1) Crude oil is a naturally occurring mixture of hydrocarbons that can be separated into fractions of different molecular sizes and weights using fractional distillation.
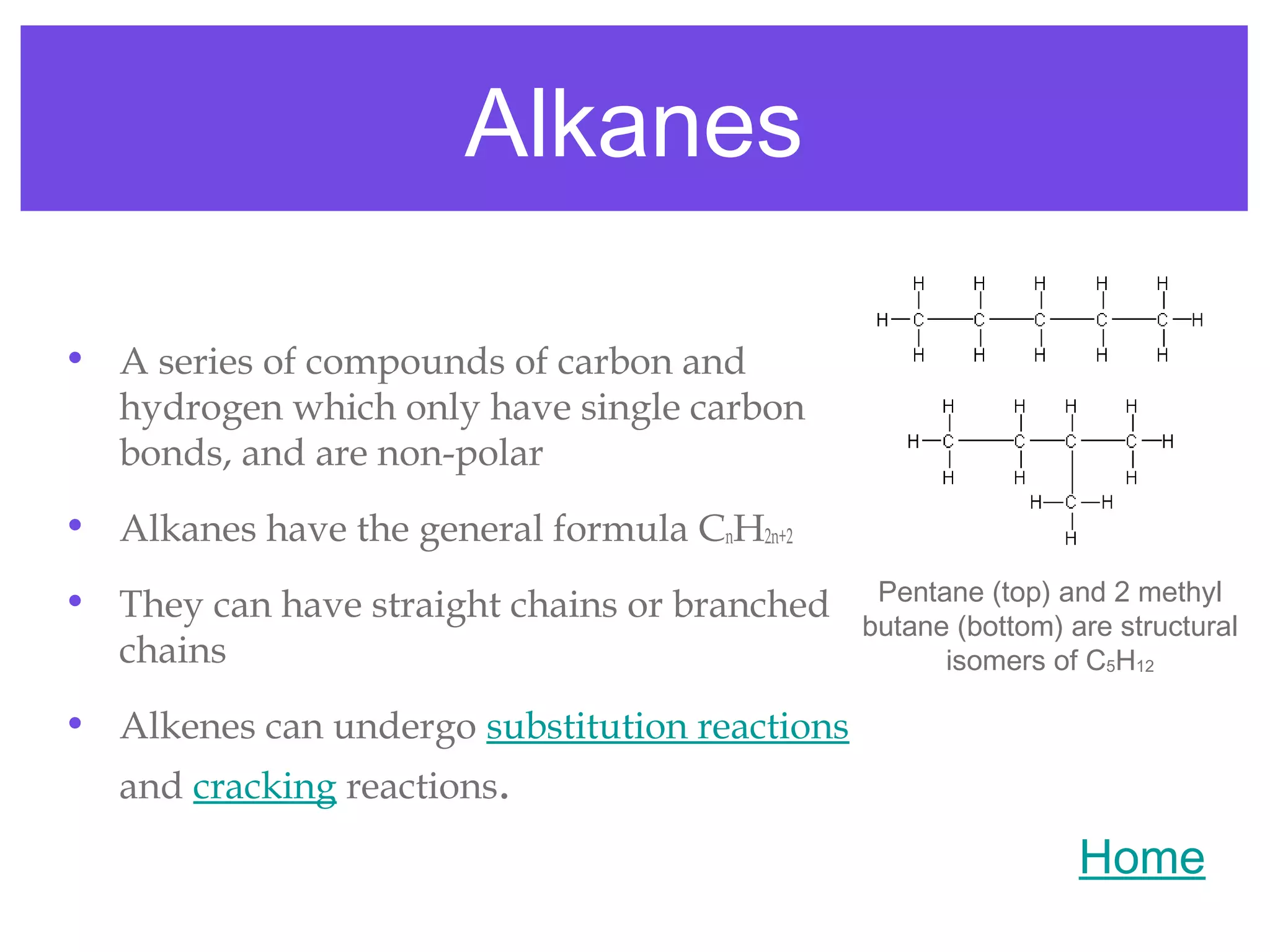
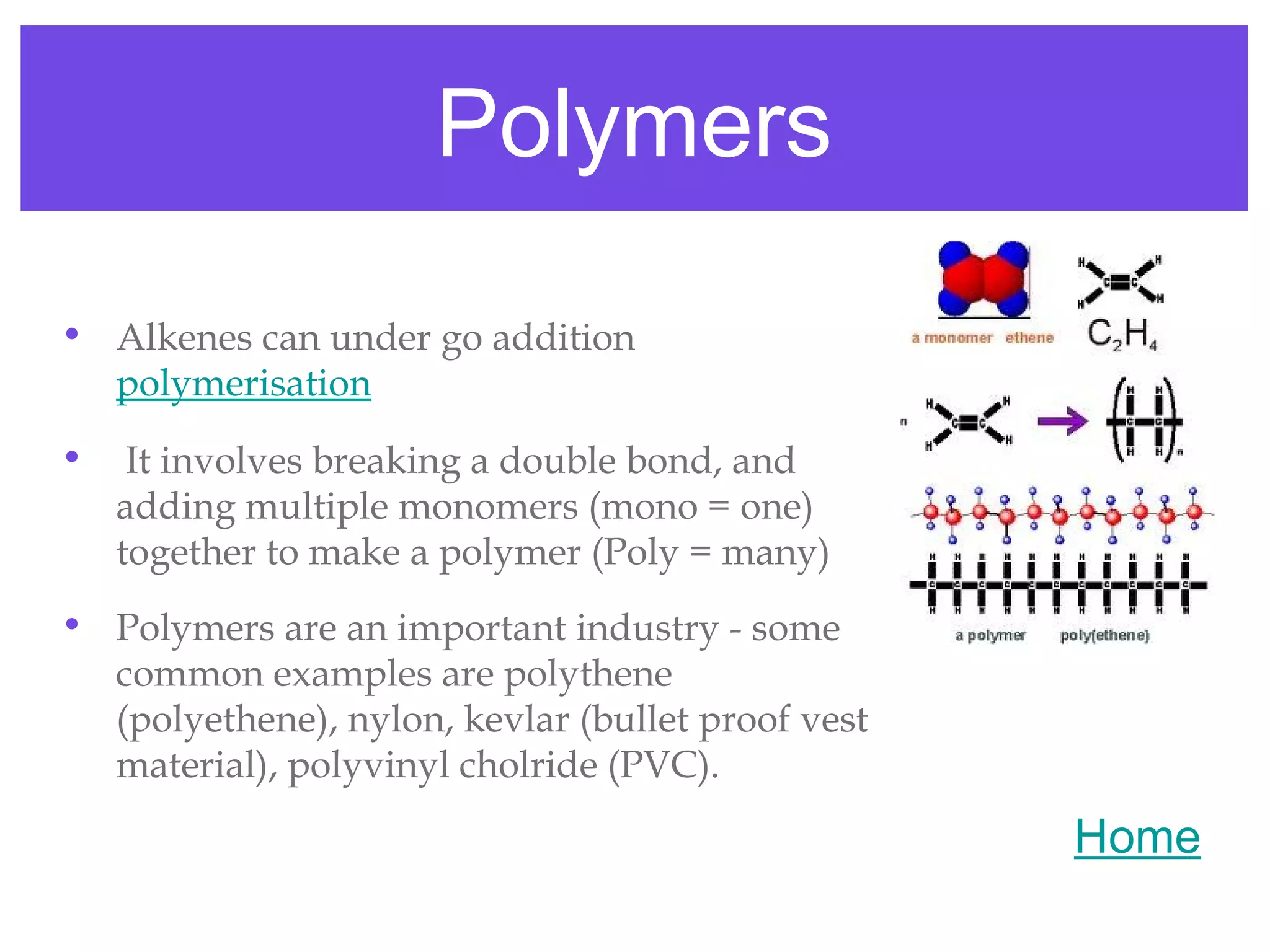
2) Alkanes, alkenes, haloalkanes, alcohols, and carboxylic acids are important organic compound classes that undergo reactions like addition, substitution, oxidation, elimination, cracking, and polymerization.
3) These compound classes are involved in important processes like the production of fuels from crude oil, and the synthesis of materials like plastics through polymerization reactions.