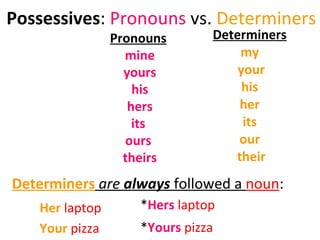
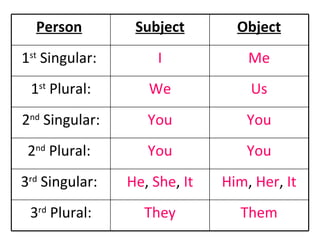
This document provides an overview of different types of pronouns in English, including subject and object pronouns, reflexive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, possessive pronouns, and interrogative pronouns. It defines what distinguishes these pronouns from other parts of speech and provides examples to illustrate their uses. Key points covered include how pronouns replace noun phrases and how their form may vary depending on whether they are used as subjects or objects.














![Reflexive Pronouns Why do we say that Reflexive Pronouns refer to the same person or thing within the same clause , and NOT within the same sentence ? Observe: [John thinks] [that he is smart]. *[John thinks] [that himself is smart]. [Mary ate] [while she was reading]. *[Mary ate] [while herself was reading]. [Mike slept] and then [ he ate lunch]. *[Mike slept] and then [ himself ate lunch].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit7-pronouns-120127114214-phpapp02/85/Unit-7-pronouns-16-320.jpg)




































![Every clause has a subject and a predicate!! [I think] [that Frank is a good man] [but he isn’t right for the job]. [While they were eating], [darkness descended over the campsite]. After she finished working she was late for our meeting, but I wasn’t upset. Although Susan doesn’t live in the U.S., her English is excellent. They acted as if nothing happened, and that was quite insensitive of them.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit7-pronouns-120127114214-phpapp02/85/Unit-7-pronouns-53-320.jpg)




















![Step-by-step procedure for identifying Question Words I. If a question word is used to actually ask a question , it is an interrogative pronoun . Example : What did you eat? II. If it is NOT used to ask a question, it is relating two clauses . If it replaces a NP, it is a Relative Pronoun - the Relative Clause is describing the NP. Example : I know the boy [ who lives here]. If it does NOT replace a NP from the main clause, it is a Subordinating Conjunction . Example : I don’t know [ when the movie starts].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit7-pronouns-120127114214-phpapp02/85/Unit-7-pronouns-74-320.jpg)