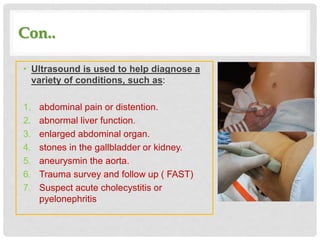
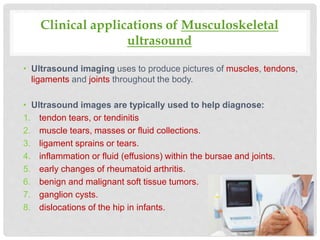
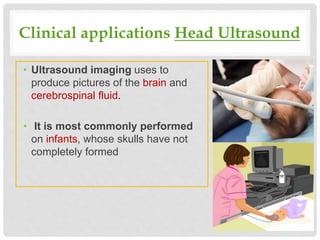
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal body structures and can be used to diagnose many conditions. It has applications in evaluating the abdomen to identify issues with organs like the liver or kidneys, in the chest to detect lung abnormalities or masses, and in musculoskeletal imaging to identify injuries to tendons, ligaments or muscles. Ultrasound is fast, painless, noninvasive and avoids radiation exposure.