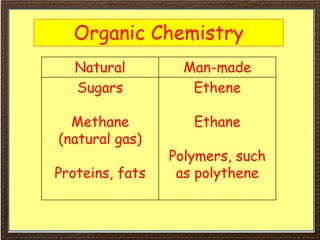
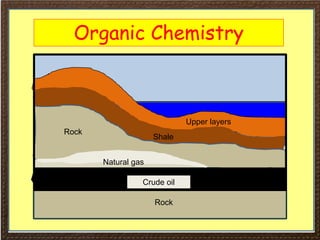
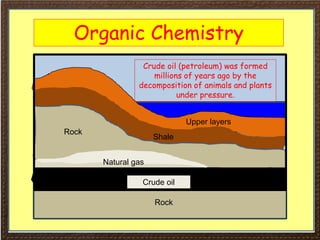
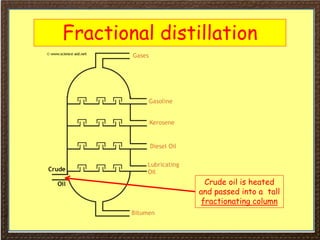
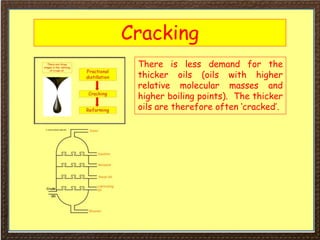
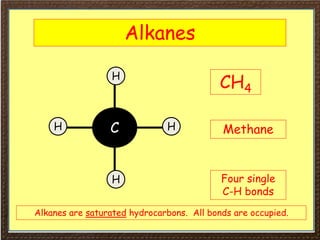
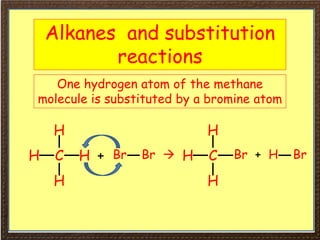
This document covers organic chemistry concepts including alkanes. It begins with an introduction to organic chemistry, noting that it involves carbon-containing compounds that often also contain hydrogen, oxygen, or other elements. Most organic compounds occur naturally, while many others are made artificially. Section 3 specifically discusses alkanes, the simplest hydrocarbons. It defines alkanes as saturated hydrocarbons that form a homologous series with the general formula CnH2n+2. Examples of alkanes and their properties like physical state are provided. Combustion reactions of alkanes and substitution reactions are also summarized.