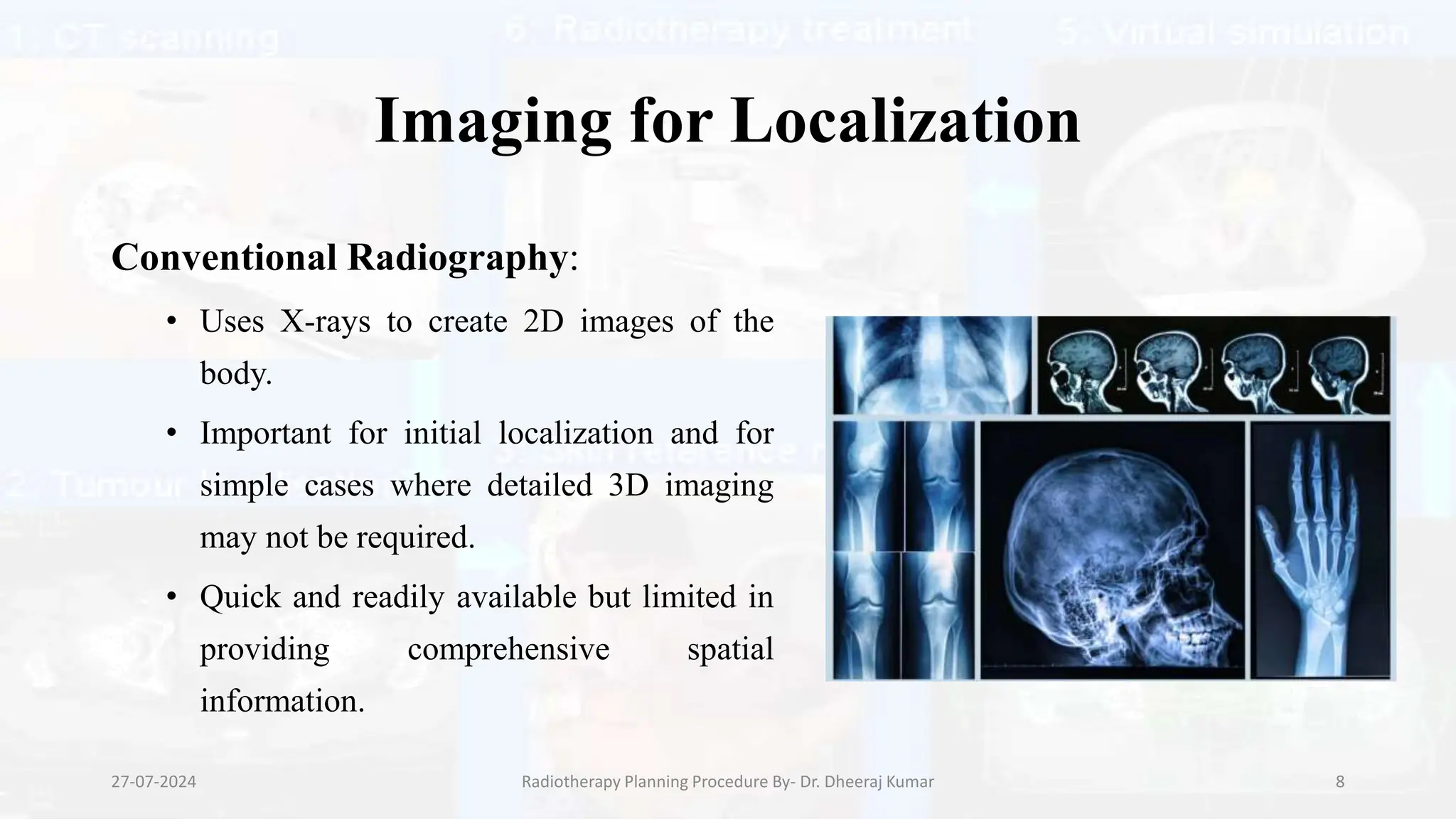
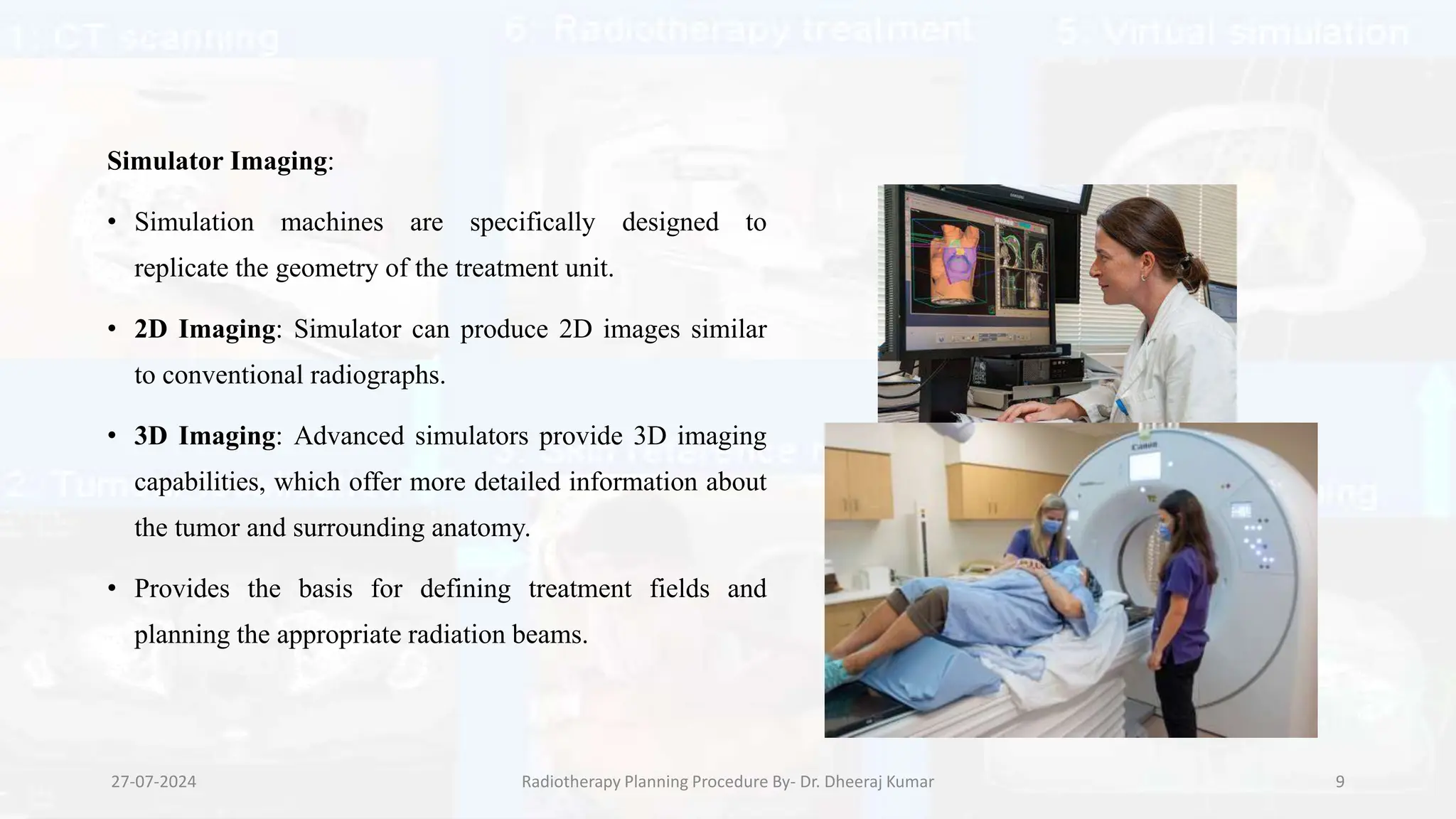
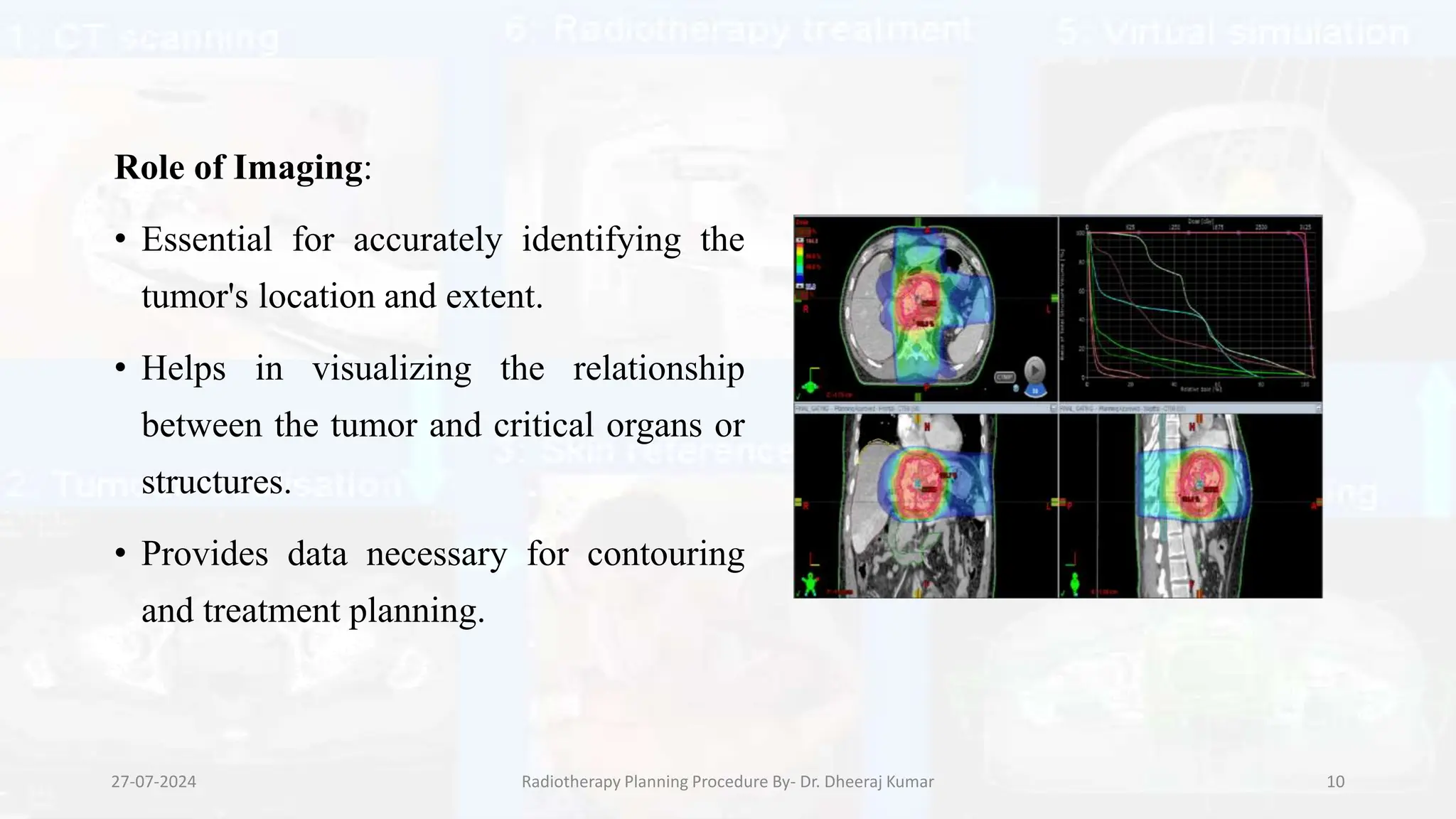
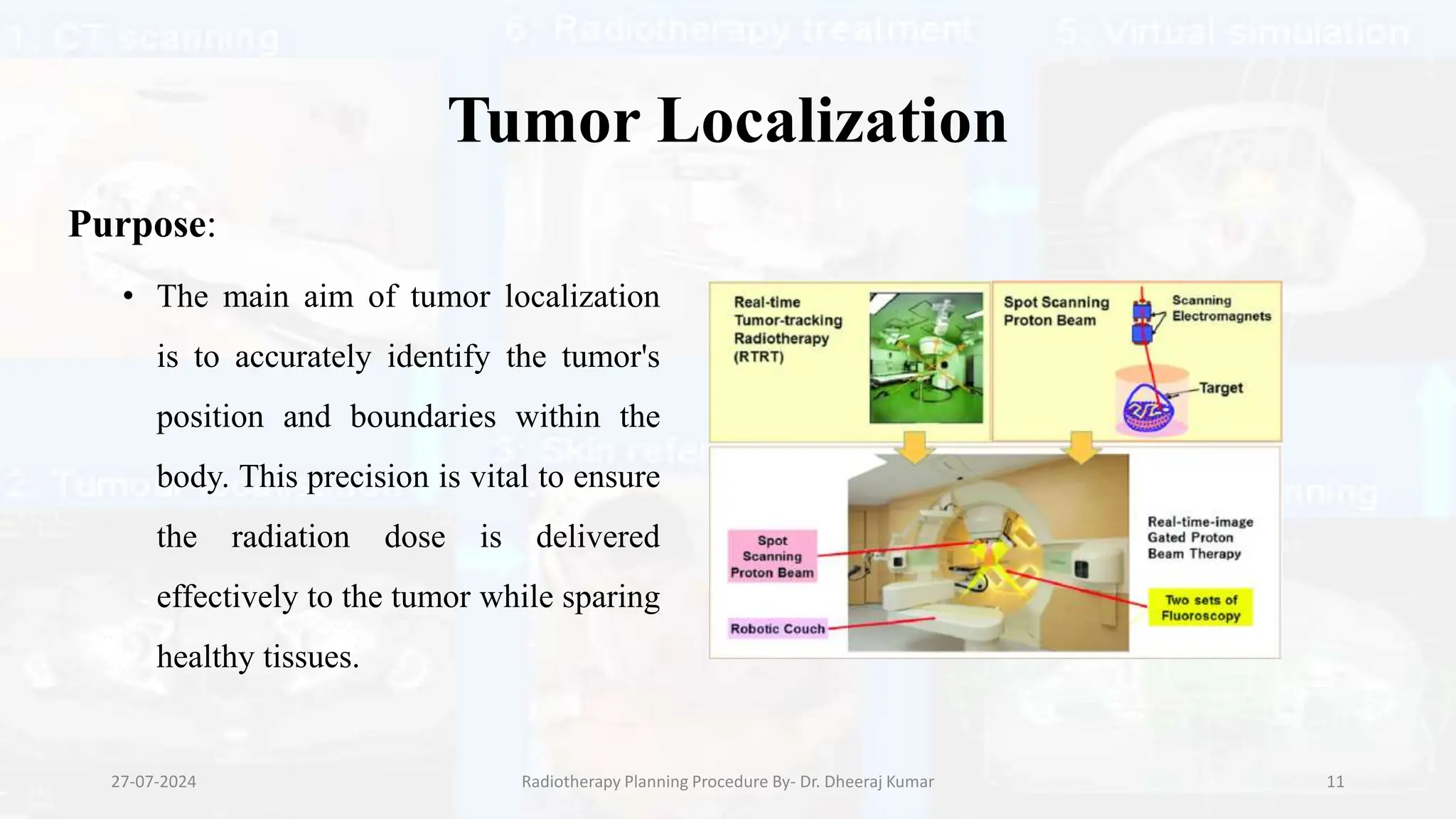
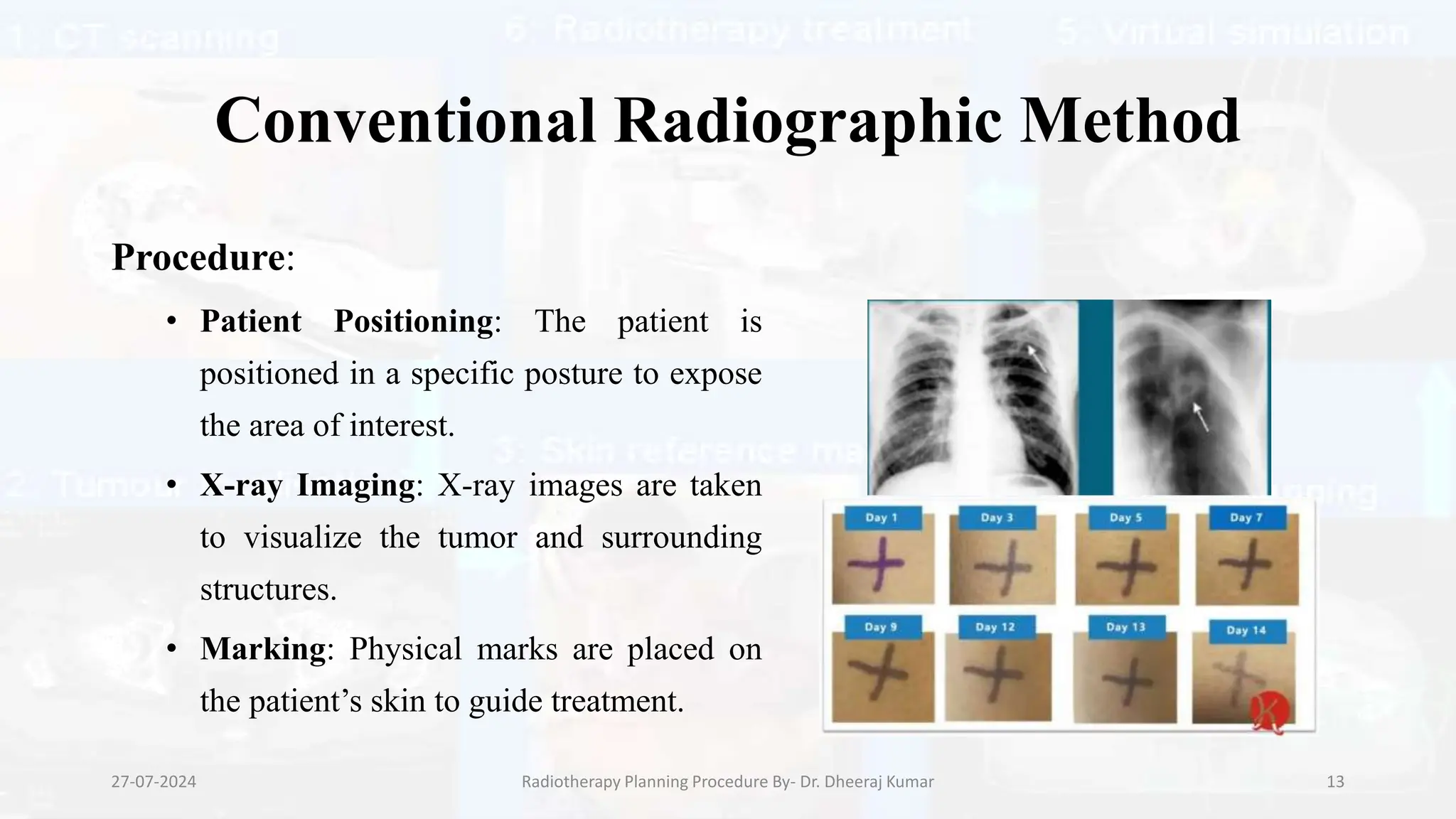
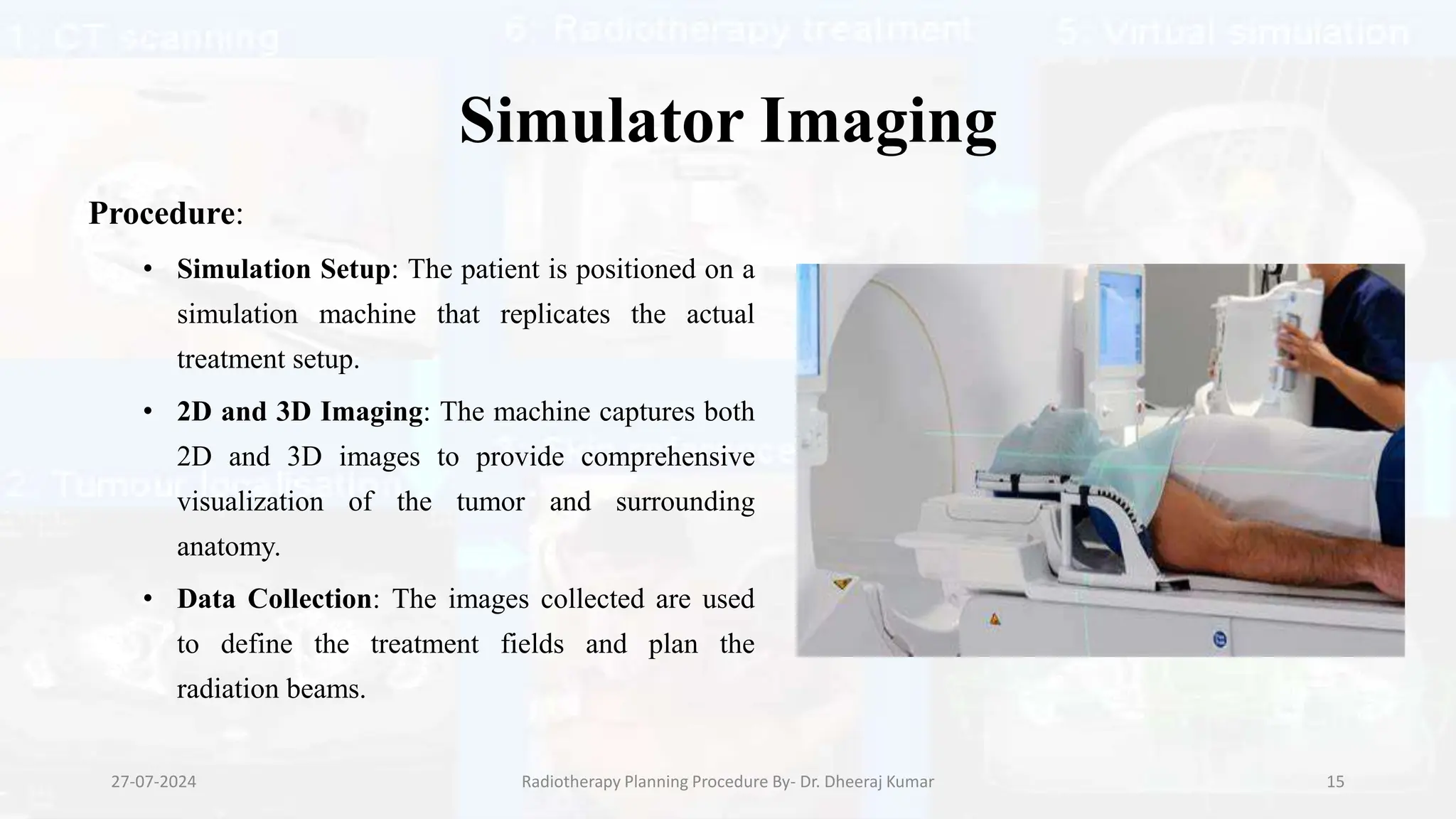
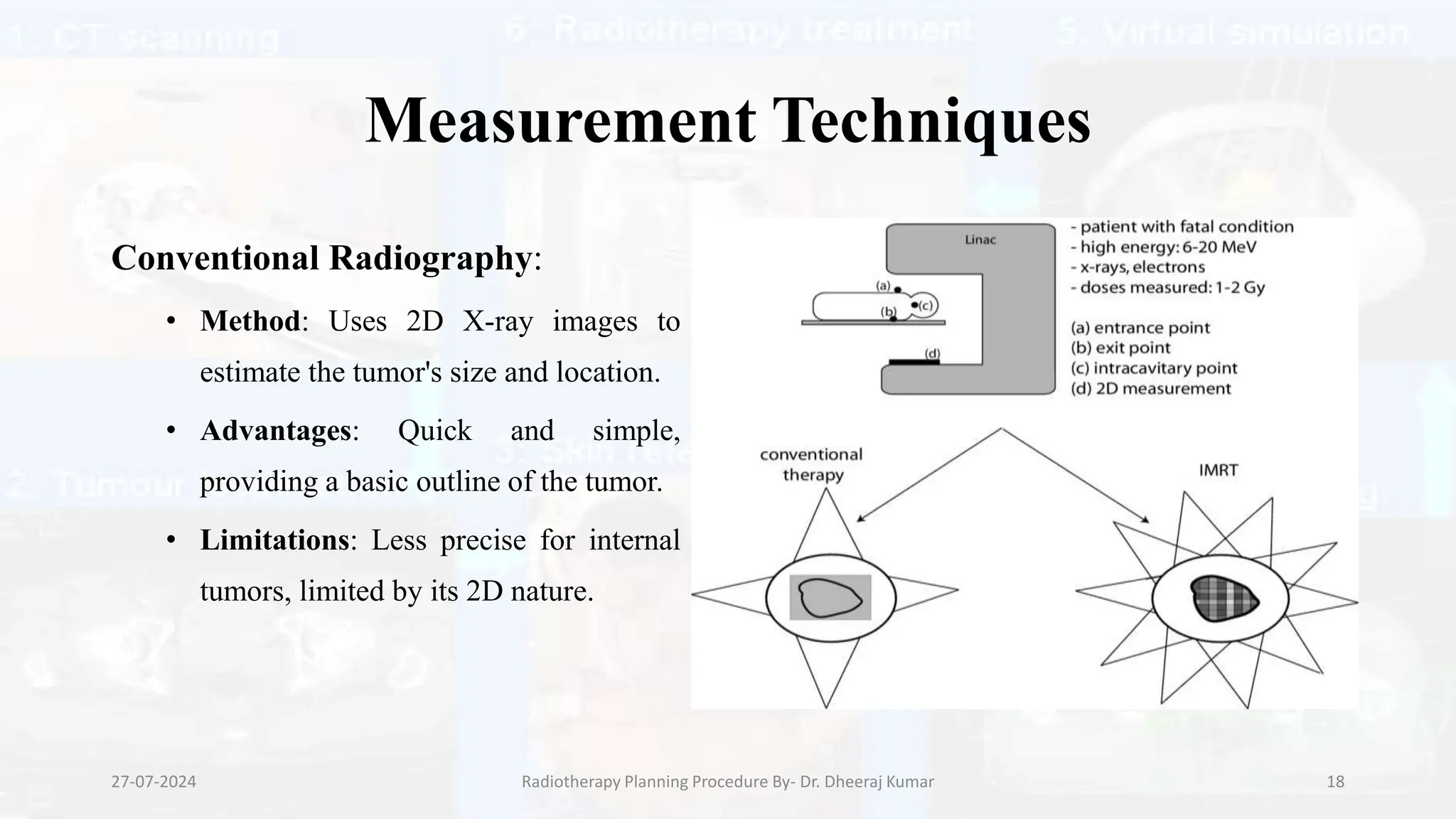
The document outlines the radiotherapy planning procedure, emphasizing its multi-step process aimed at targeting tumors while minimizing damage to healthy tissues. It covers stages such as patient preparation, imaging techniques, dose calculations, and quality assurance. Advances in imaging technologies and software tools have greatly enhanced the precision and effectiveness of treatment planning in radiotherapy.