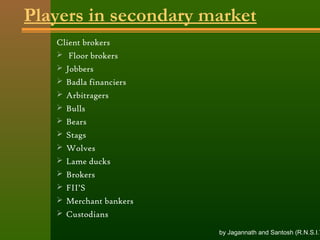
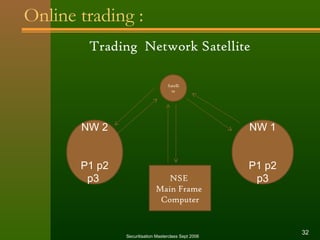
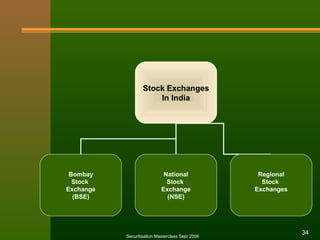
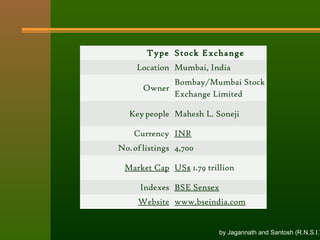
The document discusses stock exchanges and their functions. It defines a stock exchange as a centralized market for buying and selling stocks where prices are determined by supply and demand. A stock exchange assists, regulates, and controls the business of buying and selling securities. It provides a place for securities trading, listing of companies, distribution of new securities, mobilization of savings, and capital formation. The document discusses various players in the stock market like brokers, jobbers, and speculators. It also outlines the process of trading, including order placement, execution, contract notes, and settlement.