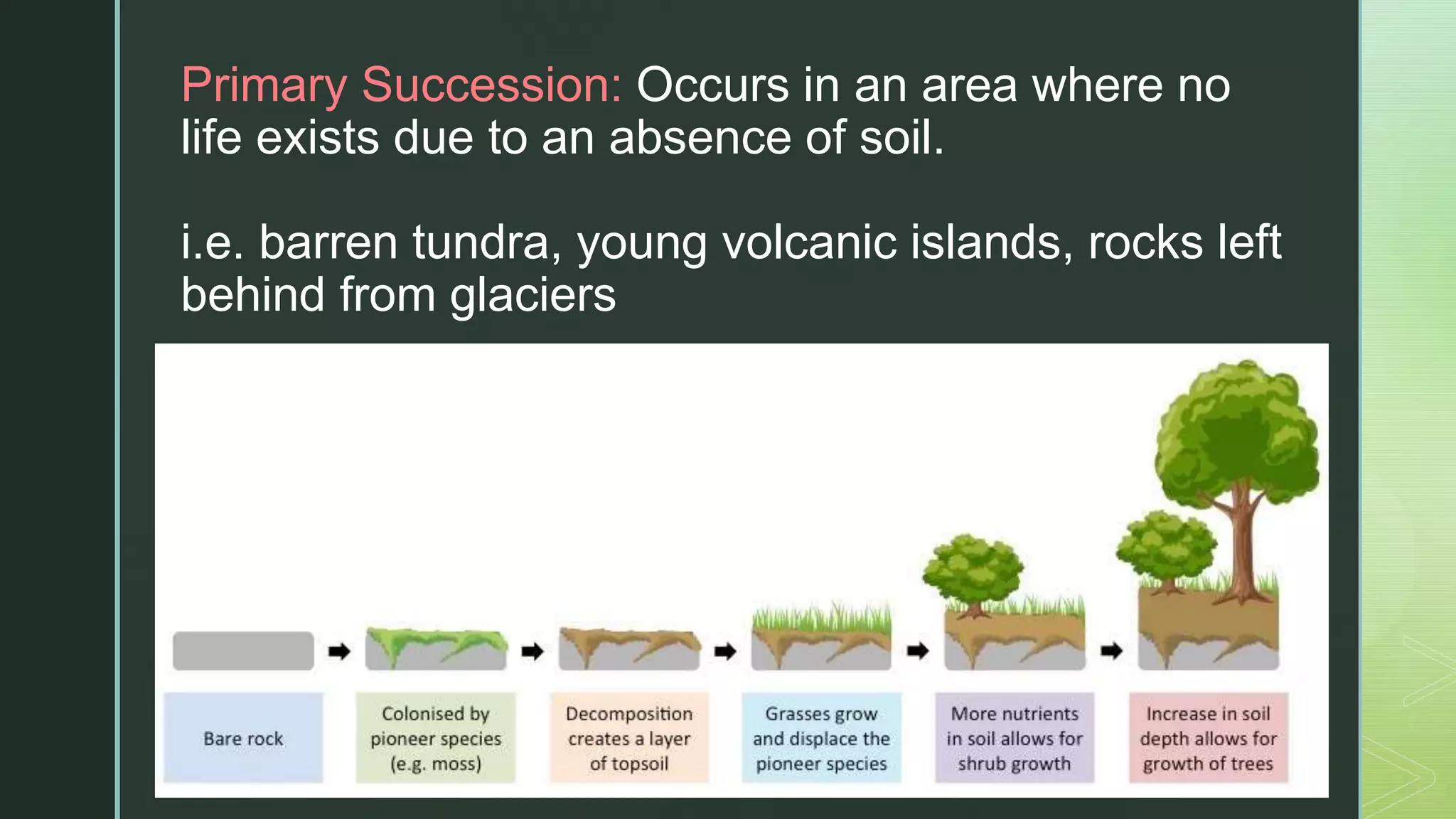
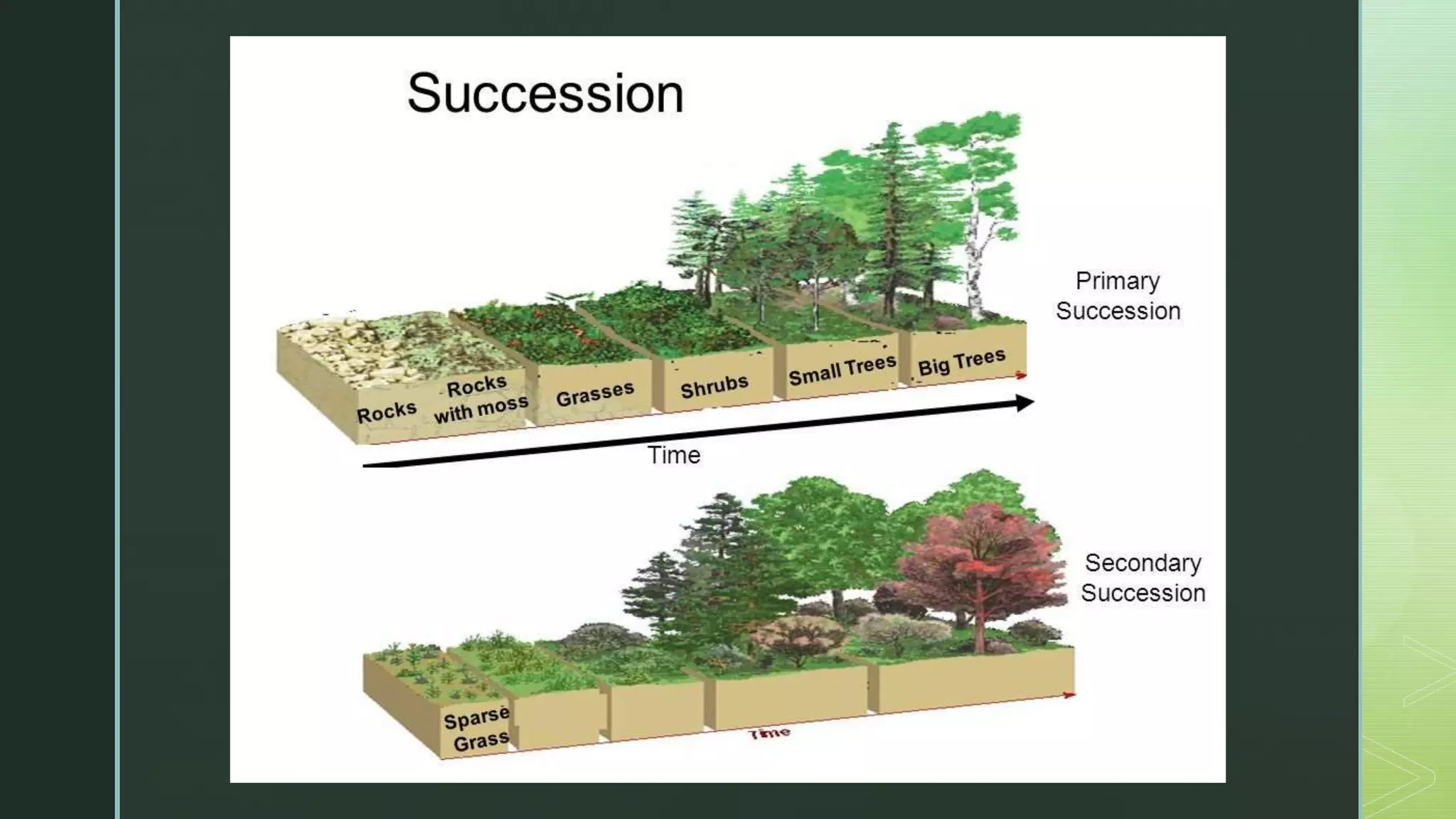
Pioneer species are the first to colonize barren areas, helping to break down rocks and pave the way for other species. Over time, the pioneer species will be replaced by new species in a process called succession. There are two types of succession: primary succession, which occurs in areas with no soil like new volcanic islands, and secondary succession, which happens after a disturbance destroys an existing community, such as after a forest fire. The final stable community achieved is called the climax community.