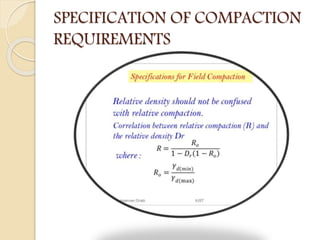
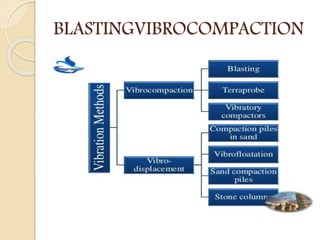
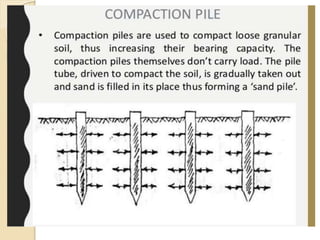
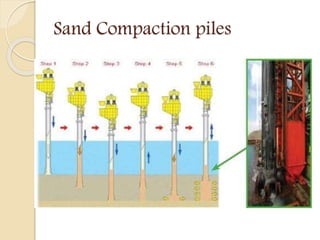
This document discusses principles of soil densification through compaction. It defines compaction as artificially decreasing soil volume by expelling air from pores to increase density. The key objectives of compaction are to increase shear strength, decrease settlement, control volume change, decrease permeability, and increase bearing capacity and slope stability. Compaction control tests indirectly assess the objectives by measuring water content, density, and penetration resistance. Specifications ensure expected performance by requiring field tests during compaction and laboratory tests on borrow materials. Other densification methods discussed include blasting, vibrocompaction, dynamic tamping, and compaction piles.