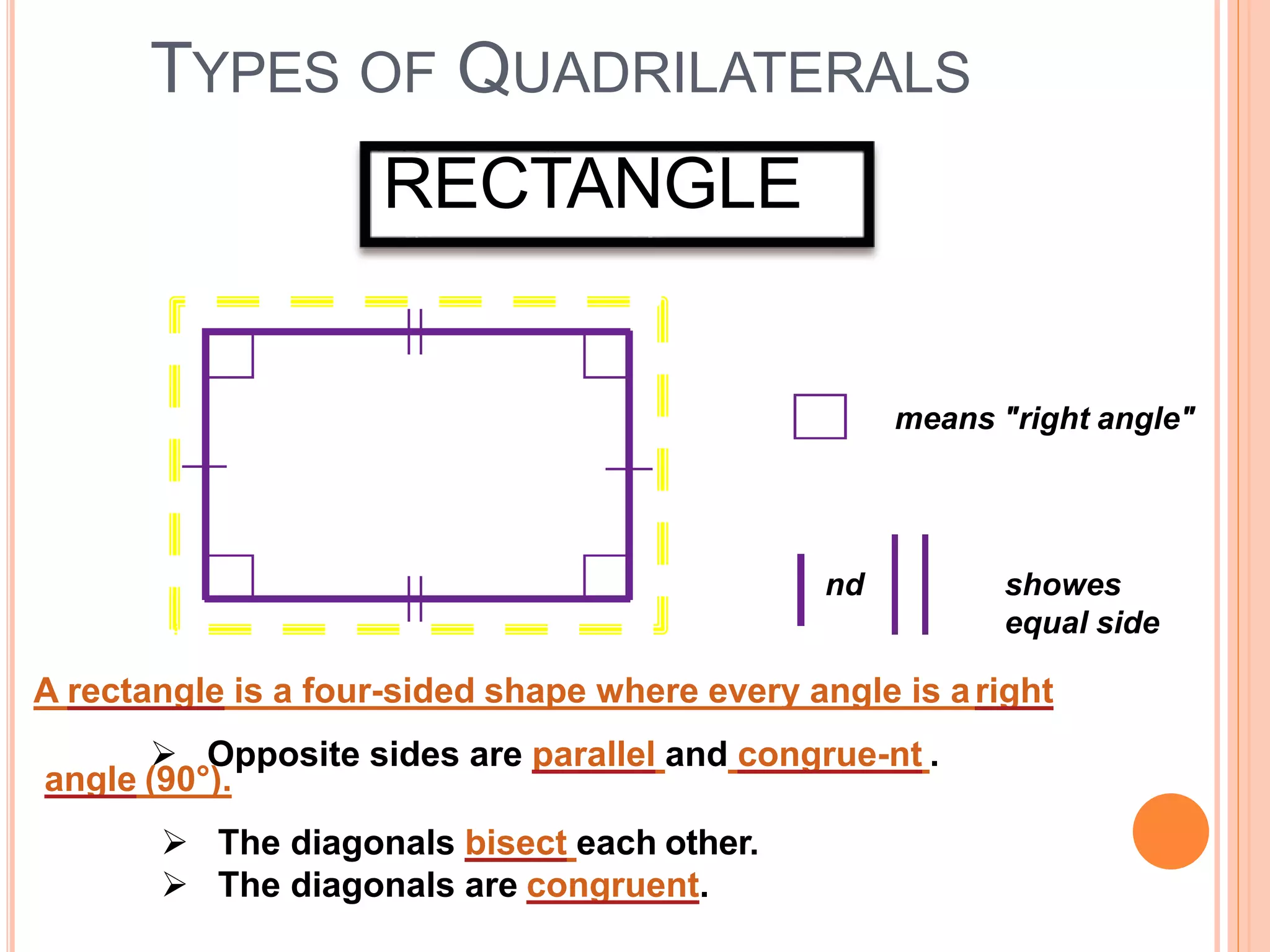
The document discusses different types of polygons and quadrilaterals. It defines a polygon as a closed plane figure bounded by three or more straight sides that meet at vertices. Quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides. There are several types of quadrilaterals including rectangles, squares, rhombi, parallelograms, trapezoids, and kites. The document provides properties and definitions for each type of quadrilateral.