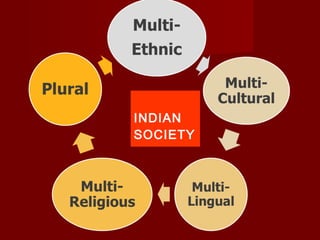
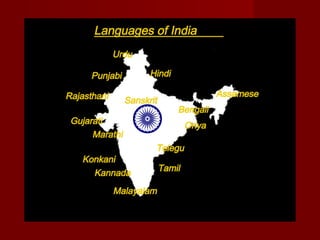
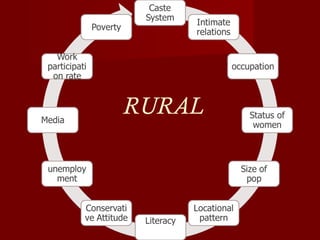
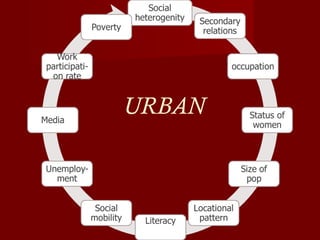
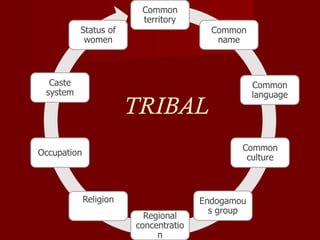
The document discusses the history, culture, society, and diversity of India. It notes that the Indus Valley Civilization was one of the earliest civilizations and the Vedic period saw the rise of Hinduism and the caste system. India's population is comprised of various ethnic groups including Proto-Austroloids, Indo-Aryans, Dravidians, and Indo-Mongolians. The country also has religious, linguistic, and regional diversity and variations in development levels between states.