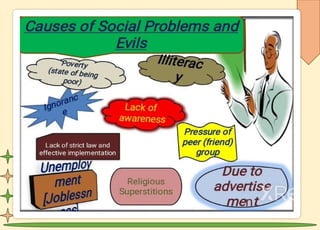
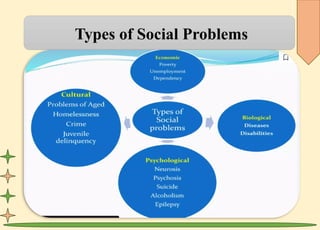
The document explores social problems affecting societies, defining them as issues impacting many individuals and highlighting their characteristics, causes, and types. It discusses the roles of government and non-governmental organizations in addressing these problems through policy, resources, and advocacy. The conclusion emphasizes the need for community action and innovative solutions to create a more equitable society.