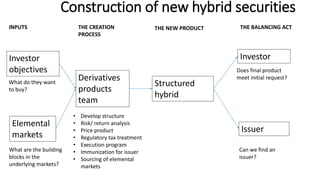
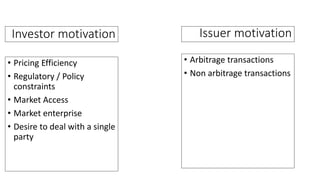
Hybrid securities combine elements from multiple markets into a single security. They are constructed from "building blocks" of elemental markets like interest rates, foreign exchange, commodities, and equities. The creation of a hybrid security involves analyzing investor objectives, available elemental markets, derivative products, and regulatory considerations to develop a new product that balances these factors. Hybrid securities provide investors and issuers ways to access new opportunities, deal with constraints, and transfer risks between markets.