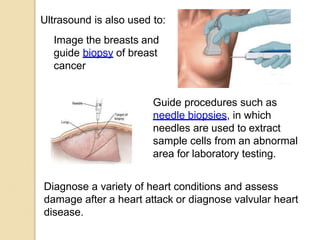
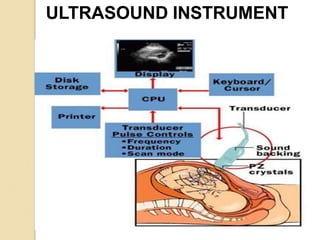
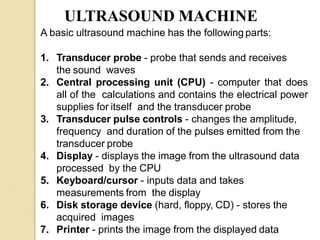
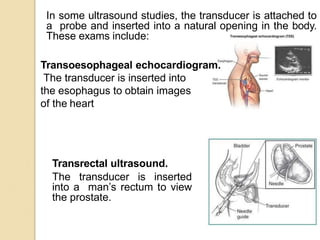
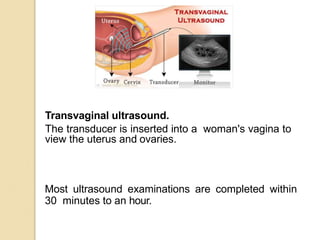
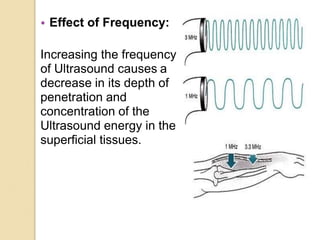
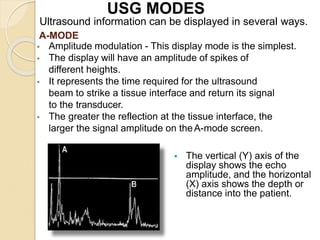
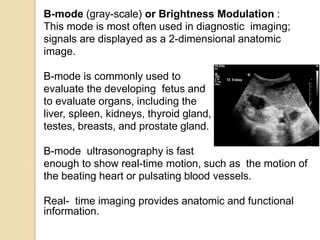
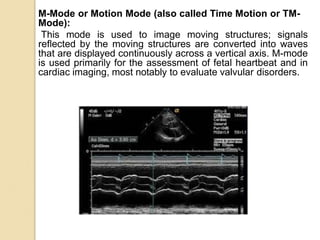
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the inside of the body. It can be used to examine many organs and tissues, as well as to guide needle biopsies. Ultrasound works by sending sound waves into the body with a transducer and measuring the echoes produced when they bounce off tissues and organs. Different echo patterns allow the visualization of both structure and movement within the body in real-time. While it provides many advantages like being non-invasive and having no known health risks, ultrasound has limitations such as poor penetration of bone or air and operator dependence.