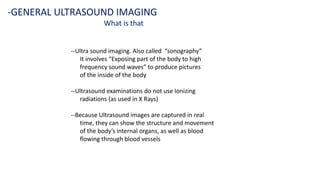
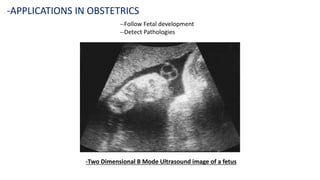
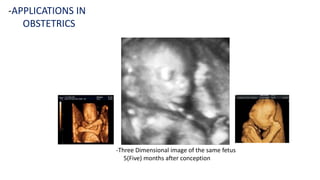
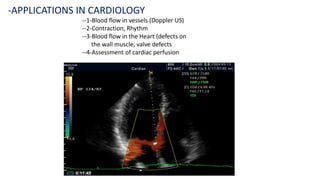
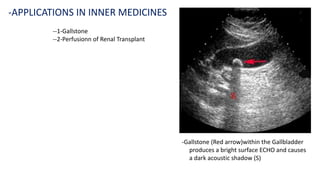
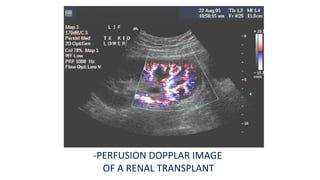
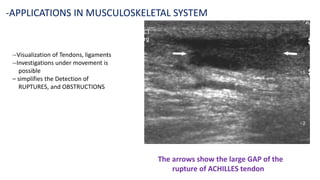
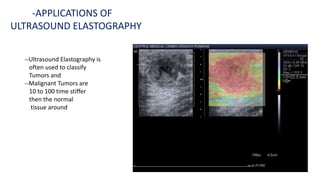
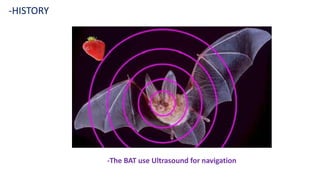
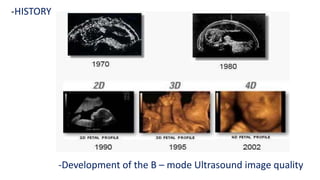
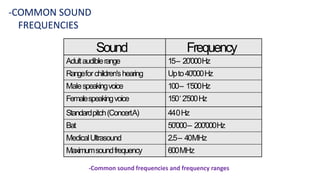
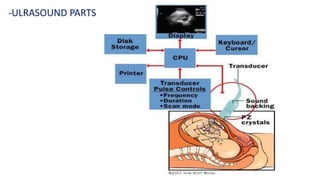
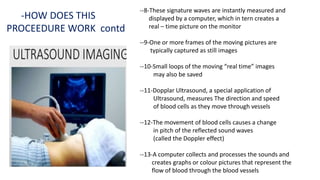
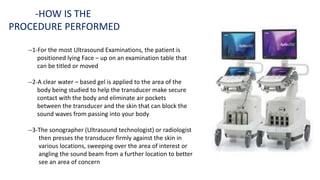
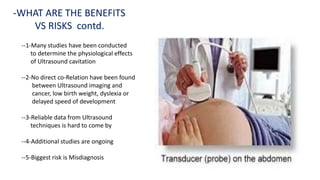
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the inside of the body. It can show internal organs, tissues, and blood flowing through blood vessels in real-time. Ultrasound has many medical uses including examining the heart and blood vessels, liver, gallbladder, spleen, kidneys, uterus and pregnancy, eyes, thyroid, muscles and tendons. It is widely used due to its safety since it does not use ionizing radiation.