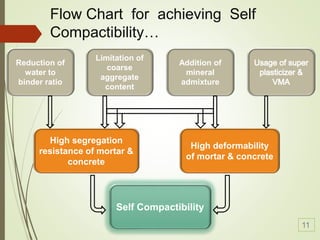
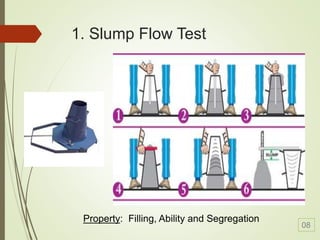
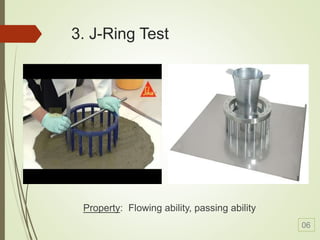
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) is a revolutionary development in concrete construction, characterized by its ability to flow and compact without vibration, leading to improved quality and performance. Its benefits include faster construction, reduced manpower, better surface finishes, and greater design flexibility, though it typically costs 10-15% more than traditional concrete. The document outlines its history, material selection, requirements, test methods for compactibility, and applications, emphasizing the need for further research and standardization.