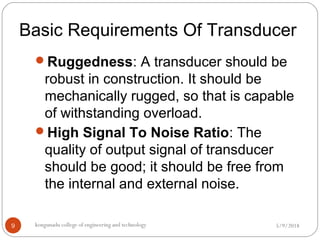
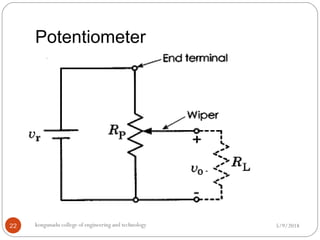
Transducers are devices that convert one form of energy to another. They are classified as either active or passive. Active transducers do not require an external power supply to produce an output signal, while passive transducers need an external power supply to amplify the input and generate an output signal. Variable resistance transducers are commonly used transducers that convert a physical quantity into a change in electrical resistance. Examples of variable resistance transducers discussed in the document include potentiometers, thermistors, strain gauges, and RTDs (resistance temperature detectors).
























![Thermistor
5/9/2018kongunadu college of engineering and technology28
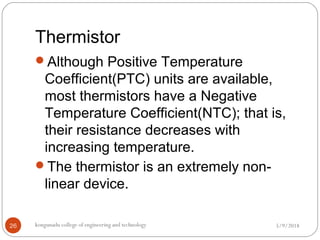
The resistance temperature relation is
generally of the form:
R = R0 exp[β(1/T – 1/T0)]
R = Resistance at temp. T, Ω
R0= Resistance at temp. T0, Ω
β = Constant, Characterstics of
material
T, T0 Absolute tempratures, K](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5-190120155217/85/Unit-5-28-320.jpg)