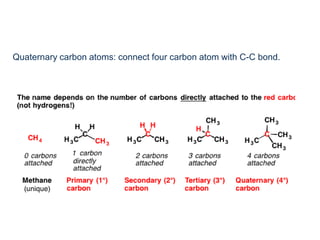
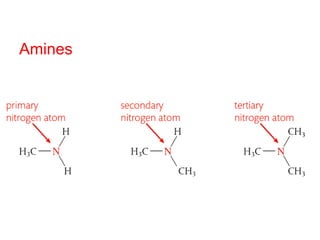
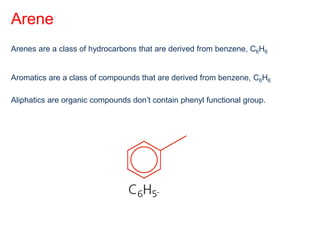
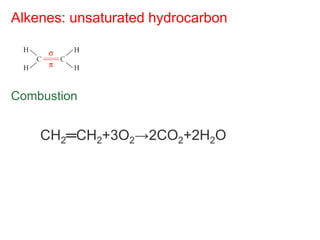
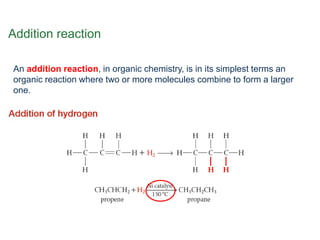
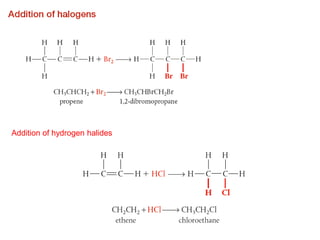
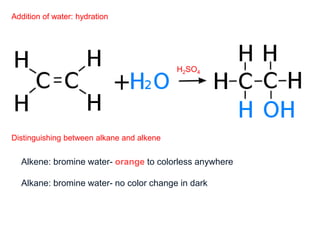
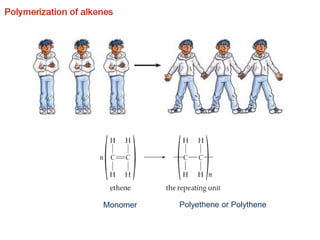
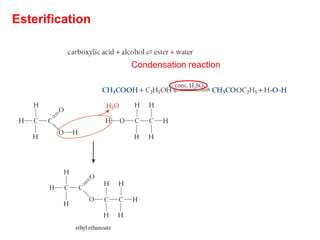
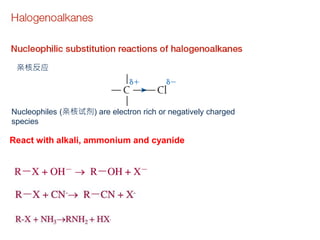
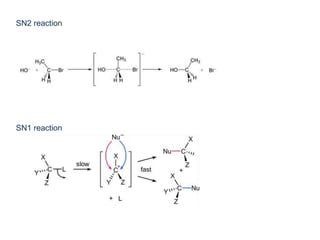
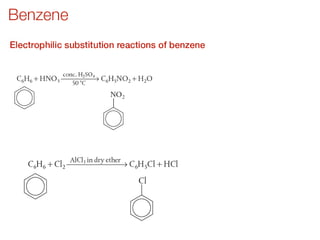
This document provides an overview of organic chemistry, including:
- Organic chemistry is the study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties/reactions.
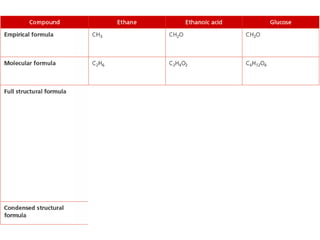
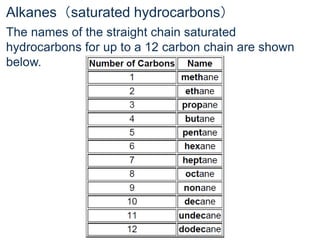
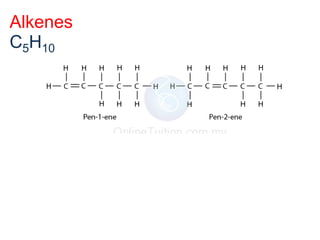
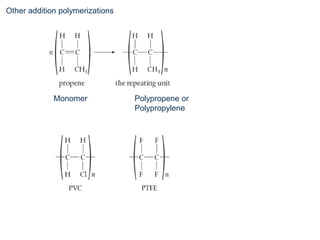
- Organic compounds contain carbon and can be classified as hydrocarbons, containing only carbon and hydrogen, or other organic functional groups.
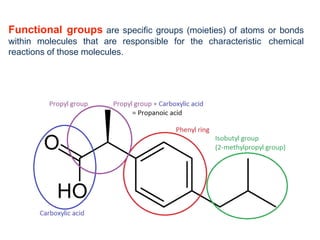
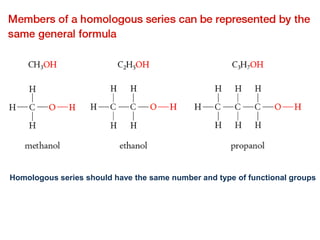
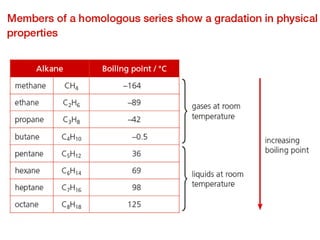
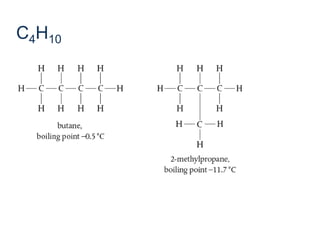
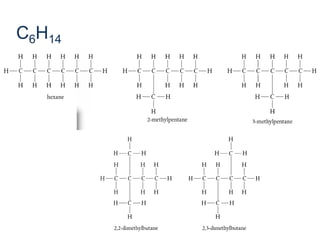
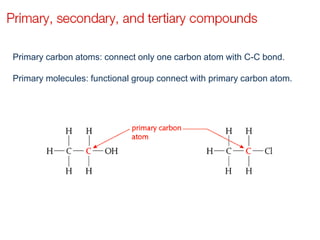
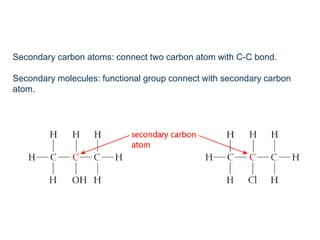
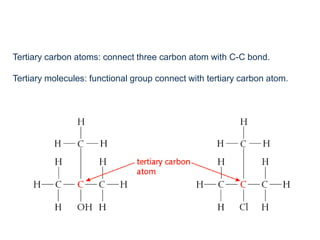
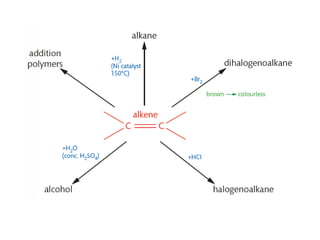
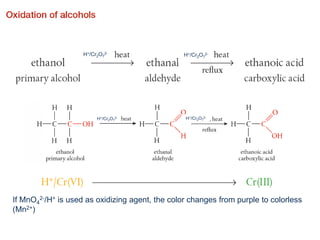
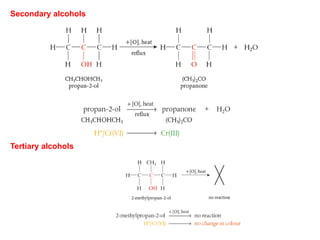
- Key concepts include functional groups, homologous series, structural formulas and structural isomers. Reaction types like addition, substitution and elimination are also covered.