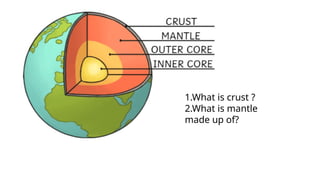
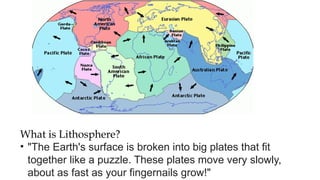
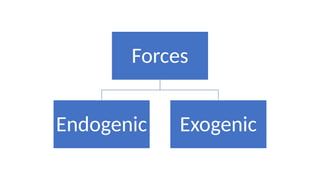
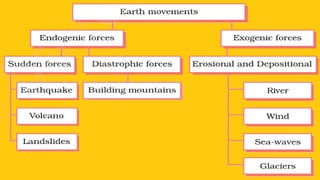
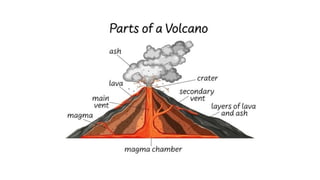
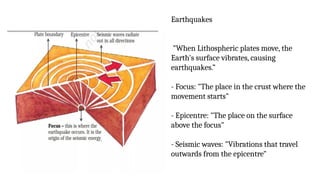
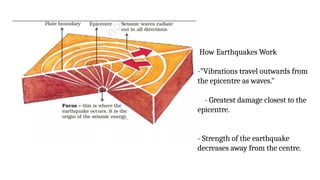
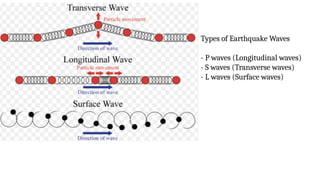
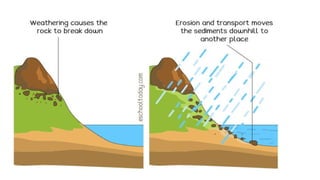
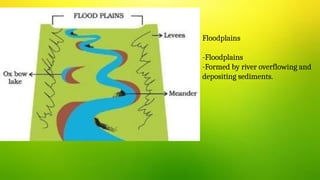
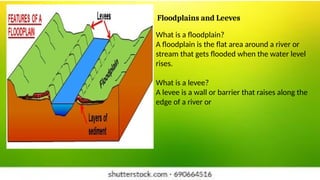
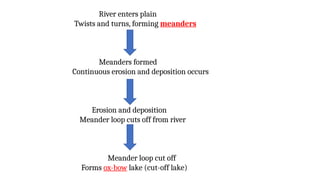
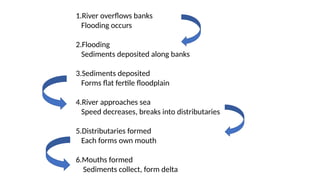
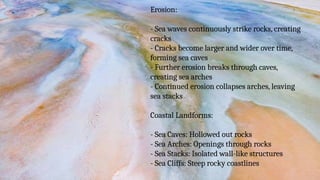
The document discusses the dynamic nature of the Earth's surface, detailing the internal structure, plate tectonics, and geological phenomena such as earthquakes and volcanoes. It explains the role of magma in driving plate movements and distinguishes between endogenic and exogenic forces that shape the Earth's landscape through processes like erosion and sediment deposition. Additionally, the document covers various landforms created by weathering, rivers, coastlines, and glacial activity.